Announcements
We are recruiting recommenders (editors) from all research fields!
Your feedback matters! If you have authored or reviewed a Registered Report at Peer Community in Registered Reports, then please take 5 minutes to leave anonymous feedback about your experience, and view community ratings.
Latest recommendations

| Id | Title | Authors | Abstract | Picture | Thematic fields | Recommender▲ | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
The Medusa effect: A registered replication report of Will, Merritt, Jenkins, and Kingstone (2021)Jing Han, Minjun Zhang, Jiaxin Liu, Yu Song, Yuki Yamada https://osf.io/yqnu8Looking (again) at Medusa: Evidence that pictorial abstraction influences mind perceptionRecommended by Chris Chambers based on reviews by Alan Kingstone and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Alan Kingstone and 1 anonymous reviewer
The Medusa effect is a recently described phenomenon in which people judge a person to be more mindful when they appear as a picture (termed L1) than as a picture within a picture (L2). Across a series of experiments, Will et al. (2021) reported that at higher levels of abstraction, images of people were judged lower in realness (how real the person seemed), experience (the ability to feel) and agency (the ability to plan and act), and also benefited less from prosocial behaviour. The findings provide an intriguing window into mind perception – the extent to which we attribute minds and mental capacities to others.
In the current study, Han et al. (2023) undertook a close replication of two experiments from the original report by Will et al. (2021), asking first, whether the level of pictorial abstraction influences ratings of realness, agency and experience, and second, whether it also influences prosocial behaviour as measured in the dictator game (with participants predicted to allocate more money to recipients presented as pictures than as pictures within pictures). In the event of a non-replication using the original materials, the authors planned to further repeat the experiments using newly generated stimuli that are better matched for cultural context and more tightly controlled along various dimensions.
Results supported all pre-registered hypotheses. Participants rated and perceived L1 stimuli as having significantly higher levels of realness, agency, and experience than L2, and they also allocated significantly more money to L1 recipients than L2 recipients in a dictator game. Furthermore, participants who judged L1 as higher than L2 on all three dimensions also differentiated significantly between L1 and L2 in the dictator game, indicating a relationship between mind perception and prosociality. Overall, the findings confirm that pictures with lower levels of abstraction are perceived as more mindful and are associated with higher levels of prosocial behavior. Consequently, the results suggest that the Medusa effect is a reproducible phenomenon.
The Stage 2 manuscript was evaluated over one round of in-depth review. Based on detailed responses to the reviewers' comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 2 criteria and awarded a positive recommendation.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/xj46z Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that was used to answer the research question was generated until after IPA.
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals: References
1. Will, P., Merritt, E., Jenkins, R., & Kingstone, A. (2021). The Medusa effect reveals levels of mind perception in pictures. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 118(32), e2106640118. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2106640118
2. Han, J., Zhang, M., Liu, J., Song, Y. & Yamada, Y. (2023).The Medusa effect: A registered replication report of Will, Merritt, Jenkins, and Kingstone (2021). Acceptance of Version 2 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/yqnu8
| The Medusa effect: A registered replication report of Will, Merritt, Jenkins, and Kingstone (2021) | Jing Han, Minjun Zhang, Jiaxin Liu, Yu Song, Yuki Yamada | <p>Will et al.'s (2021) found the Medusa effect, which refers to the tendency that people evaluate a “person in picture” more mindful than a “person in picture of a picture”. The present study tried to directly replicate the Experiments 2 and 5 of... | Social sciences | Chris Chambers | 2023-10-24 03:42:14 | View | ||
Genetically-modified animals as models of neurodevelopmental conditions: a review of systematic review reporting qualityEmma Wilson, Gillian Currie, Malcolm Macleod, Peter Kind, and Emily S Sena https://doi.org/10.31222/osf.io/s5xd4Evidence for mixed quality of systematic reviews in preclinical animal studies of neurodevelopmental conditionsRecommended by Chris Chambers based on reviews by Marietta Papadatou-Pastou based on reviews by Marietta Papadatou-Pastou
Single gene alterations have been estimated to account for nearly half of neurodevelopmental conditions (NDCs), providing a crucial opportunity for animal models to understand the underlying mechanisms, causes and potential treatments. The use of systematic reviews (SRs) can, in principle, provide a powerful means to synthesise this evidence-base; however, the reporting quality of previous SRs in preclinical animal research has been found lacking (Hunniford et al., 2021). In the current study, Wilson et al. (2023) will undertook a review of systematic reviews to assess the characteristics and reporting quality of SRs that, in turn, synthesise research in genetically-modified animals to model NDCs. In particular, the authors extracted key features of reviews (including, among others, the aim and primary research questions, relevant animal model, and number of studies in the SR), in addition to quality indicators such as risk of bias and completeness of reporting. In doing so, the authors aimed to enhance guidance on the conduct and reporting of systematic reviews in this area.
Of twelve publications that met the preregistered search criteria, the completeness and quality of reporting was variable. Among the better reported characteristics were search strategies (9 of 12 articles), reporting of funding sources (10 of 12 articles) and use of animal data (11 of 12 articles). In contrast, only two articles reported whether the study protocol was preregistered, only three articles reported methods for assessing risk of bias, and just one included methods to analyse publication bias. In addition, the authors identified 19 review registrations via PROSPERO, most of which remained unpublished after their anticipated end dates. Overall, the results highlight the importance of adherence to reporting guidelines for increasing the transparency and reproducibility of SRs in this field.
The Stage 2 manuscript was evaluated over one round of in-depth review. Based on detailed responses by the authors, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 2 criteria and awarded a positive recommendation.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/952qk Level of bias control achieved: Level 4. At least some of the data/evidence that was used to answer the research question already existed prior to IPA and was accessible in principle to the authors, but the authors certify that they did not access any part of that data/evidence prior to IPA.
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals: References
1. Hunniford V. T., Montroy J., Fergusson D. A., Avey M. T., Wever K. E., McCann S. K., Foster M., Fox G., Lafreniere M., Ghaly M., Mannell S., Godwinska K., Gentles A., Selim S., MacNeil J., Sikora L., Sena E. S., Page M. J., Macleod M., Moher D., & Lalu M. M. (2021). Epidemiology and reporting characteristics of preclinical systematic reviews. PLOS Biology, 19:e3001177. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3001177
2. Wilson, E., Currie, G., Macleod, M., Kind, P. & Sena, E. S. (2023). Genetically-modified animals as models of neurodevelopmental conditions: a review of systematic review reporting quality [Stage 2]. Acceptance of Version 3 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/s5xd4
| Genetically-modified animals as models of neurodevelopmental conditions: a review of systematic review reporting quality | Emma Wilson, Gillian Currie, Malcolm Macleod, Peter Kind, and Emily S Sena | <p><strong>Objective</strong><br>Using genetically-modified animals to model neurodevelopmental conditions (NDCs) helps better our understanding of biology underlying these conditions. Animal research has unique characteristics not shared with cli... | Medical Sciences | Chris Chambers | 2023-11-22 10:26:44 | View | ||
Progression of white matter hyperintensities is related to blood pressure increases and global cognitive decline – a registered reportFrauke Beyer, Laurenz Lammer, Markus Loeffler, Steffi Riedel-Heller, Stéphanie Debette, Arno Villringer, A. Veronica Witte https://osf.io/k24pmWhite matter lessions are associated with increases in blood pressure and global cognitive declineRecommended by Chris Chambers based on reviews by Isabel Garcia Garcia based on reviews by Isabel Garcia Garcia
Cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD) is a common and multi-faceted set of pathologies that affect the small arteries, arterioles, venules and capillaries of the brain. The disease manifests through a range of symptoms and conditions, including psychiatric disorders, abnormal gait, and urinary incontinence, while accounting for 25% of strokes and nearly 50% of dementia.
The presence of CSVD is associated with white matter lesions detected as white matter hyperintensities (WMH) using neuroimaging, which have in turn been shown to predict future stroke, cognitive decline and dementia. While vascular risk factors of CSVD (such as hypertension and obesity) are also associated with CSVD, a complete picture of the predictive relationship between WMH, cognitive decline, and blood pressure remains to be determined, as does the role of sex/gender. These inter-relationships are important to determine for improving the diagnosis and treatment of CSVD.
In the current study, Beyer et al. analysed a large emerging dataset from the LIFE-Adult project – a longitudinal, two-wave, population-based study – to ask whether higher blood pressure predicts a greater increase in WMH, and whether progression of WMH is associated with measures of memory and executive function. In addition, the authors explored the relationship between abdominal obesity and WMH progression, and the extent to which WMH progression, and its interaction with vascular risk factors, depends on sex/gender.
Results revealed no reliable association between baseline blood pressure with WMH progression. WMH progression significantly predicted global cognitive decline but not decline in executive function specifically. Exploratory analyses revealed that increases in diastolic blood pressure as well as baseline and systolic blood pressure were associated with WMH progression, specifically in frontal periventricular regions, but there was no association of waist-to-hip ratio (a proxy of abdominal fat deposits) with WMH progression nor any gender-specific associations. The authors conclude that strict control of blood pressure might confer a protective effect, limiting WMH progression and negative effects on global cognitive function in the middle-aged to older population.
The Stage 2 manuscript was evaluated over one round of in-depth review. Based on responses to the reviewer's comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 2 criteria and awarded a positive recommendation.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/qkbgj Level of bias control achieved: Level 2. At least some data/evidence that was used to answer the research question had been accessed and partially observed by the authors prior to Stage 1 in-principle acceptance, but the authors certify that they had not yet observed the key variables within the data that were used to answer the research question.
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals: References
1. Beyer, F., Lammer, L., Loeffler, M., Riedel-Heller, S., Debette, S., Villringer, A. & Witte, A. V. (2023). Progression of white matter hyperintensities is related to blood pressure increases and global cognitive decline – a registered report [Stage 2]. Acceptance of Version 2 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/k24pm
| Progression of white matter hyperintensities is related to blood pressure increases and global cognitive decline – a registered report | Frauke Beyer, Laurenz Lammer, Markus Loeffler, Steffi Riedel-Heller, Stéphanie Debette, Arno Villringer, A. Veronica Witte | <p>Introduction<br>White matter hyperintensities (WMH) reflect cerebral small vessel disease (cSVD), a major brain pathology contributing to cognitive decline and dementia. Vascular risk factors including higher diastolic blood pressure (DBP) have... | 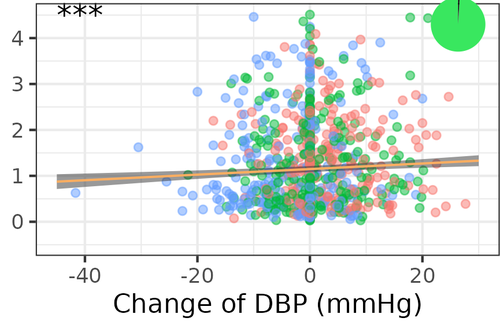 | Humanities, Medical Sciences | Chris Chambers | 2024-02-15 17:16:37 | View | |
Licensing via credentials: Replication Registered Report of Monin and Miller (2001) with extensions investigating the domain-specificity of moral credentials and associations with trait reputational concernQinyu Xiao, Lok Ching Li, Ying Lam Au, Wing Tung Chung, See Ngueh Tan, Gilad Feldman https://osf.io/zgf8yNo reliable evidence of a 'moral credential' effectRecommended by Chris Chambers based on reviews by Marek Vranka and Štěpán Bahník based on reviews by Marek Vranka and Štěpán Bahník
Does being good free people up to be bad? A large literature in social psychology suggests that it might, with evidence that moral licensing gives people a perception that actions deemed morally questionable, or socially undesirable, will be tolerated more readily if they have demonstrated a past history of praiseworthy, moral behaviour. In a formative study, Monin and Miller (2001) reported that having a track record of moral credentials as being nonprejudiced (e.g. non-sexist or non-racist) increased the willingness of participants to later express a prejudiced attitude. For example, in their Study 2 they found that participants who built up their moral credit by selecting a Black woman in a hypothetical recruitment task were then more willing to prefer a White man for a second job, compared to participants who did not have the opportunity to initially recommend a Black woman. These results have prompted a burgeoning literature on moral licensing, albeit one that is mixed and has been found to exhibit substantial publication bias.
In the current study, Xiao et al. (2024) undertook a large online replication of Study 2 in Monin and Miller (2001), asking whether previous moral behaviours that furnish participants with moral credentials make them more likely to then engage in morally questionable behaviours (N=932). The authors also extended earlier work by testing whether moral credentials license immoral behaviours more effectively in the same domain (e.g. within sex) than in a different domain (e.g. across sex and race), asking whether there is a negative relationship between expression of prejudice and trait reputational concern (fear of negative evaluation), and whether moral credentials attenuate any such observed relationship.
The results constitute a resounding non-replication, revealing no reliable evidence of a moral credential effect, no evidence that higher trait reputational concern predicts the expression of potentially problematic preferences, and no evidence that moral credentials moderate any such association. In discussing the implications of their findings, the authors call for further replication attempts and investigations of the effectiveness of experimental manipulations of moral licensing.
The Stage 2 manuscript was evaluated over one round of in-depth review. Based on detailed responses to the reviewers' comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 2 criteria and therefore awarded a positive recommendation.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/uxgrk
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that was used to answer the research question was generated until after IPA. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Monin, B., & Miller, D. T. (2001). Moral credentials and the expression of prejudice. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 81, 33-43. https://psycnet.apa.org/doi/10.1037/0022-3514.81.1.33
2. Xiao, Q., Ching Li, L., Au, Y. L., Chung, W. T., Tan, S. N. & Feldman, G. (2024). Licensing via credentials: Replication Registered Report of Monin and Miller (2001) with extensions investigating the domain-specificity of moral credentials and associations with trait reputational concern [Stage 2]. Acceptance of Version 7 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/zgf8y | Licensing via credentials: Replication Registered Report of Monin and Miller (2001) with extensions investigating the domain-specificity of moral credentials and associations with trait reputational concern | Qinyu Xiao, Lok Ching Li, Ying Lam Au, Wing Tung Chung, See Ngueh Tan, Gilad Feldman | <p>The moral credential effect is the phenomenon where an initial behavior that presumably establishes one as moral “licenses” the person to subsequently engage in morally questionable behaviors. In line with this effect, Monin and Miller (2001, S... | Social sciences | Chris Chambers | 2024-02-21 05:58:59 | View | ||
Registered Report: Are anticipatory auditory predictions enhanced in tinnitus and independent of hearing loss?L. Reisinger, G. Demarchi, S. Rösch, E. Trinka, J. Obleser, N. Weisz https://osf.io/9wqjhEvidence for the role of predictive coding in subjective tinnitusRecommended by Chris Chambers based on reviews by Will Sedley, Pia Brinkmann and Emilie Cardon based on reviews by Will Sedley, Pia Brinkmann and Emilie Cardon
Subjective tinnitus is a common disorder in which people experience a persistent sound in the absence of any external source. The underlying causes of tinnitus are debated – although the condition is strongly associated with hearing loss resulting from auditory damage, much remains to be understood about the neural processes that give rise to the phantom perception. Various classes of neurophysiological theories have been proposed, including the “altered gain” model – in which neurons in the auditory pathway increase their responsiveness to compensate for reduced auditory input following hearing loss – and the “noise cancellation” model – in which disrupted feedback connections from limbic regions are unable to tune out phantom signals. Although these theories account for much observed data, they have not been conclusively supported, and their ability to explain tinnitus is limited by the fact that hearing loss and tinnitus can arise independently and at different times.
In the current study, Reisinger et al. (2024) tested an emerging alternative theory based on a Bayesian predictive-coding framework (Sedley et al., 2016) in which the alteration of perceptual priors leads the auditory system to expect a sound that, if functioning normally, it should not expect. Using magnetoencephalography (MEG) in a sample of tinnitus patients (and carefully-matched controls for age, gender, and level of hearing loss), they asked whether tinnitus is associated with anticipatory brain activation, tuned to the carrier-frequency of an expected auditory stimulus. Specifically, the authors predicted that if the predictive-coding framework is correct then individuals with tinnitus should show different regularity-dependent pre-activations of carrier- frequency-specific information compared to the control group, while tone carrier-frequencies should be processed normally in tinnitus patients. They also predicted that any such pre-activations should not be related to levels of reported subjective tinnitus distress, as measured with the short version of the Tinnitus Questionnaire (mini-TQ).
The results broadly confirmed the hypotheses, with some caveats. Statistically significant differences in regularity-dependent pre-activations were observed between the tinnitus and control groups, however – curiously – the effects appear to be driven by below-chance decoding in the control group, complicating the interpretration. At the same time, consistent with expectations, frequency processing did not differ significantly between individuals with and without tinnitus, and the observed pre-activations were not significantly related to tinnitus distress. Overall, the findings cautiously support the conclusion that chronic tinnitus is associated with maladaptively upregulated predictive neural processing, and that this phenomenon is unlikely to be explained by either tinnitus distress or hearing loss.
The Stage 2 manuscript was evaluated over one round of in-depth review. Based on detailed responses to the reviewers' comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 2 criteria and awarded a positive recommendation.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/6gvpy
Level of bias control achieved: Level 3. At least some data/evidence that was used to the answer the research question had been previously accessed by the authors (e.g. downloaded or otherwise received), but the authors certify that they had yet observed any part of the data/evidence prior to Stage 1 IPA.
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Reisinger, L., Demarchi, G., Rösch, , S., Trinka, E., Obleser, L., & Weisz, N. (2024). Registered Report: Are anticipatory auditory predictions enhanced in tinnitus and independent of hearing loss? [Stage 2] Acceptance of Version 3 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/9wqjh
2. Sedley, W., Friston, K. J., Gander, P. E., Kumar, S., & Griffiths, T. D. (2016). An integrative tinnitus model based on sensory precision. Trends in Neurosciences, 39, 799-812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2016.10.004
| Registered Report: Are anticipatory auditory predictions enhanced in tinnitus and independent of hearing loss? | L. Reisinger, G. Demarchi, S. Rösch, E. Trinka, J. Obleser, N. Weisz | <p>Phantom perceptions occur without any identifiable environmental or bodily source. The mechanisms and key drivers behind phantom perceptions like tinnitus are not well understood. The dominant “altered-gain”-framework suggests that tinnitus res... | Life Sciences | Chris Chambers | 2024-02-21 16:17:33 | View | ||
29 Sep 2021
STAGE 1

Evaluating the pedagogical effectiveness of study preregistration in the undergraduate dissertation: A Registered ReportMadeleine Pownall; Charlotte R. Pennington; Emma Norris; Kait Clark https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/9HJBWDoes incorporating open research practices into the undergraduate curriculum decrease questionable research practices?Recommended by Corina Logan and Chris Chambers and Chris Chambers based on reviews by Kelsey McCune, Neil Lewis, Jr., Lisa Spitzer and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Kelsey McCune, Neil Lewis, Jr., Lisa Spitzer and 1 anonymous reviewer
In a time when open research practices are becoming more widely used to combat questionable research practices (QRPs) in academia, this Stage 1 Registered Report by Pownall and colleagues (2021) will empirically investigate the practice of preregistering study plans, which will allow us to better understand to what degree such practices increase awareness of QRPs and whether experience with preregistration helps reduce engagement in QRPs. This investigation is timely because results from these kinds of studies are only recently becoming available and the conclusions are providing evidence that open research practices can improve research quality and reliability (e.g., Soderberg et al. 2020, Chambers & Tzavella 2021). The authors crucially focus on the effect of preregistering the undergraduate senior thesis (of psychology students in the UK), which is a key stage in the development of an academic. This data will help shape the future of how we should teach open research practices and what effect we as teachers can have on budding research careers. The five expert peer reviews were of an extremely high quality and were very thorough. The authors did an excellent job of addressing all of the comments in their responses and revised manuscript versions, which resulted in only one round of peer review, plus a second revision based on Recommender feedback. As such, this registered report meets the Stage 1 criteria and is therefore awarded in-principle acceptance (IPA). We wish the authors the best of luck with the study and we look forward to seeing the results. URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/9hjbw Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that will be used to answer the research question yet exists and no part will be generated until after IPA. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
| Evaluating the pedagogical effectiveness of study preregistration in the undergraduate dissertation: A Registered Report | Madeleine Pownall; Charlotte R. Pennington; Emma Norris; Kait Clark | <p style="text-align: justify;">Research shows that questionable research practices (QRPs) are present in undergraduate final-year dissertation projects. One entry-level Open Science practice proposed to mitigate QRPs is ‘study preregistration’, t... | Life Sciences, Social sciences | Corina Logan | 2021-07-08 15:27:24 | View | ||
21 Mar 2023
STAGE 1

Convenience Samples and Measurement Equivalence in Replication ResearchLindsay J. Alley, Jordan Axt, Jessica Kay Flake https://osf.io/32unbDoes data from students and crowdsourced online platforms measure the same thing? Determining the external validity of combining data from these two types of subjectsRecommended by Corina Logan based on reviews by Benjamin Farrar and Shinichi Nakagawa based on reviews by Benjamin Farrar and Shinichi Nakagawa
Comparative research is how evidence is generated to support or refute broad hypotheses (e.g., Pagel 1999). However, the foundations of such research must be solid if one is to arrive at the correct conclusions. Determining the external validity (the generalizability across situations/individuals/populations) of the building blocks of comparative data sets allows one to place appropriate caveats around the robustness of their conclusions (Steckler & McLeroy 2008).
In this registered report, Alley and colleagues plan to tackle the external validity of comparative research that relies on subjects who are either university students or participating in experiments via an online platform (Alley et al. 2023). They will determine whether data from these two types of subjects have measurement equivalence - whether the same trait is measured in the same way across groups. Although they use data from studies involved in the Many Labs replication project to evaluate this question, their results will be of crucial importance to other comparative researchers whose data are generated from these two sources (students and online crowdsourcing). If Alley and colleagues show that these two types of subjects have measurement equivalence, then this indicates that it is more likely that equivalence could hold for other studies relying on these type of subjects as well. If measurement equivalence is not found, then it is a warning to others to evaluate their experimental design to improve validity. In either case, it gives researchers a way to test measurement equivalence for themselves because the code is well annotated and openly available for others to use.
The Stage 1 manuscript was evaluated over two rounds of in-depth review. Based on detailed responses to the reviewers' comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 1 criteria and therefore awarded in-principle acceptance (IPA). Level of bias control achieved: Level 2. At least some data/evidence that will be used to answer the research question has been accessed and partially observed by the authors, but the authors certify that they have not yet observed the key variables within the data that will be used to answer the research question AND they have taken additional steps to maximise bias control and rigour (e.g. conservative statistical threshold; recruitment of a blinded analyst; robustness testing, multiverse/specification analysis, or other approach)
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
Alley L. J., Axt, J., & Flake J. K. (2023). Convenience Samples and Measurement Equivalence in Replication Research, in principle acceptance of Version 4 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/7gtvf
Steckler, A. & McLeroy, K. R. (2008). The importance of external validity. American Journal of Public Health 98, 9-10. https://doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.2007.126847
Pagel, M. (1999). Inferring the historical patterns of biological evolution. Nature, 401, 877-884. https://doi.org/10.1038/44766
| Convenience Samples and Measurement Equivalence in Replication Research | Lindsay J. Alley, Jordan Axt, Jessica Kay Flake | <p>A great deal of research in psychology employs either university student or online crowdsourced convenience samples (Chandler & Shapiro, 2016; Strickland & Stoops, 2019) and there is evidence that these groups differ in meaningful ways ... | Social sciences | Corina Logan | 2022-11-29 18:37:54 | View | ||
Evaluating the Pedagogical Effectiveness of Study Preregistration in the Undergraduate DissertationMadeleine Pownall, Charlotte R. Pennington, Emma Norris, Marie Juanchich, David Smaile, Sophie Russell, Debbie Gooch, Thomas Rhys Evans, Sofia Persson, Matthew HC Mak, Loukia Tzavella, Rebecca Monk, Thomas Gough, Christopher SY Benwell, Mahmoud Elsherif, Emily Farran, Thomas Gallagher-Mitchell, Luke T. Kendrick, Julia Bahnmueller, Emily Nordmann, Mirela Zaneva, Katie Gilligan-Lee0, Marina Bazhydai, Andrew Jones, Jemma Sedgmond, Iris Holzleitner, James Reynolds, Jo Moss, Daniel Farrelly, Adam J. ... https://psyarxiv.com/xg2ahIncorporating open research practices into the undergraduate curriculum increases understanding of such practicesRecommended by Corina Logan based on reviews by Kelsey McCune, Neil Lewis, Jr., Lisa Spitzer and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Kelsey McCune, Neil Lewis, Jr., Lisa Spitzer and 1 anonymous reviewer
In a time when open research practices are becoming more widely used to combat questionable research practices (QRPs) in academia, this Registered Report by Pownall and colleagues (2023) empirically investigated the practice of preregistering study plans, which allows us to better understand to what degree such practices increase awareness of QRPs and whether experience with preregistration helps reduce engagement in QRPs. This investigation is timely because results from these kinds of studies are only recently becoming available and the conclusions are providing evidence that open research practices can improve research quality and reliability (e.g., Soderberg et al. 2021, Chambers & Tzavella 2022). The authors crucially focused on the effect of preregistering the undergraduate senior thesis (of psychology students in the UK), which is a key stage in the development of an academic.
Pownall and colleagues found that preregistration did not affect attitudes toward QRPs, but it did improve student understanding of open research practices. Using exploratory analyses, they additionally found that those who preregistered were those students who reported that they had more opportunity, motivation, and greater capability. This shows how important it is to incorporate the teaching of open research practices such that students can increase their capability, motivation, and opportunity to pursue such practices, whether it is preregistration or other practices that are better known to reduce QRPs (such as registered reports; Krypotos et al. 2022).
After four rounds of review and revisions, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 2 criteria and awarded a positive recommendation.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/9hjbw
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that was used to answer the research question was generated until after IPA.
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Chambers C. D. & Tzavella, L. (2022). The past, present, and future of Registered Reports. Nature Human Behaviour, 6, 29-42. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-021-01193-7
2. Krypotos, A. M., Mertens, G., Klugkist, I., & Engelhard, I. M. (2022). Preregistration: Definition, advantages, disadvantages, and how it can help against questionable research practices. In Avoiding Questionable Research Practices in Applied Psychology (pp. 343-357). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
3. Pownall, M., Pennington, C. R., Norris, E., Juanchich, M., Smaile, D., Russell, S., Gooch, D., Rhys Evans, T., Persson, S., Mak, M. H. C., Tzavella, L., Monk, R., Gough, T., Benwell, C. S. Y., Elsherif, M., Farran, E., Gallagher-Mitchell, T., Kendrick, L. T., Bahnmueller, J., Nordmann, E., Zaneva, M., Gilligan-Lee, K., Bazhydai, M., Jones, A., Sedgmond, J., Holzleitner, I., Reynolds, J., Moss, J., Farrelly, D., Parker, A. J. & Clark, K. (2023). Evaluating the pedagogical effectiveness of study preregistration in the undergraduate dissertation [Stage 2 Registered Report], acceptance of Version 4 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://psyarxiv.com/xg2ah
4. Soderberg C. K., Errington T. M., Schiavone S. R., Bottesini J., Thorn F. S., Vazire S., Esterling K. M. & Nosek B. A. (2021) Initial evidence of research quality of registered reports compared with the standard publishing model. Nature Human Behaviour, 5, 990–997. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-021-01142-4
| Evaluating the Pedagogical Effectiveness of Study Preregistration in the Undergraduate Dissertation | Madeleine Pownall, Charlotte R. Pennington, Emma Norris, Marie Juanchich, David Smaile, Sophie Russell, Debbie Gooch, Thomas Rhys Evans, Sofia Persson, Matthew HC Mak, Loukia Tzavella, Rebecca Monk, Thomas Gough, Christopher SY Benwell, Mahmoud El... | <p>Research shows that questionable research practices (QRPs) are present in undergraduate final-year dissertation projects. One entry-level Open Science practice proposed to mitigate QRPs is ‘study preregistration’, through which researchers outl... | Life Sciences, Social sciences | Corina Logan | 2023-03-25 11:38:54 | View | ||
Convenience Samples and Measurement Equivalence in Replication ResearchLindsay J. Alley, Jordan Axt, Jessica Kay Flake https://osf.io/s5t3vData from students and crowdsourced online platforms do not often measure the same thingRecommended by Corina Logan based on reviews by Benjamin Farrar and Shinichi Nakagawa based on reviews by Benjamin Farrar and Shinichi Nakagawa
Comparative research is how evidence is generated to support or refute broad hypotheses (e.g., Pagel 1999). However, the foundations of such research must be solid if one is to arrive at the correct conclusions. Determining the external validity (the generalizability across situations/individuals/populations) of the building blocks of comparative data sets allows one to place appropriate caveats around the robustness of their conclusions (Steckler & McLeroy 2008). In the current study, Alley and colleagues (2023) tackled the external validity of comparative research that relies on subjects who are either university students or participating in experiments via an online platform. They determined whether data from these two types of subjects have measurement equivalence - whether the same trait is measured in the same way across groups. Although they use data from studies involved in the Many Labs replication project to evaluate this question, their results are of crucial importance to other comparative researchers whose data are generated from these two sources (students and online crowdsourcing). The authors show that these two types of subjects do not often have measurement equivalence, which is a warning to others to evaluate their experimental design to improve validity. They provide useful recommendations for researchers on how to to implement equivalence testing in their studies, and they facilitate the process by providing well annotated code that is openly available for others to use. After one round of review and revision, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 2 criteria and awarded a positive recommendation. URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/7gtvf
Level of bias control achieved: Level 2. At least some data/evidence that was used to answer the research question had been accessed and partially observed by the authors prior to Stage 1 IPA, but the authors certify that they had not yet observed the key variables within the data that were used to answer the research question AND they took additional steps to maximise bias control and rigour.
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Pagel, M. (1999). Inferring the historical patterns of biological evolution. Nature, 401, 877-884. https://doi.org/10.1038/44766
2. Steckler, A. & McLeroy, K. R. (2008). The importance of external validity. American Journal of Public Health 98, 9-10. https://doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.2007.126847
3. Alley L. J., Axt, J., & Flake J. K. (2023). Convenience Samples and Measurement Equivalence in Replication Research [Stage 2 Registered Report] Acceptance of Version 2 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/s5t3v
| Convenience Samples and Measurement Equivalence in Replication Research | Lindsay J. Alley, Jordan Axt, Jessica Kay Flake | <p>A great deal of research in psychology employs either university student or online crowdsourced convenience samples (Chandler & Shapiro, 2016; Strickland & Stoops, 2019) and there is evidence that these groups differ in meaningful ways ... | Social sciences | Corina Logan | Alison Young Reusser | 2023-08-31 20:26:43 | View | |
14 Feb 2024
STAGE 1

Restriction of researcher degrees of freedom through the Psychological Research Preregistration-Quantitative (PRP-QUANT) TemplateLisa Spitzer & Stefanie Mueller https://doi.org/10.23668/psycharchives.14119Examining the restrictiveness of the PRP-QUANT TemplateRecommended by Daniel Lakens based on reviews by Marjan Bakker and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Marjan Bakker and 1 anonymous reviewer
The Psychological Research Preregistration-Quantitative Template has been created in 2022 to provide more structure and detail to preregistrations. The goal of the current study is to test if the PRP-QUANT template indeed provides greater restriction of the flexibility in a study for preregistered hypotheses than other existing templates. This question is important because one concern that has been raised about the practice of preregistration is that the quality of preregistrations is often low. Metascientific research has shown that preregistrations are often of low quality (Bakker et al., 2020), and hypothesis tests from preregistrations are still selectively reported (van den Akker, van Assen, Enting, et al., 2023). It is important to improve the quality of preregistrations, and if a better template can help, it is a cost-effective approach to improve quality if the wider adoption of the better template can be promoted.
In the current study, Spitzer and Mueller (2024) will follow the procedure of a previous meta-scientific study by Heirene et al. (2021). 74 existing preregistrations with the PRP-QUANT template are available, and will be compared with an existing dataset coded by Bakker and colleagues (2020). The sample size is limited, but allows detecting some differences that would be considered large enough to matter, even though there might be smaller differences that would not be detectable based on the currently available sample size. Nevertheless, given that there is a need for improvement, even preliminary data might already be useful to provide tentative recommendations. Restrictiveness will be coded in 23 items, and adherence to or deviations from the preregistration are coded as well. As such deviations are common, the question whether this template reduced the likelihood of deviations is important. Two coders will code all studies.
The study should provide a useful initial evaluation of the PRP-QUANT template, and has the potential to have practical implications if the PRP-QUANT template shows clear benefits. Both authors have declared COI's related to the PRP-QUANT template, making the Registered Report format a fitting approach to prevent confirmation bias from influencing the reported results.
This Stage 1 manuscript was evaluated over two rounds of in-depth review by two expert reviewers and the recommender. After the revisions, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 1 criteria and therefore awarded in-principle acceptance (IPA).
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/vhezj
Level of bias control achieved: Level 3. At least some data/evidence that will be used to the answer the research question has been previously accessed by the authors (e.g. downloaded or otherwise received), but the authors certify that they have not yet observed ANY part of the data/evidence. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. van den Akker, O. R., van Assen, M. A. L. M., Bakker, M., Elsherif, M., Wong, T. K., & Wicherts, J. M. (2023). Preregistration in practice: A comparison of preregistered and non-preregistered studies in psychology. Behavior Research Methods. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13428-023-02277-0
2. Bakker, M., Veldkamp, C. L. S., Assen, M. A. L. M. van, Crompvoets, E. A. V., Ong, H. H., Nosek, B. A., Soderberg, C. K., Mellor, D., & Wicherts, J. M. (2020). Ensuring the quality and specificity of preregistrations. PLOS Biology, 18(12), e3000937. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3000937
3. Spitzer, L. & Mueller, S. (2024). Stage 1 Registered Report: Restriction of researcher degrees of freedom through the Psychological Research Preregistration-Quantitative (PRP-QUANT) Template. In principle acceptance of Version 3 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/vhezj
4. Heirene, R., LaPlante, D., Louderback, E. R., Keen, B., Bakker, M., Serafimovska, A., & Gainsbury, S. M. (2021). Preregistration specificity & adherence: A review of preregistered gambling studies & cross-disciplinary comparison. PsyArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/nj4es
| Restriction of researcher degrees of freedom through the Psychological Research Preregistration-Quantitative (PRP-QUANT) Template | Lisa Spitzer & Stefanie Mueller | <p>Preregistration can help to restrict researcher degrees of freedom and thereby ensure the integrity of research findings. However, its ability to restrict such flexibility depends on whether researchers specify their study plan in sufficient de... |  | Social sciences | Daniel Lakens | 2023-06-01 10:39:20 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Chris Chambers
Zoltan Dienes
Corina Logan
Benoit Pujol
Maanasa Raghavan
Emily S Sena
Yuki Yamada










