Announcements
We are recruiting recommenders (editors) from all research fields!
Your feedback matters! If you have authored or reviewed a Registered Report at Peer Community in Registered Reports, then please take 5 minutes to leave anonymous feedback about your experience, and view community ratings.
Latest recommendations
| Id | Title * ▲ | Authors * | Abstract * | Picture | Thematic fields * | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
20 Jan 2025
STAGE 1

How Interviewees Determine What Interviewers Want to KnowDavid A. Neequaye, Alexandra Lorson https://osf.io/preprints/psyarxiv/8s35kDecoding Interviewer’s Intent: How Interviewees Infer Information GoalsRecommended by Yikang Zhang based on reviews by Feni Kontogianni and 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Feni Kontogianni and 2 anonymous reviewers
Investigative interviews are structured social interactions where interviewers seek information from interviewees to address various objectives (e.g., Neequaye, 2023). Across diverse contexts such as eyewitness recall or intelligence gathering (e.g., Geiselman et al., 1986; Granhag & Hartwig, 2015), interviewees must first identify their interviewer’s goals before deciding whether to cooperate or resist their requests. This is the central focus of the current study.
In a prior study, Neequaye and Lorson (2023) made an unexpected discovery: interviewees tended to assume their interviewer was interested in all the information they possessed on a topic, regardless of the specificity of the questions (high vs. low specificity). The current submission by Neequaye and Lorson (2025) seeks to replicate these findings while addressing two potential confounds from the earlier research.
Replication 1 utilizes a within-subjects design for question-specificity trials, while Replication 2 employs a between-subjects design. In both replications, participants indicate what they believe their interviewer wants to know using free-text responses rather than selecting from predefined options. The authors present clear hypotheses, predicted outcomes, and alternative predictions, supported by well-reasoned rationales. Furthermore, the methodology, including data collection and analysis plans, is described in detail and has undergone review by three experts. Based on the expert reviews and the authors’ responses, the recommender concluded that the manuscript met the Stage 1 criteria and granted in-principle acceptance.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/9suze
Level of bias control achieved: Level 4. At least some of the data/evidence that will be used to answer the research question already exists AND is accessible in principle to the authors, but the authors certify that they have not yet accessed any part of that data/evidence.
List of eligible PCI-RR-friendly journals: References
1. Geiselman, R. E., Fisher, R. P., MacKinnon, D. P., & Holland, H. L. (1986). Enhancement of eyewitness memory with the cognitive interview. The American Journal of Psychology, 99, 385-401. https://doi.org/10.2307/1422492
2. Granhag, P. A., & Hartwig, M. (2015). The Strategic Use of Evidence Technique: A Conceptual Overview. In A. Vrij & B. Verschuere (Eds.), Deception detection: Current challenges and new directions (pp. 231–251). John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118510001.ch10
3. Neequaye, D. A. (2023). Why Rapport Seems Challenging to Define and What to Do About the Challenge. Collabra: Psychology, 9, 90789. https://doi.org/10.1525/collabra.90789
4. Neequaye, D. A., & Lorson, A. (2023). How intelligence interviewees mentally identify relevant information. Royal Society Open Science, 10(8), 230986. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.230986
5. Neequaye, D. A., & Lorson, A. (2025). How Interviewees Determine What Interviewers Want to Know. In principle acceptance of Version 4 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/9suze
| How Interviewees Determine What Interviewers Want to Know | David A. Neequaye, Alexandra Lorson | <p>We examine the mechanisms by which interviewees in investigative interviews mentally organize information when deciphering what an interviewer wants to know. The overarching idea is that such a process stems from the extent to which an intervie... | Social sciences | Yikang Zhang | 2024-06-14 22:53:12 | View | ||
17 Jan 2023
STAGE 1

How long does it take to form a habit?: A Multi-Centre Replicationde Wit, S., Bieleke, M., Fletcher, P.C., Horstmann, A., Schüler, J., Brinkhof, L.P., Gunschera, L.J., Murre, J.M.J. https://osf.io/hpsft/?view_only=c8ec62553146496e8b5e4d100a0f08b5How much practice is needed before daily actions are performed in a way that feels habitual?Recommended by Zoltan Dienes based on reviews by Benjamin Gardner, Wendy Wood and Adam Takacs based on reviews by Benjamin Gardner, Wendy Wood and Adam Takacs
Even small changes in daily life can have a significant impact on one’s health, for example going to the gym at regular times and eating a healthy breakfast. But how long must we do something before it becomes a habit? Lally et al. (2010) tracked the subjective automaticity of a novel, daily (eating or exercise-related) routine. Based on 39 participants, they found a median time of 66 days. This estimate has never been replicated with their exact procedure, so the question remains of how well this holds up. Yet the estimate is useful for knowing how long we have to effortfully make ourselves perform an action until we will do it automatically.
In the current study, de Wit et al. (2023) propose a four-centre near-exact replication of Lally et al. (2010), for which they aim to test 800 subjects to provide a precise estimate of the time it takes to form a habit.
The Stage 1 manuscript was evaluated over four rounds of review. Based on detailed responses to the reviewers' comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 1 criteria and therefore awarded in-principle acceptance (IPA).
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/bj9r2 Level of bias control achieved: Level 4. At least some of the data/evidence that will be used to answer the research question already exists AND is accessible in principle to the authors (e.g. residing in a public database or with a colleague), BUT the authors certify that they have not yet accessed any part of that data/evidence.
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Lally, P., van Jaarsveld, C. H. M., Potts, H. W. W., & Wardle, J. (2010). How are habits formed: Modelling habit formation in the real world. European Journal of Social Psychology, 40, 998–1009. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejsp.674
2. de Wit, S., Bieleke, M., Fletcher, P. C., Horstmann, A., Schüler, J., Brinkhof, L. P., Gunschera, L. J., AND Murre, J. M. J. (2023). How long does it take to form a habit?: A Multi-Centre Replication, in principle acceptance of Version 4 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/bj9r2
| How long does it take to form a habit?: A Multi-Centre Replication | de Wit, S., Bieleke, M., Fletcher, P.C., Horstmann, A., Schüler, J., Brinkhof, L.P., Gunschera, L.J., Murre, J.M.J. | <p>How long does it take to form a habit? This question will be addressed by an innovative study by Lally et al. (2010), in which they tracked the subjective automaticity of a novel, daily (eating or exercise-related) routine, using the Self-Repor... | Social sciences | Zoltan Dienes | 2022-05-26 09:54:26 | View | ||
16 Oct 2024
STAGE 1

How perceptual ability shapes memory: An investigation in healthy special populationsChhavi Sachdeva, Emily Whelan, Rebecca Ovalle-Fresa, Alodie Rey-Mermet, Jamie Ward, Nicolas Rothen https://osf.io/842ud?view_only=606c99cb61c7437089176843cf06587aPutting the enhanced processing account of perception and memory to the testRecommended by Reshanne Reeder based on reviews by Ariel Kershner and Katherine Moore based on reviews by Ariel Kershner and Katherine Moore
The enhanced processing account suggests that domain-specific expertise enhances the processing of information in that domain, such as enhanced color perception in visual artists and grapheme-color synaesthetes. A previous study (Ovalle-Fresa et al., 2021) found support for this account in both synaesthetes and non-synaesthete color experts; however, to fully understand the domain specificity of enhanced processing, other domains of expertise should be investigated and compared against each other in a double dissociation.
In this Stage 1 manuscript, Sachdeva et al. (2024) will investigate whether an enhanced processing account can explain domain-specific expertise in groups of color experts (i.e., visual artists) / grapheme-color synaesthetes and spatial experts (i.e., architects) / sequence-space synaesthetes. The spatial domain was chosen to compare to color since color and spatial processing recruit two distinctive cortical visual pathways: the ventral and dorsal streams, respectively. If enhanced processing is domain specific, then color experts / grapheme-color synaesthetes should show selective perceptual and memory performance enhancements for color tasks but not spatial tasks; and vice versa for spatial experts and sequence-space synaesthetes. The authors of this planned study further propose that perceptual performance should predict memory performance in the domain of expertise only; and that synaesthetes and non-synaesthetes with the same domain of expertise should perform similarly to each other.
To address these hypotheses, four independent groups will be recruited: grapheme-color synaesthetes, visual artists, sequence-space synaesthetes, and architects. Individuals with overlapping expertise and synaesthesia (e.g., visual artists who also have grapheme-color synaesthesia) will be excluded. Perception, short-term memory, and long-term memory for color (3 tasks) and space (3 tasks) will be assessed in all groups, and the authors will compare groups (synaesthetes, non-synaesthetes), domains of expertise (color, space), and task feature (color, space) in 2x2x2 linear mixed models. For all models, the authors predict that a significant interaction between domain of expertise and task feature will provide evidence for the domain specificity of the enhanced processing account. Additional analyses concerning working memory load (one, three, or five items) in the short-term memory tasks, and testing day (one, two, or three days post-training) in the long-term memory tasks, will be conducted to more deeply explore potential performance enhancements related to domain-specific expertise. Although these analyses may potentially provide additional evidence in favor of the hypothesized direction of effects, any deviation from predicted may pose a challenge for the interpretation of results. Nevertheless, this planned study is methodologically rigorous, and comprehensive in its aims.
The Stage 1 submission was evaluated by the recommender and two expert reviewers. Following revisions, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 1 criteria and awarded in-principle acceptance (IPA).
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/6wn4m
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that will be used to answer the research question yet exists and no part will be generated until after IPA. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Ovalle-Fresa, R., Ankner, S., & Rothen, N. (2021). Enhanced perception and memory: Insights from synesthesia and expertise. Cortex, 140, 14-25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2021.01.024
2. Sachdeva, D. & Whelan, E., Ovalle-Fresa, R., Rey-Mermet, A., Ward, J., & Rothen, N.. (2024). How perceptual ability shapes memory: An investigation in healthy special populations. In principle acceptance of Version 2 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/6wn4m | How perceptual ability shapes memory: An investigation in healthy special populations | Chhavi Sachdeva, Emily Whelan, Rebecca Ovalle-Fresa, Alodie Rey-Mermet, Jamie Ward, Nicolas Rothen | <p>The enhanced processing account posits a close connection between visual perceptual ability and memory. This account finds support in studies involving special populations with conditions based on neural changes in the ventral visual pathway, s... | Life Sciences | Reshanne Reeder | Katherine Moore, Ariel Kershner | 2024-05-03 14:15:43 | View | |
08 Sep 2022
STAGE 1

How to succeed in human modified environmentsLogan CJ, Shaw R, Lukas D, McCune KB http://corinalogan.com/ManyIndividuals/mi1.htmlThe role of behavioural flexibility in promoting resilience to human environmental impactsRecommended by Chris Chambers based on reviews by Gloriana Chaverri, Vedrana Šlipogor and Alizée Vernouillet based on reviews by Gloriana Chaverri, Vedrana Šlipogor and Alizée Vernouillet
Understanding and mitigating the environmental effects of human expansion is crucial for ensuring long-term biosustainability. Recent research indicates a steep increase in urbanisation – including the expansion of cities – with global urban extent expanding by nearly 10,000 km^2 per year between 1985 and 2015 (Liu et al, 2020). The consequences of these human modified environments on animal life are significant: in order to succeed, species must adapt quickly to environmental changes, and those populations that demonstrate greater behavioural flexibility are likely to cope more effectively. These observations have, in turn, prompted the question of whether enhancing behavioural flexibility in animal species might increase their resilience to human impacts.
In the current research, Logan et al. (2022) will use a serial reversal learning paradigm to firstly understand how behavioural flexibility relates to success in avian species that are already successful in human modified environments. The authors will then deploy these flexibility interventions in more vulnerable species to establish whether behavioural training can improve success, as measured by outcomes such as foraging breadth, dispersal dynamics, and survival rate.
The Stage 1 manuscript was submitted via the programmatic track and will eventually produce three Stage 2 outputs focusing on different species (toutouwai, grackles, and jays). Following two rounds of in-depth review, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 1 criteria and awarded in-principle acceptance (IPA).
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/wbsn6
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that will be used to answer the research question yet exists and no part will be generated until after IPA. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals: References
1. Liu, X., Huang, Y., Xu, X., Li, X., Li, X., Ciais, P., Lin, P., Gong, K., Ziegler, A. D., Chen, A., et al. (2020). High-spatiotemporal-resolution mapping of global urban change from 1985 to 2015. Nature Sustainability, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41893-020-0521-x
2. Logan, C.J., Shaw, R., Lukas, D. & McCune, K.B. (2022). How to succeed in human modified environments, in principle acceptance of Version 3 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/wbsn6
| How to succeed in human modified environments | Logan CJ, Shaw R, Lukas D, McCune KB | <p>Human modifications of environments are increasing, causing global changes that other species must adjust to or suffer from. Behavioral flexibility (hereafter ‘flexibility’) could be key to coping with rapid change. Behavioral research can cont... |  | Life Sciences | Chris Chambers | 2022-05-06 12:12:05 | View | |
17 Jan 2022
STAGE 1

Identifying Gaming Disorders by Ontology: A Nationally Representative Registered ReportVeli-Matti Karhulahti, Jukka Vahlo, Marcel Martončik, Matti Munukka, Raine Koskimaa, Mikaela von Bonsdorff https://osf.io/mpz9q/Do different screening instruments for ‘gaming disorder’ measure the same or different construct(s)?Recommended by Charlotte Pennington based on reviews by Daniel Dunleavy, Linda Kaye, David Ellis and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Daniel Dunleavy, Linda Kaye, David Ellis and 1 anonymous reviewer
There is considerable debate regarding the relationship between excessive gaming and mental health problems. Whilst the diagnostic classification of “gaming disorder” has now been included in the WHO’s International Classification of Diseases (ICD-11), the APA decided not to include this diagnosis in their Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) because the literature “suffers from a lack of a standard definition from which to derive prevalence data” (APA 2013, p. 796). Furthermore, screening instruments that aim to provide diagnostic classifications derive from different ontologies and it is not known whether they identify equivalent prevalence rates of ‘gaming disorder’ or even the same individuals. In this Stage 1 Registered Report, Karhulahti et al. (2022) aim to assess how screening instruments that derive from different ontologies differ in identifying associated problem groups. A nationally representative sample of 8000 Finnish individuals will complete four screening measures to assess the degree of overlap between identified prevalence (how many?), who they identify (what characteristics?) and the health of their identified groups (how healthy?). If these four ontologically diverse instruments operate similarly, this will support the notion of a single “gaming disorder” construct. If, however, the instruments operate differently, this will suggest that efforts should be directed toward assessing the clinical (ir)relevance of multiple constructs. This rigorous study will therefore have important implications for the conceptualisation and measurement of “gaming disorder”, contributing to the debate around the mixed findings of gaming-related health problems. Four expert reviewers with field expertise assessed the Stage 1 manuscript over three rounds of in-depth review. Based on detailed and informed responses to the reviewers' comments, the recommender decided that the manuscript met the Stage 1 criteria and therefore awarded in-principle acceptance (IPA). URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/usj5b Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that will be used to answer the research question yet exists and no part will be generated until after IPA. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
| Identifying Gaming Disorders by Ontology: A Nationally Representative Registered Report | Veli-Matti Karhulahti, Jukka Vahlo, Marcel Martončik, Matti Munukka, Raine Koskimaa, Mikaela von Bonsdorff | <p style="text-align: justify;">Gaming-related health problems have been researched since the 1980s with numerous different “ontologies” as reference systems, from self-assessed “game addiction” to “pathological gambling” (in the DSM-IV), “interne... |  | Medical Sciences, Social sciences | Charlotte Pennington | 2021-08-25 23:08:26 | View | |
Identifying relevant dimensions to the measurement of social media experience via focus groups with young peopleJo Hickman Dunne, Louise Black, Molly Anderton, Pratyasha Nanda, Emily Banwell, Lily Corke Butters, Ola Demkowicz, Jade Davies, Brittany I Davidson, Pamela Qualter, Neil Humphrey, Caroline Jay, Margarita Panayiotou https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/erjvzA mental health perspective to adolescents’ social media experiencesRecommended by Veli-Matti Karhulahti based on reviews by Amy Orben, Jana Papcunova and Elena Gordon-Petrovskaya based on reviews by Amy Orben, Jana Papcunova and Elena Gordon-Petrovskaya
Measuring people’s experiences, thoughts, and mental processes has always been a core challenge of psychological science (e.g. Nisbett & Wilson 1977). When such measurement relates to rapidly changing and conceptually diverse human-technology interactions, the task becomes even more difficult due to protean, multidimensional constructs. A good understanding of a construct is a basic step in its measurement (Borsboom 2005).
In the present registered report—carried out as part of a long-term measure development project—Dunne et al. (2024) carried out a focus group study with adolescents (n=26) aged 11 to 15 in Northwest England to improve the understanding of constructs related to social media and mental health. The authors applied reflexive thematic analysis to explore adolescents’ social media use experiences and related motivations in the light of mental health. The data and research process led to a construction of five themes, which were connected to mental health in direct and indirect ways. The participants voiced direct experiences of anxiety, self-esteem, and social aspects that reflect a mental health network where social media play diverse roles. Indirect implications of coping and self-control were found to supplement the network. Taken together, the themes and their implications to wellbeing make a valuable contribution to the evolving qualitative understanding young people's social media use in the UK (e.g., Conroy et al. 2023) and serve as a useful basis for future measure development. A particular strength of the work was the engagement of three Young Researchers who co-facilitated the focus groups and were involved in the analysis. The research meets high reflexivity and transparency criteria, and the carefully constructed supplementary materials provide informative details especially for measure developers. Finally, the authors must be commended for sharing these valuable data for reuse. The Stage 2 manuscript was reviewed over two rounds by three unique reviewers. The reviewers’ expertise ranged from social media and technology use research to health psychology and qualitative methods. Based on careful revisions and detailed responses to the reviewers’ comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 2 criteria and awarded a positive recommendation. URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/w24ec Level of bias control achieved: Level 2. At least some data/evidence had been accessed and partially observed by the authors prior to IPA, but the authors certify that they have not yet observed the key variables within the data that were used to answer the research question. List of eligible PCI-RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Borsboom, D. (2005). Measuring the mind: Conceptual issues in contemporary psychometrics. Cambridge University Press. 2. Conroy, D., Chadwick, D., Fullwood, C., & Lloyd, J. (2023). “You have to know how to live with it without getting to the addiction part”: British young adult experiences of smartphone overreliance and disconnectivity. Psychology of Popular Media, 12, 471-480. https://doi.org/10.1037/ppm0000425 3. Dunne, J. H., Black, L., Banwell, E., Nanda, P., Anderton, M, Butters, L.C., Demkowicz, O., Davies, J., Davidson, B., Qualter, P., Humphrey, N., Jay, C., & Panayiotou, M. (2024). Identifying relevant dimensions to the measurement of adolescent social media experience via focus groups with young people [Stage 2]. Acceptance of Version 9 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/erjvz
4. Nisbett, R. E., & Wilson, T. D. (1977). Telling more than we can know: Verbal reports on mental processes. Psychological review, 84, 231-259. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295X.84.3.231 | Identifying relevant dimensions to the measurement of social media experience via focus groups with young people | Jo Hickman Dunne, Louise Black, Molly Anderton, Pratyasha Nanda, Emily Banwell, Lily Corke Butters, Ola Demkowicz, Jade Davies, Brittany I Davidson, Pamela Qualter, Neil Humphrey, Caroline Jay, Margarita Panayiotou | <p>While work on the relationship between social media use and adolescent mental health has allowed for some progress, research in this area is still relatively new and shows mixed evidence. This is partly the consequence of a rapidly changing fie... | Social sciences | Veli-Matti Karhulahti | 2024-05-03 20:40:41 | View | ||
16 Aug 2023
STAGE 1

Identifying relevant experiences to the measurement of social media experience via focus groups with young people: A registered reportJo Hickman Dunne, Louise Black, Emily Banwell, Pratyasha Nanda, Molly Anderton, Lily Corke Butters, Ola Demkowicz, Brittany Davidson, Pamela Qualter, Neil Humphrey, Caroline Jay, and Margarita Panayiotou https://psyarxiv.com/erjvz/A mental health perspective to adolescents’ social media experiencesRecommended by Veli-Matti Karhulahti based on reviews by Amy Orben, Jana Papcunova, Lisa Orchard, Elena Gordon-Petrovskaya and Gaurav Saxena based on reviews by Amy Orben, Jana Papcunova, Lisa Orchard, Elena Gordon-Petrovskaya and Gaurav Saxena
Measuring people’s experiences, thoughts, and mental processes has always been a core challenge of psychological science (e.g. Nisbett & Wilson 1977). When such measurement further relates to rapidly changing and conceptually diverse human-technology interactions, the task becomes even more difficult due to protean, multidimensional constructs. A good understanding of a construct is a basic step in its measurement (Borsboom 2005).
In the present registered report, Hickman Dunne et al. (2023) carry out a focus group study with adolescents (n=32) aged 11 to 15 in Northwest England to improve the understanding of constructs related to social media and mental health experiences. The work is carried out as part of a long-term measure development project. The authors apply reflexive thematic analysis to explore adolescents’ social media use experiences and related motivations in the light of mental health, in addition to which the adolescents’ own views of benefits and risks are mapped out. A particular strength of the design is the engagement of three Young Researchers who will co-facilitate the focus groups and be involved in the analysis. The research plan also meets high reflexivity and transparency criteria, and as such, can significantly contribute to future scale development as well as our general understanding of adolescents’ social media experiences. The Stage 1 manuscript was reviewed over two rounds by five unique reviewers, one of which participated in both rounds. The reviewers’ expertise ranged from social media and technology use research to health psychology and qualitative methods. Based on careful revisions and detailed responses to the reviewers’ comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 1 criteria and therefore awarded in-principle acceptance. URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/w24ec
Level of bias control achieved: Level 2. At least some data/evidence that will be used to answer the research question has been accessed and partially observed by the authors, but the authors certify that they have not yet observed the key variables within the data that will be used to answer the research question. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals: References
1. Borsboom, D. (2005). Measuring the mind: Conceptual issues in contemporary psychometrics. Cambridge University Press. 3. Nisbett, R. E., & Wilson, T. D. (1977). Telling more than we can know: Verbal reports on mental processes. Psychological review, 84, 231–259. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295X.84.3.231
2. Hickman Dunne J., Black L., Banwell E., Nanda P., Anderton M, Butters L.C., Demkowicz O., Davidson B., Qualter P., Humphrey N., Jay C., and Panayiotou M. (2023). Identifying relevant dimensions to the measurement of adolescent social media experience via focus groups with young people: A registered report. In principle acceptance of Version 5 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/w24ec | Identifying relevant experiences to the measurement of social media experience via focus groups with young people: A registered report | Jo Hickman Dunne, Louise Black, Emily Banwell, Pratyasha Nanda, Molly Anderton, Lily Corke Butters, Ola Demkowicz, Brittany Davidson, Pamela Qualter, Neil Humphrey, Caroline Jay, and Margarita Panayiotou | <p>Background: While work on the relationship between social media use and adolescent mental health has allowed for some progress, research in this area is still relatively new and shows mixed evidence. This is partly the consequence of a rapidly ... | Computer science, Social sciences | Veli-Matti Karhulahti | 2023-06-14 21:10:43 | View | ||
02 Apr 2025
STAGE 1

Impact of Acute Stress Exposure on Reactivity to Loss of Control Over ThreatMichalina Dudziak, Tom Smeets, Bram Vervliet, Tom Beckers https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/j5kgtHow does stress influence psychological and biological responses to uncontrollable threat?Recommended by Saeed Shafiei Sabet and Yuki Yamada and Yuki Yamada based on reviews by Mariela Mihaylova, Laura Meine and Genisius Hartanto based on reviews by Mariela Mihaylova, Laura Meine and Genisius Hartanto
One of the key drivers of how organisms respond to stressful events or situations is the controllability of the stressor – the extent to which the individual has (or believes) they can control the stress-inducing event or situation. A considerable literature has explored controllability and the effects of aversive events, with the general finding that uncontrollable situations more strongly impair emotion and cognition while increasing stress responses (Maier & Seligman, 1976). In a key review, Foa et al. (1992) evaluated the effects of unpredictable and uncontrollable aversive events that caused disturbance in animals. Although it remains unclear, longevity of stress exposure may play a role in responsiveness when exposed to uncontrollable threats in humans.
Here, Dudziak et al. (2025) examine whether acute stress exposure impacts reactivity to a subsequent loss of control over threat. Participants (N=128) will be assigned to a stress or a no-stress group, undergoing an acute stress induction or a non-stressful control procedure, followed by a behavioural loss-of-control task. By assessing salivary cortisol and salivary alpha-amylase assays, blood pressure measurements, and self-report ratings they hypothesize that participants exposed to acute stress will show stronger biological and psychological responses to the loss of control over threat than those in the no-stress group. The authors will also test whether individual differences in childhood adversity are associated with heightened stress responses. Overall, the findings promise to shed light on the directional relationship between threat controllability and stress reactivity, and will therefore be relevant across a range of research areas in clinical psychology, biological psychology, and associated domains.
The Stage 1 manuscript was evaluated by three expert reviewers who performed in-depth and constructive evaluation across multiple rounds of revisions. The authors were responsive in amending their manuscript based on the reviewers’ comments and dedicated much effort to increasing the clarity and interpretability of their design and sampling plan. The revised manuscript was judged to meet the Stage 1 criteria and was awarded in-principle acceptance (IPA).
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/ytvs8
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. Data collection began during the final round of Stage 1 peer review. Since no substantive revisions to the design or analysis were made after this review round, the risk of bias due to prior data observation remained zero, and the manuscript therefore qualified for Level 6. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References 1. Dudziak, M., Smeets, T., Vervliet, B., & Beckers, T. (2025). Impact of acute stress exposure on reactivity to loss of control over threat. In principle acceptance of Version 3 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/ytvs8
2. Foa, E. B., Zinbarg, R., & Rothbaum, B. O. (1992). Uncontrollability and unpredictability in post-traumatic stress disorder: An animal model. Psychological Bulletin, 112, 218-238. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.112.2.218
3. Maier, S. F., & Seligman, M. E. (1976). Learned helplessness: Theory and evidence. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 105, 3-46. https://doi.org/10.1037/0096-3445.105.1.3
| Impact of Acute Stress Exposure on Reactivity to Loss of Control Over Threat | Michalina Dudziak, Tom Smeets, Bram Vervliet, Tom Beckers | <p>Uncontrollable negative events yield increased stress responses compared to situations over which we have control. Previous studies have assessed the impact of uncontrollability of threat on stress reactivity. Less is known about whether and ho... | Social sciences | Saeed Shafiei Sabet | 2024-10-22 17:53:28 | View | ||
Impact of analytic decisions on test-retest reliability of individual and group estimates in functional magnetic resonance imaging: a multiverse analysis using the monetary incentive delay taskMichael I. Demidenko, Jeanette A. Mumford, Russell A. Poldrack https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.03.19.585755Exploring determinants of test-retest reliability in fMRI: a study with the Monetary Incentive Delay TaskRecommended by Dorothy Bishop based on reviews by Xiangzhen Kong and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Xiangzhen Kong and 1 anonymous reviewer
Functional magnetic resonance imaging has been used to explore brain-behaviour relationships for many years, with proliferation of a wide range of sophisticated analytic procedures. However, rather scant attention has been paid to the reliability of findings. Concerns have been growing failures to replicate findings in some fields, but it is hard to know how far this is a consequence of underpowered studies, flexible analytic pipelines, or variability within and between participants. Demidenko et al. (2024) took advantage of the availability of three existing datasets, including the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) study, the Michigan Longitudinal Study, and the Adolescent Risk Behavior Study, which all included a version of the Monetary Incentive Delay task measured in two sessions. These were entered into a multiverse analysis, which considered how within-subject and between-subject variance varies according to four analytic factors: smoothing (5 levels), motion correction (6 levels), task modelling (3 levels) and task contrasts (4 levels). They also considered how sample size affects estimates of reliability. The results have important implications for the those using fMRI with the Monetary Incentive Delay Task, and also raise questions more broadly about use of fMRI indices to study individual differences. Motion correction had relatively little impact on the ICC, and the effect size of the smoothing kernel was modest. Larger impacts on reliability were associated with choice of contrast (implicit baseline giving larger effects) and task parameterization. But perhaps the most sobering message from this analysis is that although activation maps from group data were reasonably reliable, the ICC, used as an index of reliability for individual levels of activation, was consistently low. This raises questions about the suitability of the Monetary Incentive Delay Task for studying individual differences. Another point is that reliability estimates become more stable as sample size increases; researchers may want to consider whether the trade-off between cost and gain in precision is justified for sample sizes above 250. I did a quick literature search on Web of Science: at the time of writing the search term ("Monetary Delay Task" AND fMRI) yielded 410 returns, indicating that this is a popular method in cognitive neuroscience. The detailed analyses reported here will repay study for those who are planning further research using this task. The Stage 2 manuscript was evaluated over one round of in-depth review. Based on detailed responses to the reviewer's and recommender's comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 2 criteria and awarded a positive recommendation. URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/nqgeh
Level of bias control achieved: Level 2. At least some data/evidence that was used to answer the research question had been accessed and partially observed by the authors prior to IPA, but the authors certify that they had not yet sufficiently observed the key variables within the data to be able to answer the research questions and they took additional steps to maximise bias control and rigour.
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References 1. Demidenko, M. I., Mumford, J. A., & Poldrack, R. A. (2024). Impact of analytic decisions on test-retest reliability of individual and group estimates in functional magnetic resonance imaging: a multiverse analysis using the monetary incentive delay task [Stage 2]. Acceptance of Version 5 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2024.03.19.585755v4 | Impact of analytic decisions on test-retest reliability of individual and group estimates in functional magnetic resonance imaging: a multiverse analysis using the monetary incentive delay task | Michael I. Demidenko, Jeanette A. Mumford, Russell A. Poldrack | <p>Empirical studies reporting low test-retest reliability of individual blood oxygen-level dependent (BOLD) signal estimates in functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) data have resurrected interest among cognitive neuroscientists in methods... | 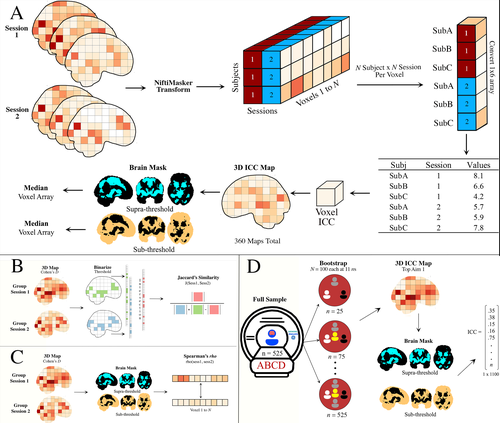 | Life Sciences, Social sciences | Dorothy Bishop | 2024-03-21 02:23:30 | View | |
14 Jan 2025
STAGE 1
Implementing a rapid geographic range expansion - the role of behavior and habitat changesCorina J Logan, Kelsey B McCune, Nancy Chen, Dieter Lukas http://corinalogan.com/Preregistrations/gxpopbehaviorhabitat.htmlThe role of behavior and habitat availability on species geographic expansionRecommended by Chris Chambers
Note from the PCI RR Managing Board: This Stage 1 recommendation was originally written by Esther Sebastián González for PCI Ecology on 06 Oct 2020 and was transferred to PCI Registered Reports on 14 Jan 2025 to facilitate the submission and evaluation of the resulting Stage 2 submissions. The link to the original recommendation and review history at PCI Ecology may be found at this link (and in PDF format here).
===
Understanding the relative importance of species-specific traits and environmental factors in modulating species distributions is an intriguing question in ecology [1]. Both behavioral flexibility (i.e., the ability to change the behavior in changing circumstances) and habitat availability are known to influence the ability of a species to expand its geographic range [2,3]. However, the role of each factor is context and species dependent and more information is needed to understand how these two factors interact. In this pre-registration, Logan et al. [4] explain how they will use Great-tailed grackles (Quiscalus mexicanus), a species with a flexible behavior and a rapid geographic range expansion, to evaluate the relative role of habitat and behavior as drivers of the species’ expansion [4]. The authors present very clear hypotheses, predicted results and also include alternative predictions. The rationales for all the hypotheses are clearly stated, and the methodology (data and analyses plans) are described with detail. The large amount of information already collected by the authors for the studied species during previous projects warrants the success of this study. It is also remarkable that the authors will make all their data available in a public repository, and that the pre-registration in already stored in GitHub, supporting open access and reproducible science. I agree with the three reviewers of this pre-registration about its value and I think its quality has largely improved during the review process. Thus, I am happy to recommend it and I am looking forward to seeing the results.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: http://corinalogan.com/Preregistrations/gxpopbehaviorhabitat.html
Level of bias control achieved: Level 1. At least some of the data/evidence that will be used to the answer the research question has been accessed and observed by the authors, including key variables, but the authors certify that they have not yet performed any of their preregistered analyses, and in addition they have taken stringent steps to reduce the risk of bias.
List of eligible PCI-RR-friendly journals: References
[1] Gaston KJ. 2003. The structure and dynamics of geographic ranges. Oxford series in Ecology and Evolution. Oxford University Press, New York.
[2] Sol D, Lefebvre L. 2000. Behavioural flexibility predicts invasion success in birds introduced to new zealand. Oikos. 90(3): 599–605. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0706.2000.900317.x
[3] Hanski I, Gilpin M. 1991. Metapopulation dynamics: Brief history and conceptual domain. Biological journal of the Linnean Society. 42(1-2): 3–16. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8312.1991.tb00548.x
[4] Logan CJ, McCune KB, Chen N, Lukas D. 2020. Implementing a rapid geographic range expansion - the role of behavior and habitat changes (http://corinalogan.com/Preregistrations/gxpopbehaviorhabitat.html) In principle acceptance by PCI Ecology of the version on 16 Dec 2021 https://github.com/corinalogan/grackles/blob/0fb956040a34986902a384a1d8355de65010effd/Files/Preregistrations/gxpopbehaviorhabitat.Rmd
=======
Full review history: [link]
| Implementing a rapid geographic range expansion - the role of behavior and habitat changes | Corina J Logan, Kelsey B McCune, Nancy Chen, Dieter Lukas | <p>It is generally thought that behavioral flexibility, the ability to change behavior when circumstances change, plays an important role in the ability of a species to rapidly expand their geographic range (Chow et al., 2016; Griffin & Guez, ... | Life Sciences | Chris Chambers | 2025-01-13 12:12:15 | View |
FOLLOW US
MANAGING BOARD
Chris Chambers
Zoltan Dienes
Corina Logan
Benoit Pujol
Maanasa Raghavan
Emily S Sena
Yuki Yamada










