Announcements
We are recruiting recommenders (editors) from all research fields!
Your feedback matters! If you have authored or reviewed a Registered Report at Peer Community in Registered Reports, then please take 5 minutes to leave anonymous feedback about your experience, and view community ratings.
Latest recommendations

| Id | Title | Authors | Abstract▲ | Picture | Thematic fields | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Progression of white matter hyperintensities is related to blood pressure increases and global cognitive decline – a registered reportFrauke Beyer, Laurenz Lammer, Markus Loeffler, Steffi Riedel-Heller, Stéphanie Debette, Arno Villringer, A. Veronica Witte https://osf.io/k24pmWhite matter lessions are associated with increases in blood pressure and global cognitive declineRecommended by Chris Chambers based on reviews by Isabel Garcia Garcia based on reviews by Isabel Garcia Garcia
Cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD) is a common and multi-faceted set of pathologies that affect the small arteries, arterioles, venules and capillaries of the brain. The disease manifests through a range of symptoms and conditions, including psychiatric disorders, abnormal gait, and urinary incontinence, while accounting for 25% of strokes and nearly 50% of dementia.
The presence of CSVD is associated with white matter lesions detected as white matter hyperintensities (WMH) using neuroimaging, which have in turn been shown to predict future stroke, cognitive decline and dementia. While vascular risk factors of CSVD (such as hypertension and obesity) are also associated with CSVD, a complete picture of the predictive relationship between WMH, cognitive decline, and blood pressure remains to be determined, as does the role of sex/gender. These inter-relationships are important to determine for improving the diagnosis and treatment of CSVD.
In the current study, Beyer et al. analysed a large emerging dataset from the LIFE-Adult project – a longitudinal, two-wave, population-based study – to ask whether higher blood pressure predicts a greater increase in WMH, and whether progression of WMH is associated with measures of memory and executive function. In addition, the authors explored the relationship between abdominal obesity and WMH progression, and the extent to which WMH progression, and its interaction with vascular risk factors, depends on sex/gender.
Results revealed no reliable association between baseline blood pressure with WMH progression. WMH progression significantly predicted global cognitive decline but not decline in executive function specifically. Exploratory analyses revealed that increases in diastolic blood pressure as well as baseline and systolic blood pressure were associated with WMH progression, specifically in frontal periventricular regions, but there was no association of waist-to-hip ratio (a proxy of abdominal fat deposits) with WMH progression nor any gender-specific associations. The authors conclude that strict control of blood pressure might confer a protective effect, limiting WMH progression and negative effects on global cognitive function in the middle-aged to older population.
The Stage 2 manuscript was evaluated over one round of in-depth review. Based on responses to the reviewer's comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 2 criteria and awarded a positive recommendation.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/qkbgj Level of bias control achieved: Level 2. At least some data/evidence that was used to answer the research question had been accessed and partially observed by the authors prior to Stage 1 in-principle acceptance, but the authors certify that they had not yet observed the key variables within the data that were used to answer the research question.
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals: References
1. Beyer, F., Lammer, L., Loeffler, M., Riedel-Heller, S., Debette, S., Villringer, A. & Witte, A. V. (2023). Progression of white matter hyperintensities is related to blood pressure increases and global cognitive decline – a registered report [Stage 2]. Acceptance of Version 2 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/k24pm
| Progression of white matter hyperintensities is related to blood pressure increases and global cognitive decline – a registered report | Frauke Beyer, Laurenz Lammer, Markus Loeffler, Steffi Riedel-Heller, Stéphanie Debette, Arno Villringer, A. Veronica Witte | <p>Introduction<br>White matter hyperintensities (WMH) reflect cerebral small vessel disease (cSVD), a major brain pathology contributing to cognitive decline and dementia. Vascular risk factors including higher diastolic blood pressure (DBP) have... | 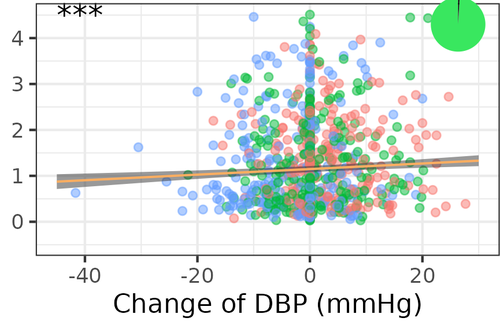 | Humanities, Medical Sciences | Chris Chambers | 2024-02-15 17:16:37 | View | |
01 Dec 2022
STAGE 1

Cerebral lateralization of writing in students at risk for dyslexia using functional Transcranial Doppler ultrasonographyAnastasia-Konstantina Papadopoulou, Filippos Vlachos, Panagiota Pervanidou, Sofia Anesiadou, Faye Antoniou, Phivos Phylactou, Nicholas A. Badcock, Marietta Papadatou-Pastou https://osf.io/u54tkLateralisation for written language in primary school students at risk for dyslexiaRecommended by Saloni Krishnan based on reviews by Margriet Groen and Todd Richards based on reviews by Margriet Groen and Todd Richards
While cerebral lateralisation for oral language is well-characterised, cerebral lateralisation for written language is much less well-understood. In this study, Papadopoulou et al. (2022) will use functional transcranial Doppler ultrasonography to assess lateralisation for written language in 7- to 9-year-old children at risk for dyslexia and neurotypical children. They will use tasks that assess efficiency in reading and writing names as well as speed and fluency in writing. The findings of this manuscript will highlight whether children with dyslexia showed atypical lateralisation for language in a written task. In addition, the authors plan to explore the correlation between lateralisation and writing competence.
The Stage 1 manuscript was evaluated over two rounds of in-depth review. Based on the edits made to the manuscript, and detailed responses to the reviewers' comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 1 criteria and therefore awarded in-principle acceptance (IPA).
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/u54tk (under temporary private embargo)
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that will be used to answer the research question yet exists and no part will be generated until after IPA. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Papadopoulou, A.-K., Vlachos, F., Pervanidou, P., Anesiadou, S., Antoniou, F., Phylactou, P., Badcock, N.A. & Papadatou-Pastou, M. (2022). Cerebral lateralization of writing in students at risk for dyslexia using functional Transcranial Doppler ultrasonography, in principle acceptance of Version 2 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/u54tk (under temporary private embargo)
| Cerebral lateralization of writing in students at risk for dyslexia using functional Transcranial Doppler ultrasonography | Anastasia-Konstantina Papadopoulou, Filippos Vlachos, Panagiota Pervanidou, Sofia Anesiadou, Faye Antoniou, Phivos Phylactou, Nicholas A. Badcock, Marietta Papadatou-Pastou | <p>It is well established that the left hemisphere is dominant in oral language in the majority of neurotypical individuals, while a more symmetrical pattern of activation in shown in cases of language disorders, such as dyslexia. Cerebral lateral... | Humanities, Life Sciences, Social sciences | Saloni Krishnan | Margriet Groen, Todd Richards | 2022-06-06 09:00:26 | View | |
18 Jan 2023
STAGE 1

Beneath the label: Assessing video games’ compliance with ESRB and PEGI loot box warning label industry self-regulationLeon Y. Xiao https://osf.io/u7ghb?view_only=60cb55c3c3c74f76a8e170fb498e2789How effective is self-regulation in loot box labelling?Recommended by Chris Chambers based on reviews by Pete Etchells and Jim Sauer based on reviews by Pete Etchells and Jim Sauer
Paid loot boxes – items bought for real-world money that offer randomised rewards – are a prevalent feature of contemporary video games (Zendle et al., 2020). Because they employ random chance to provide rewards after spending real money, loot boxes have been considered a form of gambling, raising concerns about risk of harm to children and other vulnerable users. In response, some countries have taken legal steps to regulate and even ban the use of loot boxes, with only limited success so far (Xiao, 2022). At the same time, the Entertainment Software Rating Board (ESRB) and PEGI (Pan-European Game Information) now expect games that contain loot boxes to be marked with warning labels that, in theory, will enable users (including parents) to make more informed decisions. These requirements by ESRB/PEGI are not legally binding and may be considered a form of industry self-regulation.
In the current study, Xiao (2023) will investigate the effectiveness of self-regulation in the use of loot box labels. Study 1 examines the consistency of warning labels by the ESRB and PEGI, with the expectation that if self-regulation works as it should then these labels should always (or nearly always) co-occur. Study 2 establishes the compliance rate for labelling among popular games that are known to contain loot boxes, with a rate of ≥95% considered to be successful. The findings should prove useful in identifying the success or failure of self-regulation as a means of ensuring industry compliance with loot box labelling.
The Stage 1 manuscript was evaluated over two rounds of in-depth review. Based on detailed responses to the reviewers' comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 1 criteria and therefore awarded in-principle acceptance (IPA).
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/e6qbm Level of bias control achieved: Level 3. At least some data/evidence that will be used to the answer the research question has been previously accessed by the authors (e.g. downloaded or otherwise received), but the authors certify that they have not yet observed ANY part of the data/evidence.
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Zendle, D., Meyer, R., Cairns, P., Waters, S., & Ballou, N. (2020). The prevalence of loot boxes in mobile and desktop games. Addiction, 115(9), 1768-1772. https://doi.org/10.1111/add.14973
2. Xiao, L. Y. (2022). Breaking Ban: Belgium’s ineffective gambling law regulation of video game loot boxes. Stage 2 Registered Report, acceptance of Version 2 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/hnd7w 3. Xiao, L. Y. (2023). Beneath the label: Assessing video games’ compliance with ESRB and PEGI loot box warning label industry self-regulation, in principle acceptance of Version 3 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/e6qbm
| Beneath the label: Assessing video games’ compliance with ESRB and PEGI loot box warning label industry self-regulation | Leon Y. Xiao | <p>Loot boxes in video games are a form of in-game transactions with randomised elements. Concerns have been raised about loot boxes’ similarities with gambling and their potential harms (e.g., overspending). Recognising players’ and parents’ conc... |  | Humanities, Social sciences | Chris Chambers | 2022-09-17 00:14:51 | View | |
Beneath the label: Unsatisfactory compliance with ESRB, PEGI, and IARC industry self-regulation requiring loot box presence warning labels by video game companiesLeon Y. Xiao https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/asbcgFailure of industry self-regulation in loot box labellingRecommended by Chris Chambers
Paid loot boxes – items bought for real-world money that offer randomised rewards – are a prevalent feature of contemporary video games (Zendle et al., 2020). Because they employ random chance to provide rewards after spending real money, loot boxes have been considered a form of gambling, raising concerns about risk of harm to children and other vulnerable users. In response, some countries have taken legal steps to regulate and even ban the use of loot boxes, with only limited success so far (Xiao, 2022). At the same time, the Entertainment Software Rating Board (ESRB) and PEGI (Pan-European Game Information) now expect games that contain loot boxes to be marked with warning labels that, in theory, will enable users (including parents) to make more informed decisions. These requirements by ESRB/PEGI are not legally binding and may be considered a form of industry self-regulation.
In the current study, Xiao (2023) investigated the effectiveness of self-regulation in the use of loot box labels. Study 1 examined the consistency of warning labels by the ESRB and PEGI, with the expectation that if self-regulation works as it should then these labels should always (or nearly always) co-occur. Study 2 established the compliance rate for labelling among popular games that are known to contain loot boxes, with a rate of ≥95% considered to be successful.
The results of both studies reveal deficiences in industry self-regulation. The consistency rate of warning labels by the ESRB and PEGI was just 39.4% in preregistered analyses, rising to 83.9% in an unregistered exploratory analysis that took into account industry responses to the findings. Even at this upper bound, this rate is lower than expected by complete (or near-complete) consistency. The results of Study 2 indicate that only 29% of games on the Google Play Store known to contain loot boxes were accurately labelled, indicating that 71% were non-compliant with industry requirements.
Following careful evaluation, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 2 criteria and awarded a positive recommendation.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/e6qbm Level of bias control achieved: Level 3. At least some data/evidence that was used to the answer the research question had been previously accessed by the authors (e.g. downloaded or otherwise received), but the authors certifed that they had not yet observed ANY part of the data/evidence prior to in-principle-acceptance.
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Zendle, D., Meyer, R., Cairns, P., Waters, S., & Ballou, N. (2020). The prevalence of loot boxes in mobile and desktop games. Addiction, 115(9), 1768-1772. https://doi.org/10.1111/add.14973
2. Xiao, L. Y. (2022). Breaking Ban: Belgium’s ineffective gambling law regulation of video game loot boxes. Stage 2 Registered Report, acceptance of Version 2 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/hnd7w 3. Xiao, L. Y. (2023). Beneath the label: Unsatisfactory compliance with ESRB, PEGI, and IARC industry self-regulation requiring loot box presence warning labels by video game companies, acceptance of Version 2 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/asbcg
| Beneath the label: Unsatisfactory compliance with ESRB, PEGI, and IARC industry self-regulation requiring loot box presence warning labels by video game companies | Leon Y. Xiao | <p>Loot boxes in video games are a form of in-game transactions with randomised elements. Concerns have been raised about loot boxes’ similarities with gambling and their potential harms (e.g., overspending). Recognising players’ and parents’ conc... | Humanities, Social sciences | Chris Chambers | Jim Sauer, Pete Etchells | 2023-02-12 16:17:34 | View | |
07 Apr 2022
STAGE 1

Breaking Ban: Assessing the effectiveness of Belgium’s gambling law regulation of video game loot boxesLeon Y. Xiao https://osf.io/8fvt2/Has the “ban” of loot boxes eliminated them from Belgian mobile games?Recommended by Veli-Matti Karhulahti based on reviews by Andrew Moshirnia, Joseph Macey and Jason Chin based on reviews by Andrew Moshirnia, Joseph Macey and Jason Chin
Paid loot boxes, i.e. randomised monetization methods that are similar to lottery-type gambling, have become prominent features of contemporary gaming (e.g., Macey & Bujić, 2022). Because the design structures of loot boxes vary and the value of their virtual rewards is not always clear-cut, many countries now struggle how to deal with them legally and in practice (see Drummond et al., 2020). Belgium is one of the few countries that have officially interpreted loot box monetization to widely belong under gambling regulation. Mobile games that monetize with paid loot boxes in Belgium should thus apply for a gambling license, and companies should generally not offer paid loot boxes to local underage players at all.
In this Stage 1 Registered Report, Xiao (2022) has constructed a careful plan for testing whether the “ban” in Belgium has made the local mobile game market distinct in terms of paid loot boxes. The work builds on a rapidly accumulating literature and evolving methods (e.g., Xiao et al., 2021). The author will carry out a systematic qualitative investigation of the country’s top 100 (iPhone) mobile games to investigate whether paid loot box design components have indeed been removed from the products -- and if not, whether related game companies operate with a required gambling license. Additionally, Xiao (2022) will assess Belgium’s overall paid loot box prevalence in comparison to other countries and carry out a field experiment to test whether players can easily circumvent the local regulation by transporting or downloading different versions of software. The study will produce valuable evidence regarding the effectiveness of loot box regulation in general, and more specifically, the results should be of utmost interest to Belgian legal authorities. To ensure the transparency and validity of the chosen methods as well as upcoming interpretations, the registered report format allowed the research design to be reviewed in three rounds before data collection. Three experts, representing the fields of law and gaming, reviewed the Stage 1 manuscript twice and agreed upon the acceptance of all details. Finally, the recommender carried out a third iteration with further requested revisions, which was followed by in-principle acceptance. URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/5mxp6 Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that will be used to answer the research question yet exists and no part will be generated until after IPA. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
| Breaking Ban: Assessing the effectiveness of Belgium’s gambling law regulation of video game loot boxes | Leon Y. Xiao | <p>Loot boxes in video games are gambling-like mechanics that players buy to obtain randomised rewards of varying value. Loot boxes are conceptually and psychologically similar to gambling, and loot box expenditure is positively correlated with se... | Humanities, Social sciences | Veli-Matti Karhulahti | 2022-02-07 22:54:50 | View | ||
Breaking Ban: Belgium’s ineffective gambling law regulation of video game loot boxesLeon Y. Xiao https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/hnd7wLoot boxes remain prevalent in Belgium despite their “ban”Recommended by Veli-Matti Karhulahti based on reviews by Andrew Moshirnia, Joseph Macey and Jason Chin based on reviews by Andrew Moshirnia, Joseph Macey and Jason Chin
Several countries currently struggle to legally interpret and deal with loot boxes, i.e. gambling-like mechanisms that have become common especially in contemporary videogame design. One of the few countries to take a clear regulation stance is Belgium, which officially announced that they interpret paid loot boxes as games of chance that violate their Gaming and Betting Act and can thus be criminally prosecuted (Naessens 2018). This announcement four years ago laid the basis for a unique social experiment where companies offering loot boxes in Belgium had to decide whether to modify their games, exit the market, or continue to monetize with loot boxes. In the present study, Xiao (2022) investigated the outcomes of this experiment both via hypotheses testing and exploratory analysis.
Using the 100 highest-grossing iPhone games in Belgium as data and applying comprehensive qualitative mechanical analysis to each title, Xiao (2022) tested three preregistered hypotheses regarding loot box prevalence. None of the hypotheses were confirmed: the prevalence rate of loot boxes in the Belgian App Store was not null but extremely high (82.0%), also among mobile games designed for minors (54.2–80.2%), and significantly more compared to global standards when assessed by a binomial test (p<.001). Corroborating a fourth hypothesis, Xiao was also able to access various UK loot boxes in Belgium. In exploratory research, Xiao received a confirmation from the Belgian Gaming Commission that even “simulated gambling games” (that do not yield monetary wins) also legally constitute gambling in Belgium.
The results are the first to describe outcomes of ban-driven loot box regulation globally. Despite Belgium’s clear statement that “paid loot boxes must be removed from the video games in order to comply with the Belgian Gaming and Betting Act” (Naessens 2018, p. 16), almost all highest-grossing iPhone games in the Belgian App Store keep offering them. The finding is important especially for the legal authorities around the world who are currently assessing their own positions in potential regulation: simple statements are unlikely to have immediate effects on international companies in local markets. On the other hand, it remains unknown how these companies have interpreted the statement and what are their distinct reasons for continuing to offer loot boxes in the Belgian App Store. It would be important in future research to investigate the companies’ perspectives.
This study (Xiao 2022) is important also from a meta-scientific perspective. It paves the way for Registered Reports in new disciplines and methods, and involves an exceptional field experiment that was carefully documented with open data and materials. Three external experts reviewed the Stage 2 manuscript twice, based on which the recommender awarded a positive recommendation.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/5mxp6 Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that was used to answer the research question existed prior to Stage 1 in-principle acceptance. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Naessens, P. (2018) Research Report on Loot Boxes [English Translation]. Belgian Gaming Commission. URL: https://www.gamingcommission.be/sites/default/files/2021-08/onderzoeksrapport-loot-boxen-Engels-publicatie.pdf
2. Xiao, L.Y. (2022) Breaking Ban: Belgium’s ineffective gambling law regulation of video game loot boxes. Stage 2 Registered Report, acceptance of Version 2 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/hnd7w
| Breaking Ban: Belgium’s ineffective gambling law regulation of video game loot boxes | Leon Y. Xiao | <p>Loot boxes in video games are gambling-like mechanics that players buy to obtain randomised rewards of varying value. Loot boxes are conceptually and psychologically similar to gambling, and loot box expenditure is positively correlated with se... |  | Humanities, Social sciences | Veli-Matti Karhulahti | 2022-07-28 12:29:57 | View | |
25 Mar 2024
STAGE 1

Assessing compliance with UK loot box industry self-regulation on the Apple App Store: a 6-month longitudinal study on the implementation processLeon Y. Xiao https://osf.io/7xft9Does self regulation by gaming companies for the use of loot boxes work?Recommended by Zoltan Dienes based on reviews by Chris Chambers, Lukas J. Gunschera and Andy Przybylski based on reviews by Chris Chambers, Lukas J. Gunschera and Andy Przybylski
Video games may provide the option of spending real money in exchange for probabilistically receiving game-relevant rewards; in effect, encouraging potentially young teenagers to gamble. The industry has subscribed to a set of regulatory principles to cover the use of such "loot boxes", including 1) that they will prevent loot box purchasing by under 18s unless parental consent is given; 2) that they will make it initially clear that the game contains loot boxes; and 3) that they will clearly disclose the probabilities of receiving different rewards.
Can the industry effectively self regulate? Xiao (2024) will evaluate this important question by investigating the 100 top selling games on the Apple App Store and estimating the percentage compliance to these three regulatory principles at two time points 6 months apart.
The Stage 1 manuscript was evaluated over one round of in-depth review. Based on detailed responses to the reviewers' comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 1 criteria and therefore awarded in-principle acceptance (IPA).
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/3knyb
Level of bias control achieved: Level 2. At least some data/evidence that will be used to answer the research question has been accessed and partially observed by the authors, but the authors certify that they have not yet observed the key variables within the data that will be used to answer the research question. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References 1. Xiao, L. (2024). Assessing compliance with UK loot box industry self-regulation on the Apple App Store: a 6-month longitudinal study on the implementation process. In principle acceptance of Version 3 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/3knyb | Assessing compliance with UK loot box industry self-regulation on the Apple App Store: a 6-month longitudinal study on the implementation process | Leon Y. Xiao | <p>Loot boxes in video games can be purchased with real-world money in exchange for random rewards. Stakeholders are concerned about loot boxes’ similarities with gambling and their potential harms (e.g., overspending). The UK Government has decid... |  | Humanities, Social sciences | Zoltan Dienes | 2023-08-27 22:47:03 | View | |
21 Apr 2024
STAGE 1

Cross-cultural relationships between music, emotion, and visual imagery: A comparative study of Iran, Canada, and Japan [Stage 1 Registered Report]Shafagh Hadavi, Junji Kuroda, Taiki Shimozono, Juan David Leongómez, Patrick E. Savage https://psyarxiv.com/26yg5/Testing cross-cultural difference in the emotionality and visual associations of musicRecommended by D. Samuel Schwarzkopf based on reviews by Elena Karakashevska, Juan David Leongómez and Nadine Dijkstra based on reviews by Elena Karakashevska, Juan David Leongómez and Nadine Dijkstra
For many of us, music is far more than an auditory experience. It can trigger emotional reactions, evoke memories, and wide-ranging associations with other sensory modalities and cognitive states. Music also varies between different cultures in several ways. It remains unclear in how far the broader associations music has differs between cultural contexts, both in terms of the music itself and the listener. This study by Hadavi et al. (2024) seeks to better understand these relationships. Using an online survey targeted at 72 participants from anglophone Canada, Farsi-speaking Iran, and Japan (24 from each location), the researchers aim to address two straightforward hypotheses.
First, does faster tempo of music increase ratings of emotional arousal? Second, do participants match faster tempo music with denser visual line patterns? This latter measure aims to quantify the visual imagery evoked by the musical pieces. Imagery is a loaded term that is not used consistently across the cognitive neuroscience literature; one could argue that what the researchers are actually here is in fact mainly an association between tempo and a visual representation of tempo (or frequency). It certainly seems doubtful that persons listening to a piece of music will form a mental image of a bundle of horizontal lines. Yet, irrespective of how to interpret this experimental variable, it quantifies something about the impression listeners have when experiencing music, and whether these associations differ cross-culturally. The experiment has a balanced design, incorporating excerpts of musical pieces from each of the three cultural contexts, including both solo and group music. While the sample size is comparably low, given the online nature of data collection, it is based on a power analysis and relatively large expected effect sizes.
The proposed study was evaluated by three expert reviewers and the recommender over three rounds of in-depth review, plus a final round ironing out smaller issues. Reviewer Juan David Leongómez was recruited as a co-author after the first round of revisions. Following this process, the recommender decided that the manuscript met Stage 1 criteria and awarded in-principle acceptance (IPA).
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/zdnkm
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that will be used to answer the research question yet exists and no part will be generated until after IPA. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1.Hadavi, S., Kuroda, J., Shimozono, T., Leongómez, J. D. & Savage, P. E. (2024). Cross-cultural relationships between music, emotion, and visual imagery: A comparative study of Iran, Canada, and Japan. In principle acceptance of Version 6 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/zdnkm | Cross-cultural relationships between music, emotion, and visual imagery: A comparative study of Iran, Canada, and Japan [Stage 1 Registered Report] | Shafagh Hadavi, Junji Kuroda, Taiki Shimozono, Juan David Leongómez, Patrick E. Savage | <p>Many people experience emotions and visual imagery while listening to music. Previous research has identified cross-modal associations between musical and visual features as well as cross-cultural links between music and emotion and between mus... |  | Humanities, Social sciences | D. Samuel Schwarzkopf | 2023-03-01 02:48:54 | View | |
14 Feb 2022
STAGE 1

Minimal mindfulness of the world as an active control for a full mindfulness of mental states intervention: A Registered Report and Pilot studyMax Lovell, Zoltan Dienes https://psyarxiv.com/3umz7Testing the metacognitive basis and benefits of mindfulness trainingRecommended by Robert McIntosh based on reviews by Chris Noone and Julieta Galante based on reviews by Chris Noone and Julieta Galante
Mindfulness is inherently metacognitive in that it requires monitoring of one’s own thoughts and attention in order to remain on task. Mindfulness practice is especially metacognitive when focused on internal mental states, rather than on the external world. This Registered Report will compare remote training in mindfulness of mental states with remote training in mindfulness of the world, and a wait list control, to test the idea that mindfulness of mental states has an additional metacognitive component, and that this has benefits for (self-reported) mental health. A comparison of participant expectancies between mindfulness conditions will be used to establish whether mindfulness of the world can be considered a true ‘active control’ condition. Additional comparisons will test whether this mindfulness control has benefits over the (inactive) waiting list condition. The study plan is informed by prior research, including pilot data presented in the Stage 1 report, and a sample of up to 300 participants will be tested. The Stage 1 plan has been evaluated through two round of signed external review, and a further two rounds of minor revisions, with the recommender obtaining specialist advice on key points from a relevant external expert. The recommender has judged that the manuscript now meets all Stage 1 criteria, and has awarded In Principle Acceptance (IPA). URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/tx54k Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that will be used to answer the research question yet exists and no part will be generated until after IPA. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References Lovell, M., & Dienes, Z. (2022). Minimal mindfulness of the world as an active control for a full mindfulness of mental states intervention: A Registered Report and Pilot study, in principle acceptance of version 4 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/tx54k | Minimal mindfulness of the world as an active control for a full mindfulness of mental states intervention: A Registered Report and Pilot study | Max Lovell, Zoltan Dienes | <p>Mindfulness is a continual renewal of non-elaborative attention on an object of focus, without clinging or aversion, and with equanimity. As this requires the capacity to monitor and control the extent to which one is on task, it is a metacogni... | Social sciences | Robert McIntosh | 2021-06-21 16:49:39 | View | ||
22 Oct 2023
STAGE 1

Michotte's research on perceptual impressions of causality: a pre-registered replication studyPeter A. White https://osf.io/5jx8fGaining confidence in Michotte’s classic studies on the perception of causalityRecommended by Moin Syed based on reviews by Maxine Sherman and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Maxine Sherman and 1 anonymous reviewer
Making causal judgements are part of everyday life, whether seeking to understand the action of complex humans or the relations between inanimate objects in our environments. Albert Michotte’s (1963) classic book, The perception of causality, contained an extensive report of experiments demonstrating not only that observers perceive causality of inanimate shapes, but do so in manifold ways, creating different “causal impressions.” This work has been highly influential across psychology and neuroscience.
In the current study, White (2023) proposes a series of experiments to replicate and extend Michotte’s work. Despite the fact that this research is foundational to current work on perception and understanding of causal relations, it has never been subjected to rigorous replication. Moreover, like many research studies from that era, Michotte was sparse on details about methodology and did not rely on statistical analysis. White has proposed an ambitious set of 14 experiments that directly replicate and, in some cases, extend Michotte’s experiments.
The Stage 1 manuscript was evaluated over three rounds of in-depth review, the first two rounds consisting of detailed comments from two reviewers and the third round consisting of a close read by the recommender. Based on detailed responses to the reviewers' comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 1 criteria and was therefore awarded in-principle acceptance (IPA).
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/5jx8f (under temporary private embargo)
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that will be used to answer the research question yet exists and no part will be generated until after IPA. List of eligible PCI-RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Michotte, A. (1963). The perception of causality (T. R. Miles & E. Miles, trans.). London: Methuen. (English translation of Michotte, 1954).
2. White, P. A. (2023). Michotte's research on perceptual impressions of causality: A registered replication study. In principle acceptance of Version 3 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/5jx8f
| Michotte's research on perceptual impressions of causality: a pre-registered replication study | Peter A. White | <p> Michotte (1946/1954/1963) showed that visual impressions of causality can occur in perception of simple animations of moving geometrical objects. In the launching effect, one object is perceived as maki... | Life Sciences, Social sciences | Moin Syed | 2023-05-03 13:04:00 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Chris Chambers
Zoltan Dienes
Corina Logan
Benoit Pujol
Maanasa Raghavan
Emily S Sena
Yuki Yamada










