Announcements
Please note: To accommodate reviewer and recommender holiday schedules, we will be closed to submissions from 1st July — 1st September. During this time, reviewers will be able to submit reviews and recommenders will issue decisions, but no new or revised submissions can be made by authors. The one exception to this rule is that authors using the scheduled track who submit their initial Stage 1 snapshot prior to 1st July can choose a date within the shutdown period to submit their full Stage 1 manuscript.
We are recruiting recommenders (editors) from all research fields!
Your feedback matters! If you have authored or reviewed a Registered Report at Peer Community in Registered Reports, then please take 5 minutes to leave anonymous feedback about your experience, and view community ratings.
Latest recommendations

| Id | Title * | Authors * | Abstract * | Picture | Thematic fields * | Recommender | Reviewers▲ | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Managing Disclosure Outcomes in Intelligence InterviewsDavid A. Neequaye, Timothy J. Luke, Kristina Kollback https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/tfp2cManaging costs and rewards when choosing to disclose informationRecommended by Zoltan Dienes based on reviews by Yikang Zhang and Tyler Jacobs based on reviews by Yikang Zhang and Tyler Jacobs
An interviewee in an intelligence interview can face competing interests in disclosing information: The value in cooperating because, for example, information given leads to the arrest of a narcotics gang, making the neighbourhood safer; and the risk that disclosing the information leads to reprisals from the gang. Different pieces of information will compete with each other for disclosure, depending on this balance of risks to self-interest. According to the disclosure-outcomes management model of Neequaye et al., information will be disclosed more with a high than low probability of reward, as might be straightforwardly expected, but this difference will be larger when there is a low probability of cost rather than a high probability. The high probability of cost will induce more a variable response to the possible benefits.
Neequaye et al. (2024) invited participants to assume the role of an informant, with the goal of maximizing their points according to stated probabilities of costs and benefits of disclosing pieces of information relating to given scenarios. The degree to which each type of information was disclosed in a subsequent interview wase assessed. Perceived benefits positively influenced the likelihood of disclosing information. The crucial interaction, obtained in a Pilot study, was not significant in the pre-registered replication. The study had decent power to pick up an interaction the same size as found in the pilot, but not half the size, which would still have been interesting. The Stage 2 manuscript was evaluated over one round of in-depth review. Based on detailed responses to the reviewers' comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 2 criteria.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/ru8j5
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that was used to answer the research question was generated until after IPA. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
Neequaye, D. A., Luke, T. J., & Kollback, K. (2024). Managing Disclosure Outcomes in Intelligence Interviews [Stage 2]. Acceptance of Version 11 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/tfp2c
| Managing Disclosure Outcomes in Intelligence Interviews | David A. Neequaye, Timothy J. Luke, Kristina Kollback | <p>We introduce the disclosure-outcomes management model. The model views disclosure in intelligence interviews as a behavior interviewees use to profitably navigate self-interest dilemmas. We theorized that interviewees compare the potential outc... | Social sciences | Zoltan Dienes | 2024-02-29 17:26:19 | View | ||
22 Jul 2024
STAGE 1

Probing the dual-task structure of a metacontrast-masked priming paradigm with subjective visibility judgmentsCharlott Wendt, Guido Hesselmann https://osf.io/9gakq?view_only=a5e90e4db4b545e9956b8359595c013bDo trial-wise visibility reports - and how these reports are made - alter unconscious priming effects?Recommended by D. Samuel Schwarzkopf based on reviews by Markus Kiefer, Thomas Schmidt and 3 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Markus Kiefer, Thomas Schmidt and 3 anonymous reviewers
Many studies of unconscious processing measure priming effects. Such experiments test whether a prime stimulus can exert an effect on speeded responses to a subsequently presented target stimulus even when participants are unaware of the prime. In some studies, participants are required to report their awareness of the prime in each trial - a dual-task design. Other studies conduct such visibility tests in separate experiments, so that the priming effect is measured via a single task. Both these approaches have pros and cons; however, it remains unclear to what extent they can affect the process of interest. Can the choice of experimental design and its parameters interfere with the priming effect? This could have implications for interpreting such effects, including in previous literature.
In the current study, Wendt and Hesselmann (2024) will investigate the effects of using a dual-task design in a masked priming paradigm, focusing on subjective visibility judgments. Based on power analysis, the study will test 34 participants performing both single-task and several dual-task conditions to measure reaction times and priming effects. Priming is tested via a speeded forced-choice identification of a target. The key manipulation is the non-speeded visibility rating of the prime using a Perceptual Awareness Scale, either with a graded (complex) rating or a dichotomous response. Moreover, participants will either provide their awareness judgement via a keyboard or vocally. Finally, participants will also complete a control condition to test prime visibility by testing the objective identification of the prime. These conditions will be presented in separate blocks, with the order randomised across participants. The authors hypothesise that using a dual-task slows down response times and boosts priming effects. However, they further posit that keyboard responses and graded visibility ratings, respectively, in the dual task reduce priming effects (but also slow response times) compared to vocal responses and dichotomous visibility judgements. In addition to the preregistered hypotheses, the study will also collect EEG data to explore the neural underpinnings of these processes.
The Stage 1 manuscript went through three rounds of review by the recommender and five expert reviewers. While the recommender would have preferred to see targeted, directional hypotheses explicitly specified in the design instead of non-directional main effects/interactions, he nevertheless considers this experimental design ready for commencing data collection, and therefore granted in-principle acceptance.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/ds2w5
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that will be used to answer the research question yet exists and no part will be generated until after IPA. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly Journals:
References Wendt, C. & Hesselmann, G. (2024). Probing the dual-task structure of a metacontrast-masked priming paradigm with subjective visibility judgments. In principle acceptance of Version 4 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/ds2w5 | Probing the dual-task structure of a metacontrast-masked priming paradigm with subjective visibility judgments | Charlott Wendt, Guido Hesselmann | <p>Experiments contrasting conscious and masked stimulus processing have shaped, and continue to shape, cognitive and neurobiological theories of consciousness. However, as shown by Aru et al. (2012) the contrastive approach builds on the untenabl... | Social sciences | D. Samuel Schwarzkopf | 2024-03-02 18:20:03 | View | ||
Impact of analytic decisions on test-retest reliability of individual and group estimates in functional magnetic resonance imaging: a multiverse analysis using the monetary incentive delay taskMichael I. Demidenko, Jeanette A. Mumford, Russell A. Poldrack https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2024.03.19.585755v5Exploring determinants of test-retest reliability in fMRI: a study with the Monetary Incentive Delay TaskRecommended by Dorothy Bishop based on reviews by Xiangzhen Kong and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Xiangzhen Kong and 1 anonymous reviewer
Functional magnetic resonance imaging has been used to explore brain-behaviour relationships for many years, with proliferation of a wide range of sophisticated analytic procedures. However, rather scant attention has been paid to the reliability of findings. Concerns have been growing failures to replicate findings in some fields, but it is hard to know how far this is a consequence of underpowered studies, flexible analytic pipelines, or variability within and between participants. Demidenko et al. (2024) took advantage of the availability of three existing datasets, including the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) study, the Michigan Longitudinal Study, and the Adolescent Risk Behavior Study, which all included a version of the Monetary Incentive Delay task measured in two sessions. These were entered into a multiverse analysis, which considered how within-subject and between-subject variance varies according to four analytic factors: smoothing (5 levels), motion correction (6 levels), task modelling (3 levels) and task contrasts (4 levels). They also considered how sample size affects estimates of reliability. The results have important implications for the those using fMRI with the Monetary Incentive Delay Task, and also raise questions more broadly about use of fMRI indices to study individual differences. Motion correction had relatively little impact on the ICC, and the effect size of the smoothing kernel was modest. Larger impacts on reliability were associated with choice of contrast (implicit baseline giving larger effects) and task parameterization. But perhaps the most sobering message from this analysis is that although activation maps from group data were reasonably reliable, the ICC, used as an index of reliability for individual levels of activation, was consistently low. This raises questions about the suitability of the Monetary Incentive Delay Task for studying individual differences. Another point is that reliability estimates become more stable as sample size increases; researchers may want to consider whether the trade-off between cost and gain in precision is justified for sample sizes above 250. I did a quick literature search on Web of Science: at the time of writing the search term ("Monetary Delay Task" AND fMRI) yielded 410 returns, indicating that this is a popular method in cognitive neuroscience. The detailed analyses reported here will repay study for those who are planning further research using this task. The Stage 2 manuscript was evaluated over one round of in-depth review. Based on detailed responses to the reviewer's and recommender's comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 2 criteria and awarded a positive recommendation. URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/nqgeh
Level of bias control achieved: Level 2. At least some data/evidence that was used to answer the research question had been accessed and partially observed by the authors prior to IPA, but the authors certify that they had not yet sufficiently observed the key variables within the data to be able to answer the research questions and they took additional steps to maximise bias control and rigour.
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References 1. Demidenko, M. I., Mumford, J. A., & Poldrack, R. A. (2024). Impact of analytic decisions on test-retest reliability of individual and group estimates in functional magnetic resonance imaging: a multiverse analysis using the monetary incentive delay task [Stage 2]. Acceptance of Version 5 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2024.03.19.585755v4 | Impact of analytic decisions on test-retest reliability of individual and group estimates in functional magnetic resonance imaging: a multiverse analysis using the monetary incentive delay task | Michael I. Demidenko, Jeanette A. Mumford, Russell A. Poldrack | <p>Empirical studies reporting low test-retest reliability of individual blood oxygen-level dependent (BOLD) signal estimates in functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) data have resurrected interest among cognitive neuroscientists in methods... | 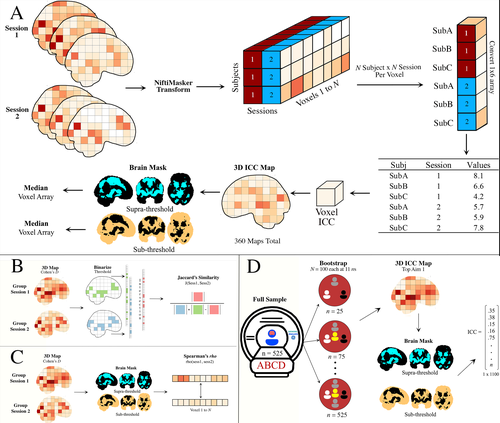 | Life Sciences, Social sciences | Dorothy Bishop | 2024-03-21 02:23:30 | View | |
Insufficient evidence of a positive association between chronic loneliness and anthropomorphism: Replication and extension Registered Report of Epley et al. (2008)Qinyu Xiao, Mahmoud Elsherif, Hoi Yan Chu, Ming Chun Tang, Ting Hin (Angus) Wong, Yiming Wu, Christina Pomareda, Gilad Feldman https://osf.io/x96knWeak-to-no evidence for a positive link between loneliness and anthropomorphismRecommended by Chris Chambers based on reviews by John Protzko based on reviews by John Protzko
Anthropomorphism is a widespread phenomenon in which people instil non-human entities or objects with human-like characteristics, such as motivations, intentions, and goals. Although common, the tendency to anthropomorphise varies between people, and a growing body of psychological research has examined the importance of various individual differences. One major theoretical account of anthropomorphism (Epley et al. 2007) suggests that sociality motivation – the drive to establish social relationships – is a key moderator of the phenomenon. In support of this account, some evidence suggests that people who experience greater loneliness (a proposed marker of sociality motivation) are more likely to anthropomorphise. In an influential series of studies, Epley et al. (2008) found that anthropomorphism and loneliness were positively correlated and that inducing participants experimentally to feel more lonely led to greater anthropomorphism. Later studies, however, produced more mixed results, particularly concerning the effectiveness of the experimental interventions.
In the current study, Elsherif et al. (2024) undertook a partial replication of Epley et al. (2008), focusing on the correlational relationship between anthropomorphism and loneliness, with extensions to examine free will beliefs, anthropomorphism for supernatural beings (in addition to objects/gadgets), and the extent to which participants judged objects/gadgets to be controllable. The results revealed no reliable evidence for a positive relationship between anthropomorphism and loneliness. Analyses of the extended questions revealed that the perceived controllability of gadgets was associated negatively with anthropomorphism and that free will belief was associated positively with belief in anthropomorphism of supernatural beings. Broadly, the current findings constitute a non-replication of Epley et al. (2008). The authors conclude by calling for more direct and conceptual replications to establish the link (if any) between sociality motivation and anthropomorphism.
The Stage 2 manuscript was evaluated over one round of in-depth review. Based on detailed responses to the reviewer's and recommender's comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 2 criteria and awarded a positive recommendation.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/by89c Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that was used to answer the research question was generated until after IPA.
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Epley, N., Waytz, A., & Cacioppo, J. T. (2007). On seeing human: A three-factor theory of anthropomorphism. Psychological Review, 114, 864–886. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295X.114.4.864
2. Epley, N., Akalis, S., Waytz, A., & Cacioppo, J. T. (2008). Creating social connection through inferential reproduction: Loneliness and perceived agency in gadgets, Gods, and greyhounds. Psychological Science, 19, 114–120. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9280.2008.02056.x
3. Elsherif, M., Pomareda, C., Xiao, Q., Chu, H. Y., Tang, M. C., Wong, T. H., Wu, Y. & Feldman, G. (2024). Insufficient evidence of a positive association between chronic loneliness and anthropomorphism: Replication and extension Registered Report of Epley et al. (2008) [Stage 2]. Acceptance of Version 6 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/x96kn
| Insufficient evidence of a positive association between chronic loneliness and anthropomorphism: Replication and extension Registered Report of Epley et al. (2008) | Qinyu Xiao, Mahmoud Elsherif, Hoi Yan Chu, Ming Chun Tang, Ting Hin (Angus) Wong, Yiming Wu, Christina Pomareda, Gilad Feldman | <p>Human beings have a fundamental need to connect with others. Epley, Akalis, et al. (2008) found that people higher in chronic loneliness had a stronger tendency to anthropomorphize non-human objects, presumably for fulfilling unmet needs for so... | Social sciences | Chris Chambers | 2024-03-27 16:17:16 | View | ||
Do prediction errors of perceived exertion inform the level of running pleasure?Damien Brevers, Guillaume Martinent, İrem Tuğçe Öz, Olivier Desmedt, Bas de Geus https://osf.io/xfgqpRunning pleasure results from finding it easier than you thought you wouldRecommended by Zoltan Dienes based on reviews by Jasmin Hutchinson and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Jasmin Hutchinson and 1 anonymous reviewer
The reward value of a stimulus is based on an error in prediction: Things going better than predicted. Could this learning principle, often tested on short acting stimuli, also apply to a long lasting episode, like going for a run? Could how rewarding a run is be based on the run going better than predicted?
Understanding the conditions under which exercise is pleasurable could of course be relevant to tempting people to do more of it! In the current study, Brevers et al. (2024) asked people before a daily run to predict the amount of perceived exertion they would experience; then just after the run, to rate the retrospective amount of perceived exertion actually experienced. The difference between the two ratings was the prediction error. Participants also rated their remembered pleasure in running. As hypothesized, the authors found that running pleasure increased linearly with how much retrospective exertion was than predicted.
The Stage 2 manuscript received one round of review from two external reviewers, then some minor comments from the recommender, after which it was judged to satisfy the Stage 2 criteria and was awarded a positive recommendation. URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/xh724
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that was used to answer the research question was generated until after IPA. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Brevers, D., Martinent, G., Oz, I. T., Desmedt, O. & de Geus, B. (2024). Do prediction errors of perceived exertion inform the level of running pleasure? [Stage 2]. In principle acceptance of Version 3 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/xfgqp | Do prediction errors of perceived exertion inform the level of running pleasure? | Damien Brevers, Guillaume Martinent, İrem Tuğçe Öz, Olivier Desmedt, Bas de Geus | <p>Humans have the ability to mentally project themselves into future events (prospective thinking) to promote the implementation of health-oriented behaviors, such as the planning of daily physical exercise sessions. Nevertheless, it is currently... | Social sciences | Zoltan Dienes | 2024-04-26 11:58:57 | View | ||
Associations of fear, anger, happiness, and hope with risk judgments: Revisiting appraisal-tendency framework with a replication and extensions Registered Report of Lerner and Keltner (2001)Sirui Lu; Emir Efendić; Gilad Feldman https://osf.io/xytswMixed evidence for the Appraisal-Tendency Framework in explaining links between emotion and decision-makingRecommended by Chris Chambers based on reviews by Kelly Wolfe and Max Primbs based on reviews by Kelly Wolfe and Max Primbs
How do emotions interact with cognition? The last 40 years has witnessed the rise of cognitive-appraisal theories, which propose that emotions can be differentiated along an axis of cognitive dimensions such as certainty, pleasantness, attentional activity, control, anticipated effort, and responsibility (Smith and Ellsworth, 1985). Early tests of such theories focused especially on the impact of the valence – pleasantness/unpleasantness – of emotions on judgment and decision-making, finding, for instance, that negative mood induction can heighten pessimistic estimates of risk (Johnson & Tversky, 1983).
The Appraisal-Tendency Framework proposed by Lerner and Keltner (2000) refined cognitive-appraisal theory by proposing that specific emotions trigger a predisposition to appraise future (or hypothetical) events in line with the central appraisal dimensions that triggered the emotion, even when the emotion and the judgment are unrelated. For example, an individual who is triggered to become fearful of a heightened risk, such as nuclear war, may then exhibit heightened pessimism about risks unrelated to war. The Appraisal-Tendency Framework also predicts relationships between traits, such as fear, anger and risk-taking/risk-seeking tendencies. In an influential paper, Lerner and Keltner (2001) reported direct empirical support for the Appraisal-Tendency Framework, which aside from its influence in cognitive/affective psychology has had considerable impact in behavioural economics, moral psychology, and studies of consumer behaviour.
In the current study, Lu et al. (2024) replicated three key studies from Lerner and Keltner (2001) in a large online sample. Through a combination of replication and extension, the authors probed the relationship between various trait emotions (including fear, anger, happiness, and hope) and trait characteristics of risk seeking and optimistic risk assessment. The authors also examined how the ambiguity of triggering events moderates the relationship between specific emotions and risk judgments.
Overall, the results provide mixed support for the predictions of the Appraisal-Tendency Framework. Trait anger and trait happiness were positively associated with risk-seeking and optimistic risk estimates, while trait fear was negatively associated with optimistic risk assessment (although a reliable association between fear and risk-seeking was not observed). The original finding of Lerner and Keltner (2001) that the valence-based approach applied to risk optimism for unambiguous events was not supported. In addition, there was no reliable evidence for a positive relationship between hope and risk-seeking preference or optimistic risk estimates. The authors conclude that future research should consider a wider range of emotions to develop a more complete understanding of the link to risk-related judgment and decision-making.
The Stage 2 manuscript was evaluated over one round of in-depth review. Based on detailed responses to the reviewers' comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 2 criteria and therefore awarded a positive recommendation.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/8yu2x Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that was used to answer the research question was generated until after IPA.
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Smith, C. A., & Ellsworth, P. C. (1985). Patterns of cognitive appraisal in emotion. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 48, 813-838. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.48.4.813
2. Johnson, E. J., & Tversky, A. (1983). Affect, generalization, and the perception of risk. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 45(1), 20–31. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.45.1.20
3. Lerner, J. S., & Keltner, D. (2000). Beyond valence: Toward a model of emotion-specific influences on judgment and choice. Cognition & Emotion, 14, 473-493. https://doi.org/10.1080/026999300402763
4. Lerner, J. S., & Keltner, D. (2001). Fear, anger, and risk. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 81, 146–159. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.81.1.146
5. Lu, S., Efendić, E., & Feldman, G. (2024). Associations of fear, anger, happiness, and hope with risk judgments: Revisiting appraisal-tendency framework with a replication and extensions Registered Report of Lerner and Keltner (2001) [Stage 2]. Acceptance of Version 2 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/xytsw | Associations of fear, anger, happiness, and hope with risk judgments: Revisiting appraisal-tendency framework with a replication and extensions Registered Report of Lerner and Keltner (2001) | Sirui Lu; Emir Efendić; Gilad Feldman | <p>The appraisal-tendency framework proposed that specific emotions predispose individuals to appraise future events corresponding to the core appraisal themes of the emotions. In a Registered Report with a US American online Amazon Mechanical Tur... | Social sciences | Chris Chambers | 2024-04-26 16:55:30 | View | ||
19 Jan 2024
STAGE 1

A systematic review of social connection inventoriesBastien Paris, Debora Brickau, Tetiana Stoianova, Maike Luhmann, Christopher Mikton, Julianne Holt-Lunstad, Marlies Maes, Hans IJzerman https://osf.io/preprints/psyarxiv/6ueydImproving the measurement of social connectionRecommended by Dorothy Bishop based on reviews by Jacek Buczny, Richard James and Alexander Wilson based on reviews by Jacek Buczny, Richard James and Alexander Wilson
This is an ambitious systematic review that uses a combination of quantitative and qualitative methods to make the measurement of the construct of social connection more rigorous. Social connection is a heterogeneous construct that includes aspects of structure, function and quality. Here, Paris et al. (2024) will use predefined methods to create a database of social connection measures, and will assess heterogeneity of items using human coders and ChatGPT. This database will form the basis of a second systematic review which will look at evidence for validity and measurement properties. This study will also look at the population groups and country of origin for which different measures were designed, making it possible to see how far culturally specific issues affect the content of measures in this domain.
The questions asked by this study are exploratory and descriptive and so the importance of pre-registration is in achieving clear criteria for how each question is addressed, rather than evidential criteria for hypothesis-testing.
The authors responded comprehensively to three reviewer reports. This study will provide a wealth of useful information for those studying social connection, and should serve to make the literature in this field more psychometrically robust and less fragmented.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/796uv
Level of bias control achieved: Level 3. At least some data/evidence that will be used to the answer the research question has been previously accessed by the authors (e.g. downloaded or otherwise received), but the authors certify that they have not yet observed ANY part of the data/evidence. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Paris, B., Brickau, D., Stoianova, T., Luhmann, M., Mikton, C., Holt-Lunstad, J., Maes, A., & IJzerman, H. (2024). A systematic review of social connection inventories. In principle acceptance of Version 3 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/796uv | A systematic review of social connection inventories | Bastien Paris, Debora Brickau, Tetiana Stoianova, Maike Luhmann, Christopher Mikton, Julianne Holt-Lunstad, Marlies Maes, Hans IJzerman | <p>Social connection is vital to health and longevity. To date, a plethora of instruments exists to measure social connection, assessing a variety of aspects of social connection like loneliness, social isolation, or social support. For comparabil... | Social sciences | Dorothy Bishop | Alexander Wilson, Jacek Buczny, Richard James | 2023-07-09 21:33:01 | View | |
Convenience Samples and Measurement Equivalence in Replication ResearchLindsay J. Alley, Jordan Axt, Jessica Kay Flake https://osf.io/s5t3vData from students and crowdsourced online platforms do not often measure the same thingRecommended by Corina Logan based on reviews by Benjamin Farrar and Shinichi Nakagawa based on reviews by Benjamin Farrar and Shinichi Nakagawa
Comparative research is how evidence is generated to support or refute broad hypotheses (e.g., Pagel 1999). However, the foundations of such research must be solid if one is to arrive at the correct conclusions. Determining the external validity (the generalizability across situations/individuals/populations) of the building blocks of comparative data sets allows one to place appropriate caveats around the robustness of their conclusions (Steckler & McLeroy 2008). In the current study, Alley and colleagues (2023) tackled the external validity of comparative research that relies on subjects who are either university students or participating in experiments via an online platform. They determined whether data from these two types of subjects have measurement equivalence - whether the same trait is measured in the same way across groups. Although they use data from studies involved in the Many Labs replication project to evaluate this question, their results are of crucial importance to other comparative researchers whose data are generated from these two sources (students and online crowdsourcing). The authors show that these two types of subjects do not often have measurement equivalence, which is a warning to others to evaluate their experimental design to improve validity. They provide useful recommendations for researchers on how to to implement equivalence testing in their studies, and they facilitate the process by providing well annotated code that is openly available for others to use. After one round of review and revision, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 2 criteria and awarded a positive recommendation. URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/7gtvf
Level of bias control achieved: Level 2. At least some data/evidence that was used to answer the research question had been accessed and partially observed by the authors prior to Stage 1 IPA, but the authors certify that they had not yet observed the key variables within the data that were used to answer the research question AND they took additional steps to maximise bias control and rigour.
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Pagel, M. (1999). Inferring the historical patterns of biological evolution. Nature, 401, 877-884. https://doi.org/10.1038/44766
2. Steckler, A. & McLeroy, K. R. (2008). The importance of external validity. American Journal of Public Health 98, 9-10. https://doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.2007.126847
3. Alley L. J., Axt, J., & Flake J. K. (2023). Convenience Samples and Measurement Equivalence in Replication Research [Stage 2 Registered Report] Acceptance of Version 2 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/s5t3v
| Convenience Samples and Measurement Equivalence in Replication Research | Lindsay J. Alley, Jordan Axt, Jessica Kay Flake | <p>A great deal of research in psychology employs either university student or online crowdsourced convenience samples (Chandler & Shapiro, 2016; Strickland & Stoops, 2019) and there is evidence that these groups differ in meaningful ways ... | Social sciences | Corina Logan | Alison Young Reusser | 2023-08-31 20:26:43 | View | |
19 Jun 2024
STAGE 1

Culture-Driven Neural Plasticity and Imprints of Body-Movement Pace on Musical Rhythm ProcessingSégolène M. R. Guérin, Emmanuel Coulon, Tomas Lenc, Rainer Polak, Peter E. Keller, Sylvie Nozaradan https://zenodo.org/doi/10.5281/zenodo.10221480The interplay of music, movement, and culture on rhythm processingRecommended by Juan David Leongómez based on reviews by Anne Keitel and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Anne Keitel and 1 anonymous reviewer
The interplay of music, movement, and cultural experience shapes rhythm perception. From bouncing babies and children at play, to tapping, clapping, and dancing, music often triggers synchronous body movements that can influence how we process rhythm. And, at the same time, long-term exposure to specific musical traditions shapes how we perceive and interpret rhythms.
However, direct behavioural and neuroscientific evidence on how these processes occur remains scarce. In this programmatic submission, comprising two complementary Stage 2 reports, Guérin et al. (2024) will investigate how body movements shape the processing of auditory information, and how previous short-term motor practice and long-term cultural experience interact to shape neural and behavioural responses to rhythmic stimuli. The authors will record in separate sessions both electroencephalography (EEG) and hand clapping, in response to rhythms from West/Central Africa. These recordings will be conducted before and after a session in which participants will clap/step to either a three or a four-beat metre that is expected to influence how they interpret a rhythm.
The first Stage 2 report, which will be conducted on African-enculturated participants, aims to demonstrate how body-movement pace flexibly imprints on human sensory processing. The authors build on various theoretical models that emphasise the role of motor production in metre perception, and predict that both neural and behavioural entrainment will improve following movement, matching the rhythmic pattern set by the previous body movements.
The second Stage 2 report aims to uncover how short-term motor practice and long-term cultural experience interact to shape responses to rhythmic stimuli, by integrating short-term motor practice and long-term cultural experience. For this, the authors will test separate groups of participants from distinct cultural backgrounds (African vs. Western-enculturated), which are predicted to show neural and behavioural differences in their preferred metric mapping before body movement, and expect that neural and behavioural entrainment will improve after movement, especially for the metre set by prior movements, and more significantly for the metre common in the participant's culture.
Together, the findings from the planned Stage 2 reports are expected to clarify how long-term cultural background and short-term motor practice imprint onto rhythm processing in humans. This research will enhance our understanding of how cultural experience, body movement, and neural plasticity interact in music processing.
The Stage 1 manuscript was evaluated over three rounds of in-depth review. Based on detailed responses to the reviewers' and recommender's comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 1 criteria and awarded in-principle acceptance (IPA).
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/skuyc
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. Data collection commenced during the later part of Stage 1 peer review; however, since no changes to the design were made after this point, the risk of bias due to prior data observation remains zero and the manuscript therefore qualifies for Level 6. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals: References
Guérin, S. M. R., Coulon, E., Lenc, T., Polak, R., Keller, P. E., & Nozaradan, S. (2024). Culture-Driven Neural Plasticity and Imprints of Body-Movement Pace on Musical Rhythm Processing. In principle acceptance of Version 2.1 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/skuyc
| Culture-Driven Neural Plasticity and Imprints of Body-Movement Pace on Musical Rhythm Processing | Ségolène M. R. Guérin, Emmanuel Coulon, Tomas Lenc, Rainer Polak, Peter E. Keller, Sylvie Nozaradan | <p>The proposed programmatic registered report aims at capturing direct neuroscientific evidence for the rhythmic, movement-related shaping of auditory information with a cross-cultural perspective. Specifically, West/Central African- and Western-... |  | Life Sciences | Juan David Leongómez | Anonymous | 2023-11-30 11:36:06 | View |
09 Feb 2023
STAGE 1

The Medusa effect: A registered replication report of Will, Merritt, Jenkins, and Kingstone (2021)Jing Han, Minjun Zhang, Jiaxin Liu, Yu Song, Yuki Yamada https://osf.io/bjt37Looking (again) at Medusa: does pictorial abstraction influence mind perception?Recommended by Chris Chambers based on reviews by Alan Kingstone, Brittany Cassidy and 3 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Alan Kingstone, Brittany Cassidy and 3 anonymous reviewers
The Medusa effect is a recently described phenomenon in which people judge a person to be more mindful when they appear as a picture than as a picture within a picture. Across a series of experiments, Will et al. (2021) reported that at higher levels of abstraction, images of people were judged lower in realness (how real the person seemed), experience (the ability to feel) and agency (the ability to plan and act), and also benefited less from prosocial behaviour. The findings provide an intriguing window into mind perception – the extent to which we attribute minds and mental capacities to others.
In the current study, Han et al. (2023) propose a close replication of two experiments from the original report by Will et al. (2021), asking first, whether the level of pictorial abstraction influences ratings of realness, agency and experience, and second, whether it also influences prosocial behaviour as measured in the dictator game (with participants predicted to allocate more money to recipients presented as pictures than as pictures within pictures). In the event of a non-replication using the original materials, the authors will further repeat the experiments using newly generated stimuli that are better matched for cultural context and more tightly controlled along various dimensions.
The Stage 1 manuscript was evaluated over two rounds of in-depth review. Based on detailed responses to the reviewers' comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 1 criteria and therefore awarded in-principle acceptance (IPA).
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/xj46z Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that will be used to answer the research question yet exists and no part will be generated until after IPA.
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals: References
1. Will, P., Merritt, E., Jenkins, R., & Kingstone, A. (2021). The Medusa effect reveals levels of mind perception in pictures. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 118(32), e2106640118. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2106640118
2. Han, J., Zhang, M., Liu, J., Song, Y. & Yamada, Y. (2023).The Medusa effect: A registered replication report of Will, Merritt, Jenkins, and Kingstone (2021), in principle acceptance of Version 2 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/xj46z
| The Medusa effect: A registered replication report of Will, Merritt, Jenkins, and Kingstone (2021) | Jing Han, Minjun Zhang, Jiaxin Liu, Yu Song, Yuki Yamada | <div>The medusa effect refers to the tendency of people to evaluate a "picture of a person" as more mindful than a "picture of a picture of a person". This phenomenon is strikingly intriguing because it suggests that when people evaluate the human... | Social sciences | Chris Chambers | Anonymous, Alan Kingstone, Anonymous, Anonymous | 2022-08-18 09:50:35 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Chris Chambers
Zoltan Dienes
Corina Logan
Benoit Pujol
Maanasa Raghavan
Emily S Sena
Yuki Yamada










