Recommendations: 3
Impact of analytic decisions on test-retest reliability of individual and group estimates in functional magnetic resonance imaging: a multiverse analysis using the monetary incentive delay task
Exploring determinants of test-retest reliability in fMRI: a study with the Monetary Incentive Delay Task
Recommended by Dorothy Bishop based on reviews by Xiangzhen Kong and 1 anonymous reviewerFunctional magnetic resonance imaging has been used to explore brain-behaviour relationships for many years, with proliferation of a wide range of sophisticated analytic procedures. However, rather scant attention has been paid to the reliability of findings. Concerns have been growing failures to replicate findings in some fields, but it is hard to know how far this is a consequence of underpowered studies, flexible analytic pipelines, or variability within and between participants.
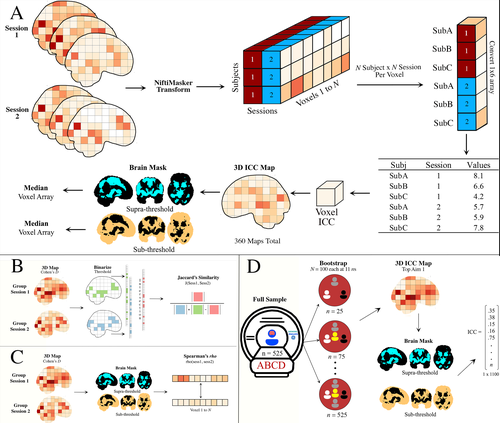
Demidenko et al. (2024) took advantage of the availability of three existing datasets, including the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) study, the Michigan Longitudinal Study, and the Adolescent Risk Behavior Study, which all included a version of the Monetary Incentive Delay task measured in two sessions. These were entered into a multiverse analysis, which considered how within-subject and between-subject variance varies according to four analytic factors: smoothing (5 levels), motion correction (6 levels), task modelling (3 levels) and task contrasts (4 levels). They also considered how sample size affects estimates of reliability.
The results have important implications for the those using fMRI with the Monetary Incentive Delay Task, and also raise questions more broadly about use of fMRI indices to study individual differences. Motion correction had relatively little impact on the ICC, and the effect size of the smoothing kernel was modest. Larger impacts on reliability were associated with choice of contrast (implicit baseline giving larger effects) and task parameterization. But perhaps the most sobering message from this analysis is that although activation maps from group data were reasonably reliable, the ICC, used as an index of reliability for individual levels of activation, was consistently low. This raises questions about the suitability of the Monetary Incentive Delay Task for studying individual differences. Another point is that reliability estimates become more stable as sample size increases; researchers may want to consider whether the trade-off between cost and gain in precision is justified for sample sizes above 250.
I did a quick literature search on Web of Science: at the time of writing the search term ("Monetary Delay Task" AND fMRI) yielded 410 returns, indicating that this is a popular method in cognitive neuroscience. The detailed analyses reported here will repay study for those who are planning further research using this task.
The Stage 2 manuscript was evaluated over one round of in-depth review. Based on detailed responses to the reviewer's and recommender's comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 2 criteria and awarded a positive recommendation.
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
- Brain and Neuroscience Advances
- Cortex
- Imaging Neuroscience
- In&Vertebrates
- NeuroImage: Reports
- Peer Community Journal
- PeerJ
- Royal Society Open Science
References
1. Demidenko, M. I., Mumford, J. A., & Poldrack, R. A. (2024). Impact of analytic decisions on test-retest reliability of individual and group estimates in functional magnetic resonance imaging: a multiverse analysis using the monetary incentive delay task [Stage 2]. Acceptance of Version 5 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2024.03.19.585755v4

Test-Retest Reliability in Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Impact of Analytical Decisions on Individual and Group Estimates in the Monetary Incentive Delay Task
Exploring determinants of test-retest reliabilty in fMRI
Recommended by Dorothy Bishop based on reviews by Xiangzhen Kong and 2 anonymous reviewersList of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
- Brain and Neuroscience Advances
- Cortex
- Imaging Neuroscience
- In&Vertebrates
- NeuroImage: Reports
- Peer Community Journal
- PeerJ
- Royal Society Open Science
References
1. Demidenko, M. I., Mumford, J. A., & Poldrack, R. A. (2023). Test-Retest Reliability in Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Impact of Analytical Decisions on Individual and Group Estimates in the Monetary Incentive Delay Task. In principle acceptance of Version 3 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/nqgeh

A systematic review of social connection inventories
Improving the measurement of social connection
Recommended by Dorothy Bishop based on reviews by Jacek Buczny, Richard James and Alexander WilsonLevel of bias control achieved: Level 3. At least some data/evidence that will be used to the answer the research question has been previously accessed by the authors (e.g. downloaded or otherwise received), but the authors certify that they have not yet observed ANY part of the data/evidence.
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
- Collabra: Psychology
- F1000Research
- International Review of Social Psychology
- Peer Community Journal
- PeerJ
- Royal Society Open Science
- Social Psychological Bulletin
- Swiss Psychology Open
1. Paris, B., Brickau, D., Stoianova, T., Luhmann, M., Mikton, C., Holt-Lunstad, J., Maes, A., & IJzerman, H. (2024). A systematic review of social connection inventories. In principle acceptance of Version 3 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/796uv
Review: 1

Cerebral laterality as assessed by functional transcranial Doppler ultrasound in left-and right-handers: A comparison between handwriting and writing using a smartphone
Does typing on a smartphone involve the same neural mechanisms as writing by hand?
Recommended by D. Samuel Schwarzkopf based on reviews by Todd Richards and Dorothy BishopLevel of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that will be used to answer the research question yet exists and no part will be generated until after IPA.
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
- Advances in Cognitive Psychology
- Brain and Neuroscience Advances
- F1000Research
- Imaging Neuroscience
- In&Vertebrates
- NeuroImage: Reports
- Peer Community Journal
- PeerJ
- Royal Society Open Science
- Studia Psychologica