BAYKOVA Reny
- School of Psychology & School of Informatics, University of Sussex, Brighton, United Kingdom
- Social sciences
Recommendations: 0
Reviews: 3
Reviews: 3
A multilab investigation into the N2pc as an indicator of attentional selectivity: Direct replication of Eimer (1996)
Is the N2pc a correlate of attentional selection? An #EEGManyLabs multi-lab registered replication of Eimer (1996)
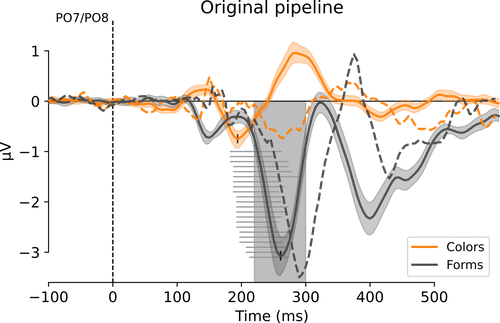
Recommended by Maxine Sherman based on reviews by Reny Baykova and Clayton HickeyIn attention research, the N2pc ERP – a lateralised negative deflection over parieto-occipital electrodes – is often interpreted as a marker of attentional selection, so much so that it is frequently used a tool in the attention literature for inferring that a stimulus was attentionally processed. This interpretation of N2pc has its roots in the seminal work of Eimer (1996), wherein the N2pc was observed when participants performed an attentional selection task with either colour or form (letter) stimuli. Despite its enormous influence in attention research, this work has never been directly replicated.
Here, Constant et al. (2025) conducted a high-powered replication attempt of the critical Study 2 of Eimer (1996), as part of the #EEGManyLabs (Pavlov et al., 2021) project. Twenty two labs across 14 countries took part and the N2pc was tested for using four pre-registered and one exploratory pipelines.
Results showed that the N2pc for form stimuli was remarkably robust, replicated by every participating lab under all four pre-registered (and one exploratory) preprocessing pipelines. By contrast, the N2pc for colour stimuli did not technically replicate, though a negative deflection was found 70ms earlier than originally reported.
This is a gold-standard replication attempt that should be an invaluable resource to the selective attention field.
The Stage 2 manuscript was evaluated over one round of in-depth review by two reviewers who also reviewed the Stage 1 report. Based on detailed responses to the reviewers' comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 2 criteria and awarded a positive recommendation.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/dw68r
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that was used to answer the research question was generated until after IPA.
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
- Advances in Cognitive Psychology
- Brain and Neuroscience Advances
- Collabra: Psychology
- Cortex
- F1000Research
- Imaging Neuroscience
- In&Vertebrates
- Journal for Reproducibility in Neuroscience
- Meta-Psychology
- Neuroimage: Reports
- Peer Community Journal
- Royal Society Open Science
- Studia Psychologica
- Swiss Psychology Open
References
1. Constant, M., Mandal, A., Asanowicz, D., Panek, B., Kotlewska, I., Yamaguchi, M., Gillmeister, H., Kerzel, D., Luque, D., Molinero, S., Vázquez-Millán, A., Pesciarelli, F., Borelli, E., Ramzaoui, H., Beck, M., Somon, B., Desantis, A., Castellanos, M. C., Martín-Arévalo, E., Manini, G., Capizzi, M., Gokce, A., Özer, D., Soyman, E., Yılmaz, E., Eayrs, J. O., London, R. E., Steendam, T., Frings, C., Pastötter, B., Szaszkó, B., Baess, P., Ayatollahi, S., León Montoya, G. A., Wetzel, N., Widmann, A., Cao, L., Low, X., Costa, T. L., Chelazzi, L., Monachesi, B., Kamp, S.-M., Knopf, L., Itier, R. J., Meixner, J., Jost, K., Botes, A., Braddock, C., Li, D., Nowacka, A., Quenault, M., Scanzi, D., Torrance, T., Corballis, P. M., Laera, G., Kliegel, M., Welke, D., Mushtaq, F., Pavlov, Y. G., & Liesefeld, H. R. (2025). A multilab investigation into the N2pc as an indicator of attentional selectivity: Direct replication of Eimer (1996) [Stage 2]. Acceptance of Version 3 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/3472y_v3
2. Eimer, M. (1996). The N2pc component as an indicator of attentional selectivity. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, 99, 225-234. https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-4694(96)95711-9
3. Pavlov, Y. G., Adamian, N., Appelhoff, S., Arvaneh, M., Benwell, C. S. Y., Beste, C., Bland, A. R., Bradford, D. E., Bublatzky, F., Busch, N. A., Clayson, P. E., Cruse, D., Czeszumski, A., Dreber, A., Dumas, G., Ehinger, B., Ganis, G., He, X., Hinojosa, J. A., Huber-Huber, C., Inzlicht, M., Jack, B. N., Johannesson, M., Jones, R., Kalenkovich, E., Kaltwasser, L., Karimi-Rouzbahani, H., Keil, A., König, P., Kouara, L., Kulke, L., Ladouceur, C. D., Langer, N., Liesefeld, H. R., Luque, D., MacNamara, A., Mudrik, L., Muthuraman, M., Neal, L. B., Nilsonne, G., Niso, G., Ocklenburg, S., Oostenveld, R., Pernet, C. R., Pourtois, G., Ruzzoli, M., Sass, S. M., Schaefer, A., Senderecka, M., Snyder, J. S., Tamnes, C. K., Tognoli, E., van Vugt, M. K., Verona, E., Vloeberghs, R., Welke, D., Wessel, J. R., Zakharov, I., & Mushtaq, F. (2021). #EEGManyLabs: Investigating the replicability of influential EEG experiments. Cortex, 144, 213-229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2021.03.013
31 Dec 2024

STAGE 1

How Does Model (Mis)Specification Impact Statistical Power, Type I Error Rate, and Parameter Bias in Moderated Mediation?
Dependence of power and type I error on model misspecification for mediated moderation
Recommended by Zoltan Dienes based on reviews by Mijke Rhemtulla, Pier-Olivier Caron and Reny BaykovaResearchers are often interested in moderated mediation. A predictor variable, such as number of counselling sessions, may predict an outcome, such as approach to a feared object, by way of a mediator, for example number of times the object was described in counselling. The strength of mediation in turn may depend on a moderator, such as vividness of imagery: Counselling reduces fear by way of imaginative exposure, particularly in those with vivid imagery. There may be a number of mediators ("indirect" paths), and any or all of these mediators may be moderated. In testing moderated mediation, a statistical model is specified which may or may not match the data generating process; in particular, there may or may not be moderators in the model corresponding to moderators that may or may not exist in the real data generating process, resulting in overspecification (more moderators of the indirect paths in the model than reality), underspecification (less moderators of indirect paths in the model than reality) or complete misspecification (where the moderated indirect paths in the model are not moderated in reality, and vice versa).
Researchers rely on the validity of tests (correct type I error rates), if they use frequentist statistics. Model misspecification may impact the validity of inferential tests for moderated mediation. Similarly, researchers need to be able to assess power for any analysis. In simulating power for mediated moderation, it may be important to know the possible extent to which the model is misspecified, and take this into account in planning numbers of participants. Fossum et al. (2024) will address this important problem with a series of simulations to determine if power is reduced meaningfully with over or under specification, or type I error and parameter estimates are biased for complete misspecification.
The Stage 1 manuscript was evaluated over two rounds of in-depth review. Based on detailed responses to reviewers’ and the recommender’s comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 1 criteria and therefore awarded in-principle acceptance.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/8gwfu
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that will be used to answer the research question yet exists and no part will be generated until after IPA.
List of eligible PCI-RR-friendly journals:
- Advances in Methods and Practices in Psychological Science
- Collabra: Psychology
- Peer Community Journal
- PeerJ
- Royal Society Open Science
- Studia Psychologica
- Swiss Psychology Open
References
Fossum, J. L., Montoya, A. K., & Anderson, S. F. (2024). How Does Model (Mis)Specification Impact Statistical Power, Type I Error Rate, and Parameter Bias in Moderated Mediation? A Registered Report. In principle acceptance of Version 3 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/8gwfu
18 May 2023

STAGE 1

A multilab investigation into the N2pc as an indicator of attentional selectivity: Direct replication of Eimer (1996)
Is the N2pc a correlate of attentional selection? An #EEGManyLabs multi-lab registered replication of Eimer (1996)
Recommended by Maxine Sherman based on reviews by Reny Baykova and Clayton HickeyThe N2pc is a lateralised ERP component that is often interpreted as a marker of attentional allocation, so much so that it is frequently used a tool in the attention literature for inferring that a stimulus was attentionally processed. This interpretation of N2pc can be traced back to the seminal work of Eimer (1996), which has been conceptually replicated many times but has never been replicated directly.
This registered direct replication by Constant et al. (2023) forms part of a larger series of large-scale, multi-lab replications of highly influential EEG papers by the #EEGManyLabs project (Pavlov et al., 2021). Seven labs (with the potential for more to sign up later), will conduct high-powered replications of the critical Experiment 2 of Eimer (1996), where in the crucial conditions, participants discriminate a target letter (M vs W) or colour (blue vs green) in the presence of a distractor. Using four preprocessing pipelines, including the original, the authors will test whether the N2pc is observed over parieto-occipital electrodes contralateral to target presentation.
The Stage 1 manuscript was evaluated over one round of in-depth review and one additional round of minor corrections. Based on detailed responses to the reviewers' comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 1 criteria and therefore awarded in-principle acceptance (IPA).
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/dw68r
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that will be used to answer the research question yet exists and no part will be generated until after IPA (so-called “primary RR”)
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
- Advances in Cognitive Psychology
- Brain and Neuroscience Advances
- Cortex
- F1000Research
- Imaging Neuroscience
- In&Vertebrates
- Journal for Reproducibility in Neuroscience
- Meta-Psychology
- Neuroimage: Reports
- Peer Community Journal
- Royal Society Open Science
- Swiss Psychology Open
References
1. Constant, M., Mandal, A., Asanowicz, D., Yamaguchi, M., Gillmeister, H., Kerzel, D., Luque, D., Pesciarelli, F., Fehr, T., Mushtaq, F., Pavlov, Y. G. & Liesefeld, H. R. (2023). A multilab investigation into the N2pc as an indicator of attentional selectivity: Direct replication of Eimer (1996), in principle acceptance of Version 3 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/dw68r
2. Eimer, M. (1996). The N2pc component as an indicator of attentional selectivity. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, 99, 225-234. https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-4694(96)95711-9
3. Pavlov, Y. G., Adamian, N., Appelhoff, S., Arvaneh, M., Benwell, C. S., Beste, C., ... & Mushtaq, F. (2021). #EEGManyLabs: Investigating the replicability of influential EEG experiments. Cortex, 144, 213-229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2021.03.013