Announcements
We are recruiting recommenders (editors) from all research fields!
Your feedback matters! If you have authored or reviewed a Registered Report at Peer Community in Registered Reports, then please take 5 minutes to leave anonymous feedback about your experience, and view community ratings.
168 records found
Latest recommendations

| Id | Title | Authors | Abstract | Picture | Thematic fields▼ | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Neuroanatomical Correlates of System-justifying Ideologies: A Pre-registered Voxel-based Morphometry Study on Right-Wing Authoritarianism and Social Dominance OrientationJan Paolo M. Balagtas, Serenella Tolomeo, Bindiya L. Ragunath, Paola Rigo, Marc H. Bornstein & Gianluca Esposito https://osf.io/nrqtzNo definitive evidence for neuroanatomical correlates of system-justifying ideologiesRecommended by Chris Chambers based on reviews by Bonni Crawford and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Bonni Crawford and 1 anonymous reviewer
According to the tenets of system justification theory, system-justifying ideologies are beliefs held by individuals to defend and justify the status quo, even when doing do perpetuates social inequalities (Jost and Hunyady, 2005). Two such well-studied ideologies to emerge from political science and social psychology are social dominance orientation (SDO) – the belief that some social groups are superior to others – and right wing authoritarianism (RWA) – the belief that people should follow conventional traditions and authorities, avoiding rebellious ideas. Although considered to be stable traits that may have a heritable basis, there has been little investigation of the neural correlates of SDO and RWA, and it remains unknown whether they are associated with common or distinct brain systems.
In the current study, Balagtas et al. report a novel investigation of the neuroanatomical correlates of both SDO and RWA in a Chinese Singaporean sample using voxel-based morphometry. Based on previous research, the authors chose to focus especially on relationships between SDO, RWA and the volume of the amygdala, ventromedial prefrontal cortex, and anterior insula.
As predicted, the results showed a reliable positive correlation between measures of RWA and SDO; however, none of the neuroanatomical hypotheses were fully supported. Preregistered whole brain analyses revealed no significant regions associated with either RWA or SDO, while ROI analyses identified overlapping (including the amygdala and ventromedial prefrontal cortex) and non-overlapping regions (including left anterior insula) associated with RWA and SDO. Exploratory robustness checks suggested that the authors' spherical ROI localisation method may have identified clusters that were not within the amygdala or left anterior insula, prompting the need for future replication in a larger sample using more precise, atlas-based analyses.
The Stage 2 manuscript was evaluated over two rounds of in-depth review. Based on detailed responses to the reviewers' comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 2 criteria and awarded a positive recommendation.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/btkwq
Level of bias control achieved: Level 4. At least some of the data/evidence that was used to answer the research question already existed AND was accessible in principle to the authors (e.g. residing in a public database or with a colleague) BUT the authors certified that they had not yet accessed any part of that data/evidence prior to IPA.
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Jost, J. T., & Hunyady, O. (2005). Antecedents and consequences of system-justifying ideologies. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 14, 260-265. https://doi.org/10.1111%2Fj.0963-7214.2005.00377.x
2. Balagtas, P. M., Tolomeo, S., Ragunath, B., Rigo, P., Bornstein, M. H. & Esposito, G. (2023). Neuroanatomical Correlates of System-justifying Ideologies: A Pre-registered Voxel-based Morphometry Study on Right-Wing Authoritarianism and Social Dominance Orientation. Stage 2 Registered Report, acceptance of Version 3 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/nrqtz
| Neuroanatomical Correlates of System-justifying Ideologies: A Pre-registered Voxel-based Morphometry Study on Right-Wing Authoritarianism and Social Dominance Orientation | Jan Paolo M. Balagtas, Serenella Tolomeo, Bindiya L. Ragunath, Paola Rigo, Marc H. Bornstein & Gianluca Esposito | <p>System-justifying ideologies are a cluster of ideals that perpetuate a hierarchical social system despite being fraught with inequalities. Right Wing Authoritarianism (RWA) and Social Dominance Orientation (SDO) are two ideologies that have rec... | Social sciences | Chris Chambers | 2022-07-27 17:53:26 | View | ||
07 Apr 2023
STAGE 1

Psychological predictors of long-term esports success: A Registered ReportMarcel Martončik, Veli-Matti Karhulahti, Yaewon Jin, Matúš Adamkovič https://osf.io/csbhkWhat psychological factors predict long-term success in esports?Recommended by Zhang Chen and Charlotte Pennington based on reviews by Justin Bonny and Maciej Behnke based on reviews by Justin Bonny and Maciej Behnke
Electronic sports (esports), the competitive play of video games, has seen a large surge in popularity over the past few decades. Millions of people nowadays participate in esports as a hobby, and many consider becoming professional esports athletes as a potential career path. However, psychological factors that may predict one's long-term success in esports have remained unclear.
In the current study, Martončik and colleagues (2023) propose to examine potential predictors of long-term esports success, in three currently most impactful PC esports games, namely League of Legends, Counter Strike: Global Offensive, and Fortnite. Based on an extensive review of the literature and four pilot studies, the authors will examine to what extent naive practice and deliberate practice, as well as other psychological factors such as attention, speed of decision-making, reaction time, teamwork, intelligence and persistence, can predictor player's highest rank in the past 12 months, as an indicator of long-term success. Deliberate practice has been proposed to play an essential role in the development of expertise in other domains, and the current study offers a test of the role of both naive and deliberate practice in long-term esports success. The novel measurement on naive and deliberate practice, developed as part of the current investigation, will also be a valuable contribution to future research on esports. Lastly, from an applied perspective, the results of the current study will be of great interest to individuals who are considering pursuing a professional career in esports, as well as professional and semi-professional esports teams and coaches. This Stage 1 manuscript was evaluated over two rounds of in-depth review. Based on the comprehensive responses to the reviewers' feedback, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 1 criteria and therefore awarded in-principle acceptance (IPA). URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/84zbv
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that will be used to answer the research question yet exists and no part will be generated until after IPA. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
Martončik, M., Karhulahti, V.-M., Jin, Y. & Adamkovič, M. (2023). Psychological predictors of long-term esports success: A Registered Report, in principle acceptance of Version 1.4 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/84zbv | Psychological predictors of long-term esports success: A Registered Report | Marcel Martončik, Veli-Matti Karhulahti, Yaewon Jin, Matúš Adamkovič | <p>The competitive play of digital games, esports, has attracted worldwide attention of hundreds of millions of young people. Although esports players are known to practice in similar ways to other athletes, it remains largely unknown what factors... | Social sciences | Zhang Chen | 2022-08-17 12:12:51 | View | ||
09 Feb 2023
STAGE 1

The Medusa effect: A registered replication report of Will, Merritt, Jenkins, and Kingstone (2021)Jing Han, Minjun Zhang, Jiaxin Liu, Yu Song, Yuki Yamada https://osf.io/bjt37Looking (again) at Medusa: does pictorial abstraction influence mind perception?Recommended by Chris Chambers based on reviews by Alan Kingstone, Brittany Cassidy and 3 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Alan Kingstone, Brittany Cassidy and 3 anonymous reviewers
The Medusa effect is a recently described phenomenon in which people judge a person to be more mindful when they appear as a picture than as a picture within a picture. Across a series of experiments, Will et al. (2021) reported that at higher levels of abstraction, images of people were judged lower in realness (how real the person seemed), experience (the ability to feel) and agency (the ability to plan and act), and also benefited less from prosocial behaviour. The findings provide an intriguing window into mind perception – the extent to which we attribute minds and mental capacities to others.
In the current study, Han et al. (2023) propose a close replication of two experiments from the original report by Will et al. (2021), asking first, whether the level of pictorial abstraction influences ratings of realness, agency and experience, and second, whether it also influences prosocial behaviour as measured in the dictator game (with participants predicted to allocate more money to recipients presented as pictures than as pictures within pictures). In the event of a non-replication using the original materials, the authors will further repeat the experiments using newly generated stimuli that are better matched for cultural context and more tightly controlled along various dimensions.
The Stage 1 manuscript was evaluated over two rounds of in-depth review. Based on detailed responses to the reviewers' comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 1 criteria and therefore awarded in-principle acceptance (IPA).
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/xj46z Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that will be used to answer the research question yet exists and no part will be generated until after IPA.
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals: References
1. Will, P., Merritt, E., Jenkins, R., & Kingstone, A. (2021). The Medusa effect reveals levels of mind perception in pictures. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 118(32), e2106640118. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2106640118
2. Han, J., Zhang, M., Liu, J., Song, Y. & Yamada, Y. (2023).The Medusa effect: A registered replication report of Will, Merritt, Jenkins, and Kingstone (2021), in principle acceptance of Version 2 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/xj46z
| The Medusa effect: A registered replication report of Will, Merritt, Jenkins, and Kingstone (2021) | Jing Han, Minjun Zhang, Jiaxin Liu, Yu Song, Yuki Yamada | <div>The medusa effect refers to the tendency of people to evaluate a "picture of a person" as more mindful than a "picture of a picture of a person". This phenomenon is strikingly intriguing because it suggests that when people evaluate the human... | Social sciences | Chris Chambers | Anonymous, Alan Kingstone, Anonymous, Anonymous | 2022-08-18 09:50:35 | View | |
Is the past farther than the future? A registered replication and test of the time-expansion hypothesis based on the filling rate of durationQinjing Zhang, Yoshitaka Masuda, Kodai Toda, Kohei Ueda, Yuki Yamada https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/pb47nThe Temporal Doppler Effect may not be a robust and culturally universal phenomenonRecommended by Ljerka Ostojic based on reviews by Chris Chambers and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Chris Chambers and 1 anonymous reviewer
The Temporal Doppler Effect refers to the subjective perception that the past is further away than the future even when both temporal distances are objectively the same from the present moment (Caruso et al., 2013). In the current study, Zhang et al. ran a replication of this phenomenon and tested one possible explanation for it, namely that people overestimate the temporal distance of the past because the past is filled with more events than the future. This is because we can access information only about planned events for the future, but have access to both planned and unplanned events that happened in the past (filled-duration illusion; Thomas & Brown, 1974).
Over two studies, the authors found that the sampled participants reported feeling that the past was psychologically closer than the future, which is the opposite of what has previously been reported and termed the Temporal Doppler Effect (Caruso et al., 2013). In addition, the authors reported inconsistent results regarding the correlations between the psychological distance and different variables associated with the filling rate of duration. The authors discuss the differences between their own results and those by Caruso et al. (2013) in terms of methodological and contextual differences and highlight cultural aspects that may be critical to consider in future replications and overall testing of this phenomenon. As such, they highlight that, at the moment, the Temporal Doppler Effect should not be considered a robust and culturally universal phenomenon.
The Stage 2 manuscript was evaluated by two reviewers who had also reviewed the stage 1 report. Following a revision by the authors, which consisted of adding the Data Availability statement, as well as a more precise summary of the results in various sections of the report, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 2 criteria and awarded a positive recommendation.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/d9ec3/
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that was used to answer the research question existed prior to Stage 1 in-principle acceptance. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Caruso, E. M., Van Boven, L., Chin, M., & Ward, A. (2013). The temporal doppler effect: When the future feels closer than the past. Psychological Science, 24, 530-536. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797612458804
2. Thomas, E. C., & Brown, I. (1974). Time perception and the filled-duration illusion. Perception & Psychophysics, 16, 449-458. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03198571
3. Zhang, Q., Masuda, Y., Ueda, K.,Toda, K., & Yamada, Y. (2022). Is the past farther than the future? A registered replication and test of the time-expansion hypothesis based on the filling rate of duration. Stage 2 Registered Report, acceptance of Version 2 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://psyarxiv.com/pb47n/
| Is the past farther than the future? A registered replication and test of the time-expansion hypothesis based on the filling rate of duration | Qinjing Zhang, Yoshitaka Masuda, Kodai Toda, Kohei Ueda, Yuki Yamada | <p>People feel some events to be psychologically closer, while others to be farther away. Caruso et al. (2013) reported the Temporal Doppler Effect (TDE), in which people feel that the past is farther than the future, despite an equivalent objecti... |  | Social sciences | Ljerka Ostojic | 2022-08-20 09:59:09 | View | |
11 Apr 2024
STAGE 1

Managing Disclosure Outcomes in Intelligence InterviewsDavid A. Neequaye, Timothy J. Luke, and Kristina Kollback, Department of Psychology, University of Gothenburg. https://psyarxiv.com/tfp2cManaging costs and rewards when choosing to disclose informationRecommended by Zoltan Dienes based on reviews by Jason Chin, Yikang Zhang and Tyler Jacobs based on reviews by Jason Chin, Yikang Zhang and Tyler Jacobs
An interviewee in an intelligence interview can face competing interests in disclosing information: The value in cooperating because, for example, information given leads to the arrest of a narcotics gang, making the neighbourhood safer; and the risk that disclosing the information leads to reprisals from the gang. Different pieces of information will compete with each other for disclosure, depending on this balance of risks to self-interest. According to the disclosure-outcomes management model of Neequaye et al., information will be disclosed more with a high than low probability of reward, as might be straightforwardly expected, but this difference will be larger when there is a low probability of cost rather than a high probability. The high probability of cost will induce more a variable response to the possible benefits.
Neequaye et al. (2023) will invite participants to assume the role of an informant, with the goal of maximizing their points according to stated probabilities of costs and benefits of disclosing pieces of information relating to given scenarios. Then the degree to which each type of information is disclosed in a subsequent interview will be assessed: this way the crucial interaction can be tested. The Stage 1 manuscript was evaluated over one round of in-depth review. Based on detailed responses to the reviewers' comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 1 criteria and therefore awarded in-principle acceptance (IPA).
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/ru8j5
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that will be used to answer the research question yet exists and no part will be generated until after IPA. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals: References
Neequaye, D. A., Luke, T. J., & Kollback, K. (2023). Managing Disclosure Outcomes in Intelligence Interviews, in principle acceptance of Version 2 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/ru8j5
| Managing Disclosure Outcomes in Intelligence Interviews | David A. Neequaye, Timothy J. Luke, and Kristina Kollback, Department of Psychology, University of Gothenburg. | <p>We introduce the disclosure-outcomes management model. The model views disclosure in intelligence interviews as a behavior interviewees use to profitably navigate self-interest dilemmas. We theorize that interviewees compare the potential outco... | Social sciences | Zoltan Dienes | 2022-09-15 15:03:59 | View | ||
17 Jan 2023
STAGE 1
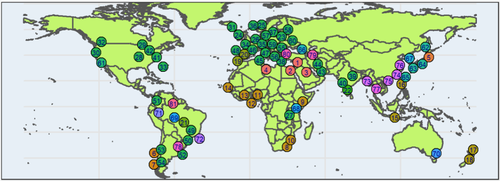
Similarities and differences in a global sample of song and speech recordingsCorresponding authors: Yuto Ozaki and Patrick E. Savage (Keio University, Japan). Full list of 80 authors is in the manuscript https://psyarxiv.com/jr9x7Exploring cross-cultural variation in speech and songRecommended by Chris Chambers based on reviews by Bob Slevc, Nai Ding and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Bob Slevc, Nai Ding and 1 anonymous reviewer
For centuries, the ubiquity of language and music across human societies has prompted scholars to speculate about their cross-cultural origins as well as their shared and unique characteristics. Depending on the extent to which contemporary theories emphasise the role of biology vs. culture, a range of hypotheses have been proposed concerning expected similarities and differences in song and speech. One class of hypotheses stemming from cultural relativism assumes a lack of universal regularities in song and speech, and therefore predicts no systematic cross-cultural relationships. On the other hand, more recent evolutionary hypotheses such as the social bonding hypothesis, motor constraint hypothesis, and sexual selection hypothesis all predict differences or similarities in specific characteristic of vocalisations, such as pitch regularity, pitch interval size, and melodic contour. Existing results are mixed in their support of these predictions.
In the current study, Ozaki et al. (2022) embark on an ambitious project to elucidate cross-cultural similarities and differences between speech and song in 81 different linguistic varieties spanning 23 language families. Understanding precisely how song and speech are related is methodologically challenging due to the multitude of confounds that can arise in comparing natural recordings. Here the authors overcome these difficulties with four types of carefully controlled recordings: singing, recitation of sung lyrics, spoken description of the song, and instrumental version of the sung melody. The authors will then examine six features that are amenable to reliable comparison, including pitch height, temporal rate, pitch stability, timbral brightness, pitch interval size, and pitch declination. With this data in hand, the authors will ask which acoustic features differ reliably between song and speech across cultures, with the expectation that song will exhibit higher pitch, slower rate and more stable pitch than speech. At the same time, the authors expect song and speech to be reliably similar in the characteristics of timbral brightness, pitch intervals and pitch contours. In addition to these confirmatory tests, the authors will explore variation across a range of additional stimulus characteristics and ancillary research questions.
The Stage 1 manuscript was evaluated over two rounds of in-depth review. Based on detailed responses to the reviewers' comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 1 criteria and therefore awarded in-principle acceptance (IPA).
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/jdhtz
Level of bias control achieved: Level 2. At least some data/evidence that will be used to answer the research question has been accessed and partially observed by the authors, but the authors certify that they have not yet observed the key variables within the data that will be used to answer the research question AND they have taken additional steps to maximise bias control and rigour.
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals: References
1. Ozaki, Y., Savage P. E. et al. (2022). Similarities and differences in a global sample of song and speech recordings, in principle acceptance of Version 2 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/jdhtz
| Similarities and differences in a global sample of song and speech recordings | Corresponding authors: Yuto Ozaki and Patrick E. Savage (Keio University, Japan). Full list of 80 authors is in the manuscript | <p>What, if any, similarities and differences between song and speech are consistent across cultures? Both song and speech are found in all known human societies and are argued to share evolutionary roots and cognitive resources, yet no studies ha... |  | Social sciences | Chris Chambers | Bob Slevc, Nai Ding | 2022-09-16 16:03:10 | View |
14 Nov 2023
STAGE 1

Scrolling to wisdom: the impact of social media news exposure on knowledge perceptionFederica Ruzzante, Gustavo Cevolani, Folco Panizza https://osf.io/dvtm6Might we know less about current events than we think we do?Recommended by Moin Syed based on reviews by Adrien Fillon, Erik Løhre and Moritz Ingendahl based on reviews by Adrien Fillon, Erik Løhre and Moritz Ingendahl
We are bombarded with news about current events from multiple sources: print media, digital media, friends, family, and more. At the same time, there is an imperative to “stay informed” and be knowledgeable of happenings both local and global. But how much knowledge do we actually gain from this bombardment of information? How informed are we really? It turns out that our perceptions of our knowledge tends to overstate our actual knowledge of a topic. This “illusion of knowledge” effect has been studied across a wide variety of contexts, but is especially relevant for understanding how people learn about and interact with politicized topics.
In the current study, Ruzzante et al. (2023) propose to further our understanding of the illusion of knowledge effect in the context of news exposure on social media. They will use an online pre-post experimental design that assesses participants’ perceived knowledge of a number of topics prior to the manipulation, which involves exposure to different social media news feeds, coming two weeks later. Central to the study, participants will be randomized to news stories that differ in their degree of self-involvement, that is how emotionally involved the topics are. Ruzzante et al. will test the hypothesis that more highly self-involved topics (e.g., abortion) will lead to a greater illusion of knowledge effect than less self-involved topics (e.g., feline immunodeficiency).
The Stage 1 manuscript was evaluated over two rounds of in-depth peer review, the first consisting of substantial comments from three scholars with relevant expertise, and the second consisting of a close review by the recommender. Based on detailed responses to the reviewers' comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 1 criteria and was therefore awarded in-principle acceptance (IPA).
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/qa7tb
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that will be used to answer the research question yet exists and no part will be generated until after IPA. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Ruzzante, F., Cevolani, G., & Panizza, F. (2023). Scrolling to wisdom: The impact of social media news exposure on knowledge perception. In principle acceptance of Version 5 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/qa7tb
| Scrolling to wisdom: the impact of social media news exposure on knowledge perception | Federica Ruzzante, Gustavo Cevolani, Folco Panizza | <p>The present study aims to test the effect of exposure to news in a social media environment on people’s perceived knowledge of selected topics and on the “illusion of knowledge” effect, i.e., the overestimation of one’s perceived knowledge rela... | Social sciences | Moin Syed | 2022-10-12 21:16:51 | View | ||
The labels and models used to describe problematic substance use impact discrete elements of stigma: A Registered ReportCharlotte R. Pennington, Rebecca L. Monk, Derek Heim, Abi K. Rose, Thomas Gough, Ross Clarke, Graham Knibb, Roshni Patel, Priya Rai, Halimah Ravat, Ramsha Ali, Georgiana Anastasiou, Fatemeh Asgari, Eve Bate, Tara Bourke, Jayme Boyles, Alix Campbell, Nic Fowler, Sian Hester, Charlotte Neil, Beth McIntyre, Ellie Ogilvy, Amie Renouf, Joni Stafford, Katie Toothill, Hin Kok Wong, Andrew Jones https://osf.io/z9bnfDifferent ways of describing problematic substance use and its treatment influence public stigmaRecommended by Zoltan Dienes based on reviews by Nicholas Sinclair-House based on reviews by Nicholas Sinclair-House
People experiencing problematic substance use are often stigmatised by the general public. This public stigma may impair such people obtaining help and the quality of help that they receive. For this reason, previous research has investigated the factors that may exacerbate or lessen stigma by focusing on the terminology used to describe problematic substance use. However, the evidence is not clear cut, with some studies suggesting that labelling the condition as a "chronically relapsing brain disease" vs a "problem" reduces certain elements of stigma and other studies finding absence of evidence. A closer look at these studies points to methodological differences that may explain their results, such as whether problematic substance use is compared with another health condition, whether the individual is described as seeking treatment or not, and whether general or discrete elements of stigma are measured.
In this Stage 2 Registered Report, Pennington et al. (2023) isolated these methodological differences to investigate if any of them influenced two different measures of stigma used in previous work. They found that greater social distance, danger and public stigma but lower blame were ascribed to drug use relative to a health concern, supporting previous research to suggest that problematic substance use is a highly stigmatised health condition. Furthermore, greater (genetic) blame was reported when drug use was labelled as a ‘chronically relapsing brain disease’ relative to a ‘problem’. The results for attributional judgement were either inconclusive or statistically equivalent. In summary, these findings suggest that the labels and models used to describe problematic substance use may impact upon public stigma in distinct ways. The authors suggest that future research should justify which measures are being used in line with theory. They also put forward the notion that addiction is a functional attribution, which may explain the mixed literature on the brain disease model of addiction to date.
The Stage 2 manuscript was evaluated over one round of specialist review and several rounds of discussion with the recommender. Based on comprehensive responses, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 2 criteria and awarded a positive recommendation.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/4vscg
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that was used to answer the research question was generated until after IPA.
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
Pennington, C. R., Monk, R. L., Heim, D., Rose, A. K., Gough, T., Clarke, R., Knibb, G., Patel, R., Rai, P., Ravat, H., Ali, R., Anastasiou, G., Asgari, F., Bate, E., Bourke, T., Boyles, J., Campbell, A., Fowler, N., Hester, S., Neil, C., McIntrye, B., Ogilvy, E., Renouf, A., Stafford, J., Toothill, K., Wong, H. K., & Jones, A. (2023). The labels and models used to describe problematic substance use impact discrete elements of stigma: A Registered Report. Stage 2 acceptance of Version 4 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/z9bnf
| The labels and models used to describe problematic substance use impact discrete elements of stigma: A Registered Report | Charlotte R. Pennington, Rebecca L. Monk, Derek Heim, Abi K. Rose, Thomas Gough, Ross Clarke, Graham Knibb, Roshni Patel, Priya Rai, Halimah Ravat, Ramsha Ali, Georgiana Anastasiou, Fatemeh Asgari, Eve Bate, Tara Bourke, Jayme Boyles, Alix Campbel... | <p>Objectives: Problematic substance use is one of the most stigmatised health conditions leading research to examine how the labels and models used to describe it influence public stigma. Two recent studies examine whether beliefs in a disease mo... | Social sciences | Zoltan Dienes | 2022-10-21 16:13:49 | View | ||
21 Mar 2023
STAGE 1

Convenience Samples and Measurement Equivalence in Replication ResearchLindsay J. Alley, Jordan Axt, Jessica Kay Flake https://osf.io/32unbDoes data from students and crowdsourced online platforms measure the same thing? Determining the external validity of combining data from these two types of subjectsRecommended by Corina Logan based on reviews by Benjamin Farrar and Shinichi Nakagawa based on reviews by Benjamin Farrar and Shinichi Nakagawa
Comparative research is how evidence is generated to support or refute broad hypotheses (e.g., Pagel 1999). However, the foundations of such research must be solid if one is to arrive at the correct conclusions. Determining the external validity (the generalizability across situations/individuals/populations) of the building blocks of comparative data sets allows one to place appropriate caveats around the robustness of their conclusions (Steckler & McLeroy 2008).
In this registered report, Alley and colleagues plan to tackle the external validity of comparative research that relies on subjects who are either university students or participating in experiments via an online platform (Alley et al. 2023). They will determine whether data from these two types of subjects have measurement equivalence - whether the same trait is measured in the same way across groups. Although they use data from studies involved in the Many Labs replication project to evaluate this question, their results will be of crucial importance to other comparative researchers whose data are generated from these two sources (students and online crowdsourcing). If Alley and colleagues show that these two types of subjects have measurement equivalence, then this indicates that it is more likely that equivalence could hold for other studies relying on these type of subjects as well. If measurement equivalence is not found, then it is a warning to others to evaluate their experimental design to improve validity. In either case, it gives researchers a way to test measurement equivalence for themselves because the code is well annotated and openly available for others to use.
The Stage 1 manuscript was evaluated over two rounds of in-depth review. Based on detailed responses to the reviewers' comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 1 criteria and therefore awarded in-principle acceptance (IPA). Level of bias control achieved: Level 2. At least some data/evidence that will be used to answer the research question has been accessed and partially observed by the authors, but the authors certify that they have not yet observed the key variables within the data that will be used to answer the research question AND they have taken additional steps to maximise bias control and rigour (e.g. conservative statistical threshold; recruitment of a blinded analyst; robustness testing, multiverse/specification analysis, or other approach)
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
Alley L. J., Axt, J., & Flake J. K. (2023). Convenience Samples and Measurement Equivalence in Replication Research, in principle acceptance of Version 4 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/7gtvf
Steckler, A. & McLeroy, K. R. (2008). The importance of external validity. American Journal of Public Health 98, 9-10. https://doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.2007.126847
Pagel, M. (1999). Inferring the historical patterns of biological evolution. Nature, 401, 877-884. https://doi.org/10.1038/44766
| Convenience Samples and Measurement Equivalence in Replication Research | Lindsay J. Alley, Jordan Axt, Jessica Kay Flake | <p>A great deal of research in psychology employs either university student or online crowdsourced convenience samples (Chandler & Shapiro, 2016; Strickland & Stoops, 2019) and there is evidence that these groups differ in meaningful ways ... | Social sciences | Corina Logan | 2022-11-29 18:37:54 | View | ||
Sight vs. sound judgments of music performance depend on relative performer quality: Cross-cultural evidence from classical piano and Tsugaru shamisen competitions [Stage 2 Registered Report]Gakuto Chiba, Yuto Ozaki, Shinya Fujii, Patrick E. Savage https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/xky4jMusic is appreciated cross-modally, but is culture- and context-dependentRecommended by Yuki Yamada based on reviews by Kyoshiro Sasaki and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Kyoshiro Sasaki and 1 anonymous reviewer
Music is not merely limited to the aural experience we garner through our auditory faculties, as commonly perceived. Rather, various studies have explored the cross-modal impact of visual stimuli on the evaluation of music. These previous studies have been confined exclusively to Western music. Hence, Chiba et al. (2023) designed a study with a focus on the Tsugaru shamisen, a renowned folk instrument indigenous to Japan, and of which the first author is an outstanding player.
The study methodology was an improved version of previous endeavors, wherein actual musical material sourced from concours performances was displayed through audio-only, video-only or both modalities. A sample of Japanese participants were then asked to evaluate the concours performances on both the piano and the Tsugaru shamisen. The results, obtained through pre-registered protocols, revealed that for both concours performances, the participants displayed a cross-modal impact of visual information on their aural evaluation of music. This effect was also found to be contingent on cultural and contextual factors. These outcomes furnish valuable evidence towards the generalizability of the interplay between sight and sound in the assessment of music. The study underwent rigorous peer-review processes in both Stage 1 and Stage 2, with three experts specializing in Japanese folk music, open science, and statistics, respectively, providing their critical assessments. Following multiple rounds of revision, the final manuscript was deemed fit for recommendation.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/ry2b6
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that was used to answer the research question was generated until after IPA.
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
Chiba G., Ozaki Y., Fujii S., & Savage P.E. (2023). Sight vs. sound judgments of music performance depend on relative performer quality: Cross-cultural evidence from classical piano and Tsugaru shamisen competitions [Stage 2 Registered Report]. Acceptance of Version 2 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/xky4j
| Sight vs. sound judgments of music performance depend on relative performer quality: Cross-cultural evidence from classical piano and Tsugaru shamisen competitions [Stage 2 Registered Report] | Gakuto Chiba, Yuto Ozaki, Shinya Fujii, Patrick E. Savage | <p>Which information dominates in evaluating performance in music? Both experts and laypeople consistently report believing that sound should be the most important domain when judging music competitions, but experimental studies of Western partici... |  | Social sciences | Yuki Yamada | 2022-11-30 08:04:37 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Chris Chambers
Zoltan Dienes
Corina Logan
Benoit Pujol
Maanasa Raghavan
Emily S Sena
Yuki Yamada










