Announcements
=============================================================================
IMPORTANT ANNOUNCEMENT: To accommodate reviewer and recommender holiday schedules, we will be closed to ALL submissions from 1st Jul - 1st Sep. During this time, reviewers can submit reviews and recommenders can issue decisions, but no new or revised submissions can be made by authors.
The one exception to this rule is that authors using the scheduled track who submit their initial Stage 1 snapshot prior to 1st Jul can choose a date within the shutdown period to submit their full Stage 1 manuscript.
We recommend that authors submit at least 1-2 weeks prior to commencement of the shutdown period to enable time to make any required revisions prior to in-depth review.
=============================================================================
We are recruiting recommenders (editors) from all research fields!
Your feedback matters! If you have authored or reviewed a Registered Report at Peer Community in Registered Reports, then please take 5 minutes to leave anonymous feedback about your experience, and view community ratings.
Latest recommendations
| Id | Title * | Authors * | Abstract * | Picture | Thematic fields * | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
01 Jun 2024
STAGE 1

Can Imagining Actions as Occurring Involuntarily Cause Intentional Behaviour to Feel Involuntary?Kevin Sheldrake, Zoltan Dienes https://osf.io/74gcnCan the sense of agency and reality be altered by our meta-cognitive models?Recommended by Anoushiravan Zahedi based on reviews by Zoltan Kekecs and Sophie Siestrup based on reviews by Zoltan Kekecs and Sophie Siestrup
Alterations in subjective experience, including alterations in the sense of agency (SoA) and reality (SoR), are commonly implicated in direct-verbal suggestions, such as hypnotic suggestions. Although extensively studied, how direct-verbal suggestions can alter the SoA and SoR is not understood (e.g., see Martin & Pacherie, 2019; Zahedi et al., 2024). One class of theories postulates that the alterations in SoA and SoR are related to meta-cognition. For instance, the intention to move or form a mental image can be kept out of conscious awareness, creating a sense of involuntariness (Dienes & Perner, 2007).
Relying on this theory, in the current study Sheldrake and Dienes (2024) postulate that the metacognitive processes related to these alterations can occur by appropriate use of imagination. In other words, by imagining the movement or object to be hallucinated and further imagining the underlying process was outside of awareness, one can elicit alterations in SoA and SoR. To this end, an intervention is devised whereby the participant is repeatedly asked to consider what might help or hinder them from imagining they are unaware of the relevant intention and thereby adjust their imagination. A control group will be asked to increase the feeling of involuntariness or altered reality simply by repeated practice. Afterward, participants will be asked in a test phase the extent to which the suggested experience felt involuntary. The Stage 1 manuscript was evaluated over three rounds of in-depth review. Based on detailed responses to the reviewers' comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 1 criteria and therefore awarded in-principle acceptance (IPA).
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/f8hsd Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that will be used to answer the research question yet exists and no part will be generated until after IPA. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals: References 1. Dienes, Z. & Perner, J. (2007). Executive control without conscious awareness: The cold control theory of hypnosis. In G. A. Jamieson (Ed.), Hypnosis and conscious states: The cognitive neuroscience perspective (pp. 293-314). Oxford University Press.
2. Martin, J. R. & Pacherie, E. (2019). Alterations of agency in hypnosis: A new predictive coding model. Psychol Rev, 126(1), 133-152. https://doi.org/10.1037/rev0000134
3. Sheldrake, K. & Dienes, Z. (2043). Can Imagining Actions as Occurring Involuntarily Cause Intentional Behaviour to Feel Involuntary? In principle acceptance of Version 6 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/f8hsd
4. Zahedi, A., Lynn, S. J., & Sommer, W. (2024). Cognitive Simulation along with Neural Adaptation Explain Effects of Suggestions: A Novel Theoretical Framework. Frontiers in Psychology. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1388347
| Can Imagining Actions as Occurring Involuntarily Cause Intentional Behaviour to Feel Involuntary? | Kevin Sheldrake, Zoltan Dienes | <p>The cold control theory of response to imaginative suggestions calling for distortions in veridical experience (including hypnotic suggestions) states that behavioural and cognitive responses are generated intentionally, but are perceived as in... | Social sciences | Anoushiravan Zahedi | Zoltan Kekecs | 2023-11-25 16:24:53 | View | |
31 May 2024
STAGE 1

Unveiling the Positivity Bias on Social Media: A Registered Experimental Study On Facebook, Instagram, And XA. Masciantonio, N. Heiser, A. Cherbonnier https://osf.io/c9ysvSocial media positivity biasRecommended by Veli-Matti Karhulahti based on reviews by Linda Kaye, Marcel Martončik, Julius Klingelhoefer and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Linda Kaye, Marcel Martončik, Julius Klingelhoefer and 1 anonymous reviewer
Both research and public debates around social media use tend to involve a premise of positivity bias, which refers to presenting one’s life in an overly positive light by various different means. This premise contributes to multiple potentially important follow-up hypotheses, such as the fear of missing out and low self-image effects, due to repeated consumption of positive social media content (e.g., Bayer et al. 2020, for a review). The positivity bias of social media use, itself, has received limited research attention, however.
In the present study, Masciantonio and colleagues (2024) will test positivity bias in the context of three social media platforms: Facebook, Instagram, and X. The experiment involves recruiting participants into platform-specific user groups and crafting posts to be shared with friends as well as respective social media audiences. If positivity bias manifests in this context, the social media posts should introduce more positive valence in comparison to offline sharing—and if the platforms differ in their encouragement of positivity bias, they should introduce significant between-platform differences in valence. The Stage 1 plan was reviewed by four independent experts representing relevant areas of methodological and topic expertise. Three reviewers proceeded throughout three rounds of review, after which the study was considered having met all Stage 1 criteria and the recommender granted in-principle acceptance. URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/9z6hm Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that will be used to answer the research question yet exists and no part will be generated until after IPA. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Bayer, J. B., Triệu, P., & Ellison, N. B. (2020). Social media elements, ecologies, and effects. Annual review of psychology, 71, 471-497. https:// doi.org/10.1146/annurev-psych-010419-050944 2. Masciantonio, A., Heiser, N., & Cherbonnier, A. (2024). Unveiling the Positivity Bias on Social Media: A Registered Experimental Study On Facebook, Instagram, And X. In principle acceptance of Version 4 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/9z6hm
| Unveiling the Positivity Bias on Social Media: A Registered Experimental Study On Facebook, Instagram, And X | A. Masciantonio, N. Heiser, A. Cherbonnier | <p>Social media has transformed how people engage with the world around them. The positivity bias on social media, in particular, warrants in-depth investigation. This is particularly true as previous research has concentrated on one specific plat... | Social sciences | Veli-Matti Karhulahti | 2024-01-15 10:33:52 | View | ||
31 May 2024
STAGE 1

Representativeness heuristic in intuitive predictions: Replication Registered Report of problems reviewed in Kahneman and Tversky (1973)Hong Ching (Bruce) Chan, Gilad Feldman https://osf.io/9cqp6The Representativeness Heuristic Revisited: Registered Replication Report of Kahneman and Tversky (1973)Recommended by Rima-Maria Rahal based on reviews by Peter Anthony White, Regis Kakinohana and Naseem Dillman-Hasso based on reviews by Peter Anthony White, Regis Kakinohana and Naseem Dillman-Hasso
Revisiting a true classic, this registered replication report addresses Kahneman and Tversky’s (1973) introduction of the representativeness heuristic. The heuristic refers to deviations of judgments from normative evaluations of the evidence when the stimulus fits to a prototype. For instance, when an individual is described by features stereotypically associated with a certain target group (e.g., a person who attends dance training several times a week and has a passion for singing and performing), likelihood judgments that the individual belongs to a target group (K-Pop artists) compared to a non-target group (e.g., accountants) are inflated.
The impact of the original research on the field is clearly immense and long-lasting. All the better that a systematic replication attempt is being undertaken in this registered report, which addresses studies 1 through 7 of Kahneman and Tversky’s classic 1973 paper. Chan and Feldman (2024) propose a well-powered online study, in which all studies from the original article are presented to participants within-subjects. The materials are carefully constructed and closely documented in the accompanying OSF project, where in-depth information on planned data analyses is supported with a simulated dataset. The Stage 1 manuscript was evaluated over three rounds of in-depth review. Based on detailed responses to the reviewers' comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 1 criteria and therefore awarded in-principle acceptance (IPA). URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/er2cq
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. Data collection commenced during the later part of Stage 1 peer review; however, since no substantive changes to the design were made after this point, the risk of bias due to prior data observation remains zero and the manuscript therefore qualifies for Level 6.
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Chan, H. C. & Feldman, G. (2024). Representativeness heuristic in intuitive predictions: Replication Registered Report of problems reviewed in Kahneman and Tversky (1973). In principle acceptance of Version 5 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/er2cq 2. Kahneman, D., & Tversky, A. (1973). On the psychology of prediction. Psychological Review, 80(4), 237–251. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0034747
| Representativeness heuristic in intuitive predictions: Replication Registered Report of problems reviewed in Kahneman and Tversky (1973) | Hong Ching (Bruce) Chan, Gilad Feldman | <p>[IMPORTANT: Abstract, method, and results were written using a randomized dataset produced by Qualtrics to simulate what these sections will look like after data collection. These will be updated following the data collection. For the purpose o... | Social sciences | Rima-Maria Rahal | 2023-11-29 15:19:07 | View | ||
30 May 2024
STAGE 1

Does learning more about others impact liking them?: Replication and extension Registered Report of Norton et al. (2007)’s Lure of AmbiguityZöe Horsham, Ashleigh Haydock-Symonds, Hirotaka Imada, Hiu Ching Tai, Wing Lam Lau, Tsz Lui Shum, Yuqing Zeng, Hiu Tang Chow, Gilad Feldman https://osf.io/eygzpDoes familiarity really breed contempt?Recommended by Yuki Yamada based on reviews by Philipp Schoenegger and Zoltan Kekecs based on reviews by Philipp Schoenegger and Zoltan Kekecs
In interpersonal evaluation, the amount of information available about the other person has a significant impact. Norton et al. (2007) conducted systematic experiments suggesting a 'less is more' effect – that a lack of information leads to a more positive evaluation. However, subsequent studies have not always reached the same conclusion.
In the current study, Horsham et al. (2024) aim to address this issue by conducting direct and conceptual replications of the Norton et al. (2007) experiments, as well as additional extensive experiments focusing on the effects of curiosity. The authors seek to confirm in a reliable way the relationship between ambiguity and liking, and even to clarify the factors that mediate this relationship. The results should significantly advance our understanding of the importance of information management in interpersonal relationships.
The Stage 1 manuscript was peer-reviewed by two experts; after four rounds of review and based on their revisions and detailed responses to the reviewers' comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 1 criteria and awarded it in-principle acceptance (IPA).
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/7mc4y
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that will be used to answer the research question yet exists and no part will be generated until after IPA. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Norton, M. I., Frost, J. H., & Ariely, D. (2007). Less is more: The lure of ambiguity, or why familiarity breeds contempt. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 92, 97-105. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.92.1.97
2. Horsham, Z., Haydock-Symonds, A., Imada, H., Tai, H. C., Lau, W. L., Shum, T. L., Zeng, Y., Chow, H. T., & Feldman, G., (2024). Does learning more about others impact liking them? Replication and extension Registered Report of Norton et al. (2007)’s Lure of Ambiguity. In principle acceptance of Version 4 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/7mc4y
| Does learning more about others impact liking them?: Replication and extension Registered Report of Norton et al. (2007)’s Lure of Ambiguity | Zöe Horsham, Ashleigh Haydock-Symonds, Hirotaka Imada, Hiu Ching Tai, Wing Lam Lau, Tsz Lui Shum, Yuqing Zeng, Hiu Tang Chow, Gilad Feldman | <p>[IMPORTANT: Abstract, method, and results were written using a randomized dataset produced by Qualtrics to simulate what these sections will look like after data collection. These will be updated following the data collection. For the purpose o... | Social sciences | Yuki Yamada | Zoltan Kekecs | 2023-07-11 12:33:00 | View | |
30 May 2024
STAGE 1

Gaming Disorder: A Qualitative Meta-synthesis of Case StudiesTiina Auranen, Matúš Adamkovič, Veli-Matti Karhulahti, Marcel Martoncik, Yaewon Jin, Miia Siutila, Valtteri Kauraoja, Solip Park https://osf.io/sv2rmWhat can qualitative research tell us about Gaming Disorder?Recommended by Mateo Leganes-Fonteneau and Chris Chambers and Chris Chambers based on reviews by Simone Amendola, Gemma Lucy Smart and Ting Pan based on reviews by Simone Amendola, Gemma Lucy Smart and Ting Pan
How can qualitative research and case studies inform theoretical models of gaming disorder? Gaming Disorder has generated a large amount of research, with up to 95% of it focusing on quantitative studies. As a result, most of the meta-analyses and review studies focus on quantitative research and disregard qualitative approaches. However, studying the direct experiences of gamers can provide more detailed and direct evidence that can feed into theoretical models.
In this Stage 1 manuscript, Auranen et al. (2024) will perform a qualitative meta-analysis of gaming disorder case studies, case reports, and case series of treatment-seekers using a 3-phase approach. First, they will focus on examining the reported problems of participants, the reported reasons for seeking help to reduce their gaming, and the causal link between gaming and reported problems, including the context of these problematic behaviors. Second, thematic synthesis will generate construct themes regarding the contexts of the individuals and the reported problems. Lastly, the authors will examine the relevance of findings in regards to the coping model, value fulfillment theory and the theory of cultural dissonance.
The Stage 1 submission was evaluated by the recommender and three expert reviewers, one of which was recused due to conflicts of interest that emerged after the first round of revisions. The recommender and co-recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 1 criteria and therefore awarded in-principle acceptance (IPA).
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/hzc5a
Level of bias control achieved: Level 4. At least some of the data/evidence that will be used to answer the research question already exists AND is accessible in principle to the authors (e.g. residing in a public database or with a colleague), BUT the authors certify that they have not yet accessed any part of that data/evidence.
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals: References Auranen, T., Adamkovič, M., Martončik, M., Park, S., Kauraoja, V., Siutila, M., Jin, Y., & Karhulahti, V.-M. (2024). Gaming Disorder: A qualitative meta-synthesis of related case studies. In principle acceptance of Version 3 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/hzc5a
| Gaming Disorder: A Qualitative Meta-synthesis of Case Studies | Tiina Auranen, Matúš Adamkovič, Veli-Matti Karhulahti, Marcel Martoncik, Yaewon Jin, Miia Siutila, Valtteri Kauraoja, Solip Park | <p>Several meta-analyses and reviews have been published on gaming-related health problems, which are today studied mainly in the context of the World Health Organization’s new mental disorder construct, “gaming disorder”. However, none of those r... | Medical Sciences, Social sciences | Mateo Leganes-Fonteneau | Ting Pan | 2023-11-24 14:00:19 | View | |
30 May 2024
STAGE 1
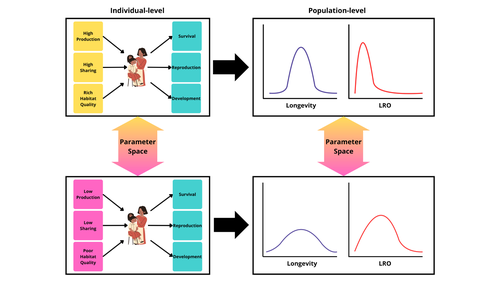
The role of resource dynamics in the distribution of life cycles within a female human populationPablo J. Varas Enríquez, Daniel Redhead, Monique Borgerhoff Mulder, Heidi Colleran, Dieter Lukas https://osf.io/nzeq9An agent-based model of the role of resource dynamics and the environment in human female life cyclesRecommended by Claudio Tennie based on reviews by Cecilia Padilla-Iglesias and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Cecilia Padilla-Iglesias and 1 anonymous reviewer
Among primates, the human female life cycle appears special. Aspects of these life cycles have been linked to the acquisition and distribution of resources and to environmental factors, as well as to individual differences across human females. Many questions remain regarding the causal roles that these (or also other) factors might have played in the evolution of human female life cycles – and also whether generalizing statements about these life cycles can adequately capture the wide range of the observed phenomena.
In the current study, Varas Enriquez et al. (2024) outline a plan for an agent-based model approach to study the factors that guide and channel variability in female life cycles in humans (within biological constraints), via the effects that their model will capture. The authors’ model has a particular eye towards the effects of resource dynamics (resource production and resource transfers) and environmental conditions – and their interplay. The results of this agent based model will be thoroughly analysed to better understand the evolution of the specific female human life cycle range.
The study plan was refined after one round of review, which led to input from two external reviewers and the recommender. The revised (second) version was judged to satisfy the Stage 1 criteria for in-principle acceptance.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/24c7z
Level of bias control achieved: Level 2. At least some data/evidence that will be used to answer the research question has been accessed and partially observed by the authors, but the authors certify that they have not yet observed the key variables within the data that will be used to answer the research question AND they have taken additional steps to maximise bias control and rigour (e.g. conservative statistical threshold; recruitment of a blinded analyst; robustness testing, multiverse/specification analysis, or other approach) List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals: References
Varas Enríquez, P. J., Lukas, D., Colleran, H, Mulder, M. B., & Redhead, D. (2024) The role of resource dynamics in the distribution of life cycles within a female human population. In principle acceptance of Version 2 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/24c7z
| The role of resource dynamics in the distribution of life cycles within a female human population | Pablo J. Varas Enríquez, Daniel Redhead, Monique Borgerhoff Mulder, Heidi Colleran, Dieter Lukas | <p>The evolution of the female human life cycle, which is characterised by having a reproductive career nested within juvenile and post-reproductive periods, has been linked to the surplus of adult resource production and downwards inter-generatio... |  | Life Sciences, Medical Sciences, Social sciences | Claudio Tennie | 2023-11-13 15:45:52 | View | |
The importance of conceptual knowledge when becoming familiar with faces during naturalistic viewingKira N. Noad and Timothy J. Andrews https://osf.io/thgrzA registered test of the role of contextual information in perceptual learning of facesRecommended by Robert McIntosh based on reviews by Haiyang Jin based on reviews by Haiyang Jin
When we familiarise with new faces over repeated exposures, it is generally in situations that have meaning for us. Seeing a face more often tends to go along with learning more about the person, and their likely contexts and actions. In this Registered Report, Noad and Andrews (2024) tested whether meaningful context during exposure improves the consolidation of faces into long-term memory. Participants were shown video clips from the TV series Life on Mars, either in their original chronological sequence, which provides meaningful context, or in a scrambled sequence. It was expected that the original sequence would provide a better conceptual understanding, and this was confirmed by free recall and structured question tests. Face recognition memory was tested with images of the actor from the original clips (‘in show’) and the same actor from another show (‘out-of-show’), to test whether memory was modulated by the similarity of appearance to that at encoding. Face recognition was tested immediately after exposure and after four weeks, to allow time for consolidation. As expected, recognition memory was better for participants in the meaningful context condition, and for in-show faces. However, meaningful context did not lead to less forgetting of the faces at the follow up test, even for in-show faces, which did not support the original predictions. An exploratory analysis found that a metric of overlap between pairs of participants’ conceptual understanding was related to overlap in the set of faces they recognised. This relationship was stronger after four weeks, which suggests increased interaction of conceptual knowledge and face recognition after consolidation.
The Stage 2 manuscript was assessed over two rounds of review, and the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 2 criteria for recommendation.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/8wp6f
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that was used to answer the research question was generated until after IPA. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Noad, K. & Andrews, T. J. (2024). The importance of conceptual knowledge when becoming familiar with faces during naturalistic viewing [Stage 2]. Acceptance of Version 4 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/thgrz | The importance of conceptual knowledge when becoming familiar with faces during naturalistic viewing | Kira N. Noad and Timothy J. Andrews | <p>Although the ability to recognise familiar faces is a critical part of everyday life, the process by which a face becomes familiar in the real world is not fully understood. Previous research has focussed on the importance of perceptual experie... | Life Sciences, Social sciences | Robert McIntosh | 2024-01-17 16:00:17 | View | ||
21 May 2024
STAGE 1

The importance of consolidating perceptual experience and contextual knowledge in face recognitionKira Noad and Timothy J. Andrews https://osf.io/6rb47?view_only=a59c340099d44a8db190a1b382b3b4d8How does perceptual and contextual information influence the recognition of faces?Recommended by Robert McIntosh based on reviews by Lisa DeBruine and Haiyang Jin based on reviews by Lisa DeBruine and Haiyang Jin
When we familiarise with new faces over repeated exposures, it is in situations that have meaning for us. Here, Noad and Andrews (2023) ask whether meaningful context during exposure matters for the consolidation of faces into long-term memory. Participants will be shown video clips from TV shows that are ordered either in their original chronological sequence, preserving meaningful context, or in a scrambled sequence. It is expected that the original sequence will provide a better understanding of the narrative. The critical question is whether this will also be associated with differences in memory for the faces. Memory will be tested with images of the actor from the original clips (‘in show’) or images of the same actor from another show (‘out-of-show’), both immediately after exposure and following a four-week delay. It is predicted that memory for faces will be better retained across the delay when the original exposure was in a meaningful context, and that this benefit will be enhanced for ‘in-show’ images, where the person’s appearance matches with the original context. The pre-registered predictions and the targeted effect sizes for this study are informed by pilot data reported within the manuscript.
The Stage 1 manuscript was evaluated through an initial round of editorial review, followed by a further round of external review, after which the recommender judged that it met the Stage 1 criteria for in-principle acceptance (IPA).
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/8wp6f
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that will be used to answer the research question yet exists and no part will be generated until after IPA. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References 1. Noad, K. & Andrews, T. J. (2023). The importance of consolidating perceptual experience and contextual knowledge in face recognition, in principle acceptance of Version 4 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/8wp6f | The importance of consolidating perceptual experience and contextual knowledge in face recognition | Kira Noad and Timothy J. Andrews | <p>Although the ability to recognise familiar faces is a critical part of everyday life, the process by which a face becomes familiar in the real world is not fully understood. Previous research has focussed on the importance of perceptual experie... | Life Sciences | Robert McIntosh | 2022-09-09 14:33:57 | View | ||
07 May 2024
STAGE 1

Revisiting the Psychology of Waste: Replication and extensions Registered Report of Arkes (1996)Zijin Zhu, Gilad Feldman https://osf.io/xcthsWhen do perceptions of wastefulness affect how people make choices?Recommended by Douglas Markant based on reviews by Travis Carter and Quentin Andre based on reviews by Travis Carter and Quentin Andre
How do perceptions of wastefulness affect how people make choices? In an influential set of studies examining different conceptions of wasteful behavior (overspending, underutilization, and sunk costs), Arkes (1996) found a systematic aversion to wastefulness in decision making, even when choosing to avoid wastefulness has no economic value or works against personal interest. While these findings have been influential in basic and applied research, there have been no attempts to directly replicate the results. Moreover, the original study has several methodological limitations, including the use of relatively small samples and gaps in statistical analysis and reporting.
In this Stage 1 manuscript, Zhu and Feldman (2024) propose to conduct a high-powered replication of Arkes (1996) using an online sample of participants. The authors will incorporate several extensions to improve methodological rigor relative to the original article, including added comprehension checks, checks of the wastefulness manipulations, a within-subjects design, and a quantitative analysis of participants’ self-reported motivations for their choices. The results of the study will provide insight into the robustness of the original findings, while also better distinguishing wastefulness aversion from other potential reasons behind participants' decisions.
The Stage 1 submission was evaluated by the recommender and two expert reviewers. After two rounds of revision, the recommender determined that the manuscript met the Stage 1 criteria and awarded in-principle acceptance (IPA).
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/r7tsw
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that will be used to answer the research question yet exists and no part will be generated until after IPA. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Arkes, H. R. (1996). The psychology of waste. Journal of Behavioral Decision Making, 9,
213-224. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1099-0771(199609)9:3%3C213::AID-BDM230%3E3.0.CO;2-1 2. Zhu, Z. & Feldman, G. (2024). Revisiting the Psychology of Waste: Replication and extensions Registered Report of Arkes (1996). In principle acceptance of Version 3 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/r7tsw
| Revisiting the Psychology of Waste: Replication and extensions Registered Report of Arkes (1996) | Zijin Zhu, Gilad Feldman | <p>[IMPORTANT: Abstract, method, and results were written using a randomized dataset produced by Qualtrics to simulate what these sections will look like after data collection. These will be updated following the data collection. For the purpose o... | Social sciences | Douglas Markant | 2024-01-11 06:55:16 | View | ||
30 Apr 2024
STAGE 1

A climate action intervention to boost individual and collective climate mitigation behaviors in young adultsAnna Castiglione, Cameron Brick, Gianluca Esposito, Andrea Bizzego https://osf.io/zh3w9Putting climate action intervention to the test: Part 1Recommended by Chris Chambers based on reviews by Helen Landmann, Jana Kesenheimer and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Helen Landmann, Jana Kesenheimer and 1 anonymous reviewer
It is increasingly recognised that resolving the climate crisis will require not only the reform of law and government policy but collective grassroots action to change individual behaviour and put public pressure on political leaders, companies and institutions to cut emissions. The capacity, however, for individual citizens to take such steps is limited by lack of knowledge/awareness of means and opportunities as well as psychological barriers that can make such actions seem impossible, fruitless or against the person's immediate self-interest. Interventions designed to overcome these obstacles and promote individual behaviour change have met with only limited success, with many based on weak psychological evidence and the outcome measures used to evaluate their success prone to error and bias.
In the current submission, Castiglione et al. (2024) propose a series of five studies to test, evaluate, and optimise a longitudinal intervention for engaging young adults (aged 18-35) in individual and collective climate action. Building on existing theory and evidence, the authors have designed an intensive 6-week educational intervention that draws on 12 psychological factors linked to pro-environmental behaviour, including emotional engagement, self-efficacy, collective efficacy, theory of change, cognitive alternatives, perceived behavioral control, implementation intentions, social norms, self-identity, collective identity, appraisal, and faith in institutions. Through the use of ecological momentary assessment (EMA), they plan to measure these targeted psychological correlates as well as individual and collective climate engagement of participants before and after the intervention (and in active groups vs. controls), and then again after a further three months.
The current submission is novel in being the first at PCI RR (and possibly the first RR anywhere) to propose an incremental programmatic workflow that combines two innovations: a single Stage 1 protocol leading to multiple Stage 2 outputs (under the PCI RR programmatic track) and a prespecification in which the design of the intervention in later studies is (for now) determined only broadly, with specific parameters to be shaped by the results of the first set of studies (under the PCI RR incremental registrations policy). This particular Stage 1 manuscript specifies the design of study 1 in two samples (high-school and university students in Italy; producing one Stage 2 output for each sample) and the general design of subsequent studies. The details of this later research in study 2 (in the same two populations) and study 3 (university students in the Netherlands) will be developed sequentially based on the results of the previous Stage 2 outputs and the state of the literature at that time.
The Stage 1 manuscript was evaluated over two rounds of in-depth review. Based on detailed responses to the reviewers' comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 1 criteria and therefore awarded in-principle acceptance (IPA). Following the completion of study 1, the authors will submit an updated Stage 1 manuscript for re-evaluation that updates the plans for later studies accordingly, hence the current recommendation is labelled "Part 1".
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/zh3w9 (under temporary private embargo)
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that will be used to answer the research question yet exists and no part will be generated until after IPA. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
Castiglione, A., Brick, C., Esposito, G., & Bizzego, A. (2024). A climate action intervention to boost individual and collective climate mitigation behaviors in young adults. In principle acceptance of Version 3 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/zh3w9
| A climate action intervention to boost individual and collective climate mitigation behaviors in young adults | Anna Castiglione, Cameron Brick, Gianluca Esposito, Andrea Bizzego | <p>We present a programmatic research line to test whether a longitudinal intervention aiming to increase key psychological correlates of pro-environmental behavior motivates young adults to take climate action. In five longitudinal studies, we wi... | Social sciences | Chris Chambers | Tyler Jacobs, Matt Williams | 2024-01-11 16:25:49 | View |
FOLLOW US
MANAGING BOARD
Chris Chambers
Zoltan Dienes
Corina Logan
Benoit Pujol
Maanasa Raghavan
Emily S Sena
Yuki Yamada










