Announcements
We are recruiting recommenders (editors) from all research fields!
Your feedback matters! If you have authored or reviewed a Registered Report at Peer Community in Registered Reports, then please take 5 minutes to leave anonymous feedback about your experience, and view community ratings.
279 records found
Latest recommendations
| Id | Title * | Authors * | Abstract * | Picture | Thematic fields * | Recommender | Reviewers▲ | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
05 Mar 2025
STAGE 1
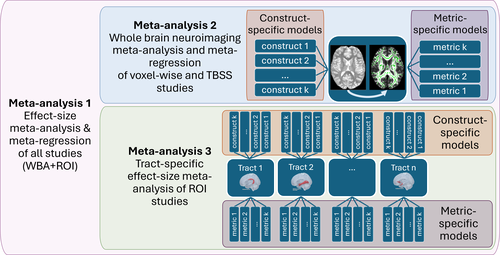
Social cognition as a matter of structural brain connections? A systematic review and diffusion weighted imaging meta-analysisRita Hansl, Lara Z. Maliske, Sofie L. Valk, Philipp Kanske https://osf.io/6n3jySocial cognition and white matter integrity: Systematic review and diffusion weighted imaging meta-analysisRecommended by Marietta Papadatou-Pastou based on reviews by Sebastian Ocklenburg and Katie Lavigne based on reviews by Sebastian Ocklenburg and Katie Lavigne
Social cognition involves complex processes including empathy, mentalizing, and compassion, which rely on structural connectivity and specifically white matter (WM) integrity. Prior research suggests that deficits in social cognition are linked to deficient structural connectivity, indicating that the latter might be an essential foundation for social cognitive abilities. In the current study, Hansl et al. (2025) explore the relationship between social cognition and white matter (WM) integrity in the brain across different populations, by means of a systematic review and meta-analyses. Using diffusion-weighted imaging data, the authors aim to identify specific WM tracts most associated with social cognition. Meta-analyses of region-of-interest (ROI)-based studies will provide further insights, while meta-regression and subgroup analyses will examine differences across social cognitive constructs, imaging metrics, clinical conditions, and age groups. The findings could clarify global and specific WM contributions to social cognition, guiding future research on brain structure-function relationships in social cognition across various populations.
The Stage 1 submission was evaluated by two expert reviewers. After two rounds of revision, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 1 criteria and awarded in-principle acceptance (IPA).
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/6n3jy (under temporary private embargo)
Level of bias control achieved: Level 2. At least some data/evidence that will be used to answer the research question has been accessed and partially observed by the authors, but the authors certify that they have not yet observed the key variables within the data that will be used to answer the research question and they have taken additional steps to maximise bias control and rigour.
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Hansl, R., Maliske, L. Z., Valk, S. L., & Kanske, P. (2025). Social cognition as a matter of structural brain connections? A systematic review and diffusion weighted imaging meta-analysis. In principle acceptance of Version 3 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/6n3jy
| Social cognition as a matter of structural brain connections? A systematic review and diffusion weighted imaging meta-analysis | Rita Hansl, Lara Z. Maliske, Sofie L. Valk, Philipp Kanske | <p>Social cognition encompasses several cognitive and affective processes essential for successful social interaction and communication (e.g. empathy, mentalizing, compassion). The interplay of the various processes necessary for understanding the... |  | Life Sciences | Marietta Papadatou-Pastou | 2024-09-20 13:51:12 | View | |
Can adults automatically process and translate between numerical representations?I. Xenidou-Dervou, C. Appleton, S. Rossi, N. Guy, C. Gilmore https://osf.io/me6tnThe role of working memory in translating between different number processing systemsRecommended by Zoltan Dienes based on reviews by Hannah Dorothea Loenneker and Xinru Yao based on reviews by Hannah Dorothea Loenneker and Xinru Yao
People can represent quantities in different ways. Numbers can be represented non-symbolically through an Object Tracking System (for small quantities, when one immediately perceives how many objects are there) and an Approximate Number System (for large quantities), and symbolically, for example with Arabic symbols or words. One unresolved question is the extent to which using these numerical representations, and transferring between them, can be done automatically, or rather involves components of working memory. Key relevant working memory components are the phonological loop and the visuospatial sketchpad.
In this study, Xenidou-Dervou and colleagues (2025) asked subjects to perform a dot comparison task with small and large numbers, to engage the non-symbolic systems, and a digit comparison task, to engage the symbolic system, and a cross modal task to engage translation between the systems. Participants either performed these tasks alone or with a secondary task, one that loaded either the phonological loop or else the visuospatial sketchpad. In the comparison of symbolic numerals, the visual secondary task itself was performed more poorly in dual rather than single task conditions, indicating the involvement of the visual spatial sketchpad in use of symbolic numerals. The visual secondary task interfered with non-symbolic number judgements, indicating involvement of the visuospatial sketch pad with the non-symbolic system as well. Finally, the translation between the systems also involved the visuospatial sketchpad, as shown by the secondary task itself suffering dual task interference. In sum, there was evidence for the visuospatial sketchpad, but not for the phonological loop, playing a role in simple comparisons using either or both of the symbolic and non-symbolic number systems. The Stage 2 manuscript was evaluated over two rounds of in-depth review. Based on detailed responses to the reviewers’ comments and edits to the Stage 2 report, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 2 criteria for recommendation. URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/32qdw Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that was used to answer the research question was generated until after IPA. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
Xenidou-Dervou, I., Appleton, C., Rossi, S., Guy, N., & Gilmore, C. (2025). Can adults automatically process and translate between numerical representations? [Stage 2]. Acceptance of Version 3 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/me6tn
| Can adults automatically process and translate between numerical representations? | I. Xenidou-Dervou, C. Appleton, S. Rossi, N. Guy, C. Gilmore | <p>Arithmetic, and the ability to use numbers, is an important skill. Numbers can be represented in three ways: through number words, Arabic symbols or non-symbolically. Much research attention has focused on how associations form between these th... | Social sciences | Zoltan Dienes | 2024-09-27 12:50:27 | View | ||
Michotte's research on perceptual impressions of causality: a registered replication studyPeter A. White https://osf.io/jdac7Michotte’s classic studies on the perception of causality: Replications, extensions and a sound base for further researchRecommended by Moin Syed based on reviews by Maxine Sherman and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Maxine Sherman and 1 anonymous reviewer
Making causal judgements are part of everyday life, whether seeking to understand the action of complex humans or the relations between inanimate objects in our environments. Albert Michotte’s (1963) classic book, The perception of causality, contained an extensive report of experiments demonstrating not only that observers perceive causality of inanimate shapes, but do so in manifold ways, creating different “causal impressions.” This work has been highly influential across psychology and neuroscience.
In the current study, White (2025) conducted 14 experiments aimed at replicating and extending Michotte’s work. Despite the fact that this research is foundational to current work on perception and understanding of causal relations, it has never been subject to rigorous replication. Moreover, like many research studies from that era, Michotte was sparse on details about methodology and did not rely on statistical analysis. White carried out an ambitious set of 14 experiments and 18 hypotheses that directly replicated and, in some cases, extended Michotte’s experiments. The results of the experiments were mixed, with the hypotheses evenly divided among being supported, partially supported, and not supported. The current effort by White not only brings rigorous contemporary data to classic studies of perceptual impressions of causality, but the results point to important new directions for future study on the topic. In particular, the findings suggest a need to broaden our investigations of causal explanations of movement beyond launching (i.e., contact of one object leading to motion of another) to also consider entraining (i.e., joint movement following contact) and pulling. The collected studies provide fertile ground for further testing a variety of mechanisms that explain different perceptual impressions of causality.
The Stage 2 manuscript was evaluated over three rounds of in-depth review, the first two rounds consisting of detailed comments from two reviewers and the third round consisting of a close read by the recommender. Based on detailed responses to the reviewers' comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 2 criteria and awarded a positive recommendation.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/5jx8f
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that was used to answer the research question was generated until after IPA. List of eligible PCI-RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Michotte, A. (1963). The perception of causality (T. R. Miles & E. Miles, trans.). London: Methuen. (English translation of Michotte, 1954).
2. White, P. A. (2025). Michotte's research on perceptual impressions of causality: A registered replication study [Stage 2]. Acceptance of Version 3 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/jdac7
| Michotte's research on perceptual impressions of causality: a registered replication study | Peter A. White | <p> Michotte (1946/1954/1963) showed that visual impressions of causality can occur in perception of simple animations of moving geometrical objects. In the launching effect, one object is perceived a... | Social sciences | Moin Syed | 2024-10-07 10:53:33 | View | ||
Do Ecological Valid Stop Signals Aid Detour Performance? A Comparison of Four Bird SpeciesAnneleen Dewulf, Clara Garcia-Co, Wendt Müller, Joah R. Madden, An Martel, Luc Lens, Frederick Verbruggen https://osf.io/j2k9hWhat is the role of sensory perception in cognitive task performance? An improved replication of detour performance in four different bird speciesRecommended by Dieter Lukas based on reviews by Christian Nawroth and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Christian Nawroth and 1 anonymous reviewer
The detour task, where an individual has to go around a see-through barrier in order to reach a goal, is one of the oldest paradigms used in animal cognition research (Kabadayi et al. 2018). While these previous tests have documented variation in the ability of animals to inhibit going straight for the visible reward, the cognitive underpinnings of this behaviour are as yet not fully understood. In the current study, Dewulf et al. (2025) assessed one of the specific cognitive processes that might be involved in this behaviour, the ability to identify the transparent object as a barrier. Through experimental procedures relying on large samples of individuals from four bird species, they compared the role of signal detection in inhibitory response performance in a detour task. The authors found that, unlike suggested in previous work with these four species (Regolin et al. 1994, Zucca et al. 2005), changing the markings on the barriers to potentially better match those experienced by individuals in their natural environments did not improve their performance. Nevertheless, the detailed further explorations suggest that in order to understand variation in how quickly individuals and species solve the detour task, it is important to consider that different cognitive processes are involved. Their work therefore provides a basis to better understand and further investigate why species might differ in their performance in the detour task.
The Stage 2 manuscript was evaluated over two rounds of in-depth review, the first round consisting of detailed comments from two reviewers and the second round consisting of a close read by the recommender. Based on detailed responses to the reviewers' comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 2 criteria and awarded a positive recommendation.
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that was used to answer the research question was generated until after IPA.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/qvxgh
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Dewulf, A., Garcia-Co, C., Müller, W., Madden, J.R., Martel, A., Lens, L. & Verbruggen, F. (2025). Do Ecological Valid Stop Signals Aid Detour Performance? A Comparison of Four Bird Species [Stage 2]. Acceptance of Version 3 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/j2k9h
2. Kabadayi, C., Bobrowicz, K., & Osvath, M. (2018). The detour paradigm in animal cognition. Animal Cognition, 21, 21-35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10071-017-1152-0
3. Regolin, L., Vallortigara, G., & Zanforlin, M. (1995). Object and spatial representations in detour problems by chicks. Animal Behaviour, 49, 195-199. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-3472(95)80167-7
4. Zucca, P., Antonelli, F., & Vallortigara, G. (2005). Detour behaviour in three species of birds: quails (Coturnix sp.), herring gulls (Larus cachinnans) and canaries (Serinus canaria). Animal Cognition, 8, 122-128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10071-004-0243-x
| Do Ecological Valid Stop Signals Aid Detour Performance? A Comparison of Four Bird Species | Anneleen Dewulf, Clara Garcia-Co, Wendt Müller, Joah R. Madden, An Martel, Luc Lens, Frederick Verbruggen | <p>Response inhibition, or the stopping of actions, is considered a key component of flexible and adaptive behaviour. Across fields, response inhibition is often treated as a unitary cognitive mechanism. However, we propose that response inhibitio... | Life Sciences, Social sciences | Dieter Lukas | 2024-10-22 14:00:30 | View | ||
02 Apr 2025
STAGE 1

Impact of Acute Stress Exposure on Reactivity to Loss of Control Over ThreatMichalina Dudziak, Tom Smeets, Bram Vervliet, Tom Beckers https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/j5kgtHow does stress influence psychological and biological responses to uncontrollable threat?Recommended by Saeed Shafiei Sabet and Yuki Yamada and Yuki Yamada based on reviews by Mariela Mihaylova, Laura Meine and Genisius Hartanto based on reviews by Mariela Mihaylova, Laura Meine and Genisius Hartanto
One of the key drivers of how organisms respond to stressful events or situations is the controllability of the stressor – the extent to which the individual has (or believes) they can control the stress-inducing event or situation. A considerable literature has explored controllability and the effects of aversive events, with the general finding that uncontrollable situations more strongly impair emotion and cognition while increasing stress responses (Maier & Seligman, 1976). In a key review, Foa et al. (1992) evaluated the effects of unpredictable and uncontrollable aversive events that caused disturbance in animals. Although it remains unclear, longevity of stress exposure may play a role in responsiveness when exposed to uncontrollable threats in humans.
Here, Dudziak et al. (2025) examine whether acute stress exposure impacts reactivity to a subsequent loss of control over threat. Participants (N=128) will be assigned to a stress or a no-stress group, undergoing an acute stress induction or a non-stressful control procedure, followed by a behavioural loss-of-control task. By assessing salivary cortisol and salivary alpha-amylase assays, blood pressure measurements, and self-report ratings they hypothesize that participants exposed to acute stress will show stronger biological and psychological responses to the loss of control over threat than those in the no-stress group. The authors will also test whether individual differences in childhood adversity are associated with heightened stress responses. Overall, the findings promise to shed light on the directional relationship between threat controllability and stress reactivity, and will therefore be relevant across a range of research areas in clinical psychology, biological psychology, and associated domains.
The Stage 1 manuscript was evaluated by three expert reviewers who performed in-depth and constructive evaluation across multiple rounds of revisions. The authors were responsive in amending their manuscript based on the reviewers’ comments and dedicated much effort to increasing the clarity and interpretability of their design and sampling plan. The revised manuscript was judged to meet the Stage 1 criteria and was awarded in-principle acceptance (IPA).
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/dca3g
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. Data collection began during the final round of Stage 1 peer review. Since no substantive revisions to the design or analysis were made after this review round, the risk of bias due to prior data observation remained zero, and the manuscript therefore qualified for Level 6. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References 1. Dudziak, M., Smeets, T., Vervliet, B., & Beckers, T. (2025). Impact of acute stress exposure on reactivity to loss of control over threat. In principle acceptance of Version 3 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/dca3g
2. Foa, E. B., Zinbarg, R., & Rothbaum, B. O. (1992). Uncontrollability and unpredictability in post-traumatic stress disorder: An animal model. Psychological Bulletin, 112, 218-238. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.112.2.218
3. Maier, S. F., & Seligman, M. E. (1976). Learned helplessness: Theory and evidence. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 105, 3-46. https://doi.org/10.1037/0096-3445.105.1.3
| Impact of Acute Stress Exposure on Reactivity to Loss of Control Over Threat | Michalina Dudziak, Tom Smeets, Bram Vervliet, Tom Beckers | <p>Uncontrollable negative events yield increased stress responses compared to situations over which we have control. Previous studies have assessed the impact of uncontrollability of threat on stress reactivity. Less is known about whether and ho... | Social sciences | Saeed Shafiei Sabet | 2024-10-22 17:53:28 | View | ||
On the neural substrates of mind wandering and dynamic thought: A drug and brain stimulation studyTara Rasmussen, Paul E. Dux and Hannah Filmer https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.11.02.620526Does dopamine availability influence the effect of brain stimulation on mind-wandering?Recommended by Maxine Sherman based on reviews by Chris Chambers and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Chris Chambers and 1 anonymous reviewer
Mind-wandering broadly refers to the phenomenon by which a person's thoughts are directed towards internally generated states as opposed to being directed towards those that are task-relevant. It has been proposed that mind-wandering and cognitive control are supported by overlapping neural systems. While neuroimaging work has implicated prefrontal cortex in both mind-wandering and cognitive control, studies testing its causal role using transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) have been inconclusive.
Here, Rasmussen and colleagues (2025) put to a strict test the question of whether the effects of prefrontal cortex tDCS on mind-wandering are mediated by dopaminergic availablility, which is known to be important for cognitive control. Using noninvasive brain stimuluation (prefrontal cortex tDCS vs sham) and a pharmacological intervention (levodopa vs. placebo), they found that contrary to some previous work, stimulation of prefrontal cortex does not alter mind-wandering. By contrast, in the absence of stimulation, increasing dopamine availability via levodopa reduced the frequency of freely moving thought. Together, these results clarify the degree to which prefrontal cortex tDCS and dopamine play a causal role in mind-wandering
The Stage 2 manuscript was evaluated over one round of in-depth review. Based on detailed responses to the reviewers' comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 2 criteria and awarded a positive recommendation.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/ujp7e
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that was used to answer the research question was generated until after IPA. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals: References
Rasmussen, T., Dux, P. E. & Filmer, H. (2025). On the neural substrates of mind wandering and dynamic thought: A drug and brain stimulation study [Stage 2]. Acceptance of Version 2 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.11.02.620526
| On the neural substrates of mind wandering and dynamic thought: A drug and brain stimulation study | Tara Rasmussen, Paul E. Dux and Hannah Filmer | <p>The impact of mind wandering on our daily lives ranges from diminishing productivity, to facilitating creativity and problem solving. There is evidence that distinct internal thought types can be modulated by transcranial direct current stimula... | Life Sciences, Medical Sciences | Maxine Sherman | 2024-10-28 03:18:20 | View | ||
The effects of false feedback on state memory distrust toward commission and omission, and recognition memory errorsYikang Zhang, Henry Otgaar, Robert A. Nash, Chunlin Li https://osf.io/z8mv5Exploring how feedback on memory accuracy shifts criteriaRecommended by Zoltan Dienes based on reviews by Dan Wright, Romuald Polczyk, Greg Neil and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Dan Wright, Romuald Polczyk, Greg Neil and 1 anonymous reviewer
We may not believe what our memory tells us: Memory may deliver a compelling recollection we believe did not happen (we know we were not there at the time); and we may know an event happened that we fail to remember. That is, there can be distrust in remembering and distrust in forgetting. Previous work by the authors has looked at this through a signal detection lens, reporting in separate studies that people who have distrust in remembering have either a high or low criterion for saying "old" (Zhang et al, 2023, 2024). A plausible explanation for these contrasting results is that the criterion can either be the means by which false memories are generated enabling the distrust (low criterion); or rather, in conditions where accuracy is at stake, the means for compensating for the distrust (high criterion).
In the current study by Zhang et al (2025), participants were incentivised to be as accurate as possible, and in a memory test given feedback about commission errors or, in another group, ommission errors. The manipulation check indicated that the feedback did not increase (by a meaningful amount) distrust in remembering or distrust in forgetting, respectively, compared to a no feedback control group. Nonetheless, the authors found that people adjusted the criterion to say "old" in a compensatory way in each group. The possible mechanisms underlying these criterion shifts are discussed by the authors, who grapple with the distinction between response criterion shifts versus genuine meta-memory belief changes, and for the latter case, whether any memory distrust change could be contextual versus global (the manipulation check measured the latter).
The Stage 2 manuscript was evaluated over one round of in-depth review by four reviewers. Based on detailed responses to the reviewers' and recommender's comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 2 criteria for recommendation.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/x69qt
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that was used to answer the research question was generated until after IPA. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Zhang, Y., Qi, F., Otgaar, H., Nash, R. A., & Jelicic, M. (2023). A Tale of Two Distrusts: Memory Distrust towards Commission and Omission Errors in the Chinese Context. Journal of Applied Research in Memory and Cognition. https://doi.org/10.1037/mac0000134
2. Zhang, Y., Otgaar, H., Nash, R. A., & Rosar, L. (2024). Time and memory distrust shape the dynamics of recollection and belief-in-occurrence. Memory, 32, 484–501. https://doi.org/10.1080/09658211.2024.2336166
3. Zhang, Y., Otgaar, H., Nash, R. A., & Li, C. (2025). The effects of false feedback on state memory distrust toward commission and omission, and recognition memory errors [Stage 2]. Acceptance of Version 6 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/z8mv5
| The effects of false feedback on state memory distrust toward commission and omission, and recognition memory errors | Yikang Zhang, Henry Otgaar, Robert A. Nash, Chunlin Li | <p>Memory distrust refers to the subjective appraisal of one’s memory functioning and it has two aspects: distrust over making omission errors (e.g., forgetting) and distrust over making commission errors (e.g., falsely remembering). Although thes... | Social sciences | Zoltan Dienes | 2024-11-05 16:42:53 | View | ||
The effect of stimulus saliency on the modulation of ongoing neural oscillations related to thermonociception: a Registered ReportChiara Leu, Sébastien Forest, Valéry Legrain, Giulia Liberati https://osf.io/98edqAre there oscillatory markers of pain intensity?Recommended by Zoltan Dienes based on reviews by Markus Ploner and Bjoern Horing based on reviews by Markus Ploner and Bjoern Horing
Rhythmic changes in pain can lead to corresponding modulations of EEG amplitudes in theta, alpha, and beta bands. But the question remains open as to whether these modulations are actually tracking pain, or maybe rather saliency or stimulus intensity. The question is of some importance because a marker of pain per se could be useful for tracking felt pain without a verbal response, and could be useful in investigating interventions for treating pain (such as suggestion). Here, Leu et al. (2025) addressed the question of whether modulations reflect saliency or else the intensity of pain, by using an oddball paradigm in which most trials are a pain stimulus of a certain intensity, and oddball trials will sometimes occur, at either a higher intensity or a lower intensity than the baseline ones. If the modulations reflected salience, the modulation at the frequency of the oddball would be similar for high and low intensity oddballs. However, if the modulations reflected pain intensity, the modulations for the low rather than high oddball condition would be lower.
In fact, the baseline and oddball stimulations were found to be perceived significantly differently only in the high oddball condition; and consistantly, the oddballl stimulus significantly modulated ongoing oscillations in only the high oddball condition. Thus, whether oscillations are modulated by pain intensity or salience could not be picked apart in this study. The study does however raise an important isssue, indicate how it could be addressed, and provide data relevant for clearly resolving the issue in the future.
The Stage 2 manuscript was evaluated over two rounds of in-depth peer review. Based on detailed responses to the reviewers' comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 2 criteria for acceptance.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/qbrf2
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that was used to answer the research question was generated until after IPA. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Leu, C., Forest, S., Legrain, V., & Liberati, G. (2025). The effect of stimulus saliency on the modulation of pain-related ongoing neural oscillations: a Registered Report [Stage 2]. Acceptance of Version 3 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/98edq | The effect of stimulus saliency on the modulation of ongoing neural oscillations related to thermonociception: a Registered Report | Chiara Leu, Sébastien Forest, Valéry Legrain, Giulia Liberati | <p>Ongoing oscillations have been shown to be modulated in different frequency bands following phasic, tonic as well as periodic thermonociceptive stimulation. Yet, it remains unclear whether these modulations are related to pain perception, salie... | Life Sciences, Medical Sciences | Zoltan Dienes | 2024-11-11 14:11:31 | View | ||
Is it Worth the Hustle? A Multi-Country Replication of the Effort Moralization Effect and an Extension to Generational Differences in the Appreciation of EffortTassilo T. Tissot, Leopold H. O. Roth https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/ck4st_v6Are people who exert more effort in a task seen as more moral?Recommended by Adrien Fillon based on reviews by Jared Celniker, Ignazio Ziano and Michael Inzlicht based on reviews by Jared Celniker, Ignazio Ziano and Michael Inzlicht
This study seeks to understand cultural and age differences in the effort moralization effect, a phenomenon in which people who put more effort into a task are considered more moral, regardless of the quality or the morality associated with the task. This is shown in common phrases such as the “great resignation” or “quiet quitting”, which are mostly used against younger members of the population, in particular generation Z.
Tissot and Roth (2025) conducted a replication of a study from Celniker et al. (2023) which found evidence for this effect, with new samples from Mexico and Germany, to test potential cultural and age differences.
The results indicated a generalization of the effort moralization effect in Germany and Mexico, with important heterogeneity in the effect found, and effects sizes that were smaller than in the original study conducted in the USA. However, no effect was found regarding age, as younger individuals judged effort as being important in the same way as older individuals. It is possible, therefore, that the effort moralization effect is a consistent bias that persists regardless of age.
The Stage 2 manuscript was evaluated over three rounds of in-depth review. Based on detailed responses to the reviewers’ and recommender’s comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 2 criteria and awarded a positive recommendation.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/tvgw2
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that was used to answer the research question was generated until after IPA.
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References 1. Celniker, J. B., Gregory, A., Koo, H. J., Piff, P. K., Ditto, P. H., & Shariff, A. F. (2023). The moralization of effort. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 152, 60–79. https://doi.org/10.1037/xge0001259
2. Tissot, T. T. & Roth, L. H. O. (2025). Is it Worth the Hustle? A Multi-Country Replication of the Effort Moralization Effect and an Extension to Generational Differences in the Appreciation of Effort [Stage 2]. Acceptance of Version 6 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/ck4st_v6
| Is it Worth the Hustle? A Multi-Country Replication of the Effort Moralization Effect and an Extension to Generational Differences in the Appreciation of Effort | Tassilo T. Tissot, Leopold H. O. Roth | <p>Inferring moral character of individuals is an adaptive need for social decision-making. The effort moralization effect describes the finding that people who exert more effort in a task are seen as more moral, even if higher effort does not enh... | Social sciences | Adrien Fillon | 2024-11-15 10:14:56 | View | ||
Action interpretation determines the effects of go/no-go and approach/avoidance actions on food choiceZhang Chen, Pieter Van Dessel, Jordi Serverius, Daxun Zhu, Bernd Figner https://osf.io/preprints/psyarxiv/6xhw4_v2Does interpretation of actions as either avoid or inhibit influence choice behaviour for candy?Recommended by Andrew Jones based on reviews by Alexander MacLellan and Katrijn HoubenExperimental research demonstrates that executing or inhibiting motor responses (or approaching / avoiding) towards a stimulus can alter the valuation of the stimulus (Yang et al., 2022). There are competing theories as to the proposed mechanisms of value change, such as increased response conflict or prediction errors (Houben & Aulbach, 2023). However, research has mostly examined response execution/inhibition and approach/avoidance in isolation and the few studies that have examined these together have focused on stimulus evaluation as an outcome.
In the current study Chen et al. (2025) set out to examine how action interpretations (e.g. go vs approach) can impact individuals food-choices. This is important for cognitive bias modification approaches which aim to manipulate these actions to promote behaviour change (Iannazzo et al., 2024; Veling et al., 2021), but also theoretical accounts which suggest certain motor-responses acquire valence. Here there are two groups randomised to receive instructions to either go/no-go or approach/avoid images of candy in novel training task (Chen et al., 2019).
The results of the experiment suggested that despite both groups making the same responses (pressing a space bar vs not), the framing of the response as go vs approach and no-go vs avoidance influenced subsequent food-choice (i.e. responses framed as approach increased the probability of choosing approach items over avoidance items, but not go items over no-go items). As the authors state, these findings cast doubt on theoretical models which suggest there are ‘hardwired’ links between specific go/approach responses and appetitive systems or specific no-go/avoidance responses and aversive systems. They also suggest these responses aren’t valenced, but acquire valence through interpretation of the action. These findings can also inform future studies into cognitive bias modification. The Stage 2 manuscript was evaluated over two rounds of in-depth review by two reviewers with expertise in the relevant area, who also assessed the Stage 1 manuscript. Based on the authors’ careful responses and revisions, the revised manuscript was judged to meet the Stage 2 criteria and was awarded a positive recommendation. URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/bn5xa
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that was used to answer the research question was generated until after IPA. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Chen, Z., Van Dessel, P., Serverius, J., Zhu, D. & Figner, B. (2025). Action interpretation determines the effects of go/no-go and approach/avoidance actions on food choice. Acceptance of Version 2 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/6xhw4_v2
2. Chen, Z., & Van Dessel, P. (2024). Action Interpretation Determines the Effects of Go/No-Go and Approach/Avoidance Actions on Stimulus Evaluation. Open Mind, 8, 898–923. https://doi.org/10.1162/opmi_a_00151
3. Houben, K. and Aulbach, M. (2023). Is there a difference between stopping and avoiding? A review of the mechanisms underlying Go/No-Go and Approach-Avoidance training for food choice. Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences, 49, 101245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cobeha.2022.101245
4. Iannazzo, L. H., Hayden, M. J., Lawrence, N. S., Kakoschke, N., Hughes, L. K., Van Egmond, K., … Staiger, P. K. (2024). Inhibitory control training to reduce appetitive behaviour: a meta-analytic investigation of effectiveness, potential moderators, and underlying mechanisms of change. Health Psychology Review, 1–31. https://doi.org/10.1080/17437199.2024.2410018 5. Veling, H., Verpaalen, I. A. M., Liu, H., Mosannenzadeh, F., Becker, D., & Holland, R. W. (2021). How can food choice best be trained? Approach-avoidance versus go/no-go training. Appetite, 163, 105226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2021.105226 6. Yang, Y., Qi, L., Morys, F., Wu, Q. & Chen, H. (2022). Food-Specific Inhibition Training for Food Devaluation: A Meta-Analysis. Nutrients, 14, 1363. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14071363
| Action interpretation determines the effects of go/no-go and approach/avoidance actions on food choice | Zhang Chen, Pieter Van Dessel, Jordi Serverius, Daxun Zhu, Bernd Figner | <p>Executing go/no-go and approach/avoidance responses toward objects can increase people's choices of go over no-go items, and of approach over avoidance items. Some theoretical accounts explain these effects as the results of merely executing th... | Social sciences | Andrew Jones | 2024-11-24 11:21:55 | View |
FOLLOW US
MANAGING BOARD
Chris Chambers
Zoltan Dienes
Corina Logan
Benoit Pujol
Maanasa Raghavan
Emily S Sena
Yuki Yamada










