Announcements
=============================================================================
IMPORTANT ANNOUNCEMENT: To accommodate reviewer and recommender holiday schedules, we will be closed to ALL submissions from 1st Jul - 1st Sep. During this time, reviewers can submit reviews and recommenders can issue decisions, but no new or revised submissions can be made by authors.
The one exception to this rule is that authors using the scheduled track who submit their initial Stage 1 snapshot prior to 1st Jul can choose a date within the shutdown period to submit their full Stage 1 manuscript.
We recommend that authors submit at least 1-2 weeks prior to commencement of the shutdown period to enable time to make any required revisions prior to in-depth review.
=============================================================================
We are recruiting recommenders (editors) from all research fields!
Your feedback matters! If you have authored or reviewed a Registered Report at Peer Community in Registered Reports, then please take 5 minutes to leave anonymous feedback about your experience, and view community ratings.
Latest recommendations
| Id | Title * | Authors * | Abstract * | Picture | Thematic fields * | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Impact of analytic decisions on test-retest reliability of individual and group estimates in functional magnetic resonance imaging: a multiverse analysis using the monetary incentive delay taskMichael I. Demidenko, Jeanette A. Mumford, Russell A. Poldrack https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.03.19.585755Exploring determinants of test-retest reliability in fMRI: a study with the Monetary Incentive Delay TaskRecommended by Dorothy Bishop based on reviews by Xiangzhen Kong and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Xiangzhen Kong and 1 anonymous reviewer
Functional magnetic resonance imaging has been used to explore brain-behaviour relationships for many years, with proliferation of a wide range of sophisticated analytic procedures. However, rather scant attention has been paid to the reliability of findings. Concerns have been growing failures to replicate findings in some fields, but it is hard to know how far this is a consequence of underpowered studies, flexible analytic pipelines, or variability within and between participants. Demidenko et al. (2024) took advantage of the availability of three existing datasets, including the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) study, the Michigan Longitudinal Study, and the Adolescent Risk Behavior Study, which all included a version of the Monetary Incentive Delay task measured in two sessions. These were entered into a multiverse analysis, which considered how within-subject and between-subject variance varies according to four analytic factors: smoothing (5 levels), motion correction (6 levels), task modelling (3 levels) and task contrasts (4 levels). They also considered how sample size affects estimates of reliability. The results have important implications for the those using fMRI with the Monetary Incentive Delay Task, and also raise questions more broadly about use of fMRI indices to study individual differences. Motion correction had relatively little impact on the ICC, and the effect size of the smoothing kernel was modest. Larger impacts on reliability were associated with choice of contrast (implicit baseline giving larger effects) and task parameterization. But perhaps the most sobering message from this analysis is that although activation maps from group data were reasonably reliable, the ICC, used as an index of reliability for individual levels of activation, was consistently low. This raises questions about the suitability of the Monetary Incentive Delay Task for studying individual differences. Another point is that reliability estimates become more stable as sample size increases; researchers may want to consider whether the trade-off between cost and gain in precision is justified for sample sizes above 250. I did a quick literature search on Web of Science: at the time of writing the search term ("Monetary Delay Task" AND fMRI) yielded 410 returns, indicating that this is a popular method in cognitive neuroscience. The detailed analyses reported here will repay study for those who are planning further research using this task. The Stage 2 manuscript was evaluated over one round of in-depth review. Based on detailed responses to the reviewer's and recommender's comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 2 criteria and awarded a positive recommendation. URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/nqgeh
Level of bias control achieved: Level 2. At least some data/evidence that was used to answer the research question had been accessed and partially observed by the authors prior to IPA, but the authors certify that they had not yet sufficiently observed the key variables within the data to be able to answer the research questions and they took additional steps to maximise bias control and rigour.
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References 1. Demidenko, M. I., Mumford, J. A., & Poldrack, R. A. (2024). Impact of analytic decisions on test-retest reliability of individual and group estimates in functional magnetic resonance imaging: a multiverse analysis using the monetary incentive delay task [Stage 2]. Acceptance of Version 5 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2024.03.19.585755v4 | Impact of analytic decisions on test-retest reliability of individual and group estimates in functional magnetic resonance imaging: a multiverse analysis using the monetary incentive delay task | Michael I. Demidenko, Jeanette A. Mumford, Russell A. Poldrack | <p>Empirical studies reporting low test-retest reliability of individual blood oxygen-level dependent (BOLD) signal estimates in functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) data have resurrected interest among cognitive neuroscientists in methods... | 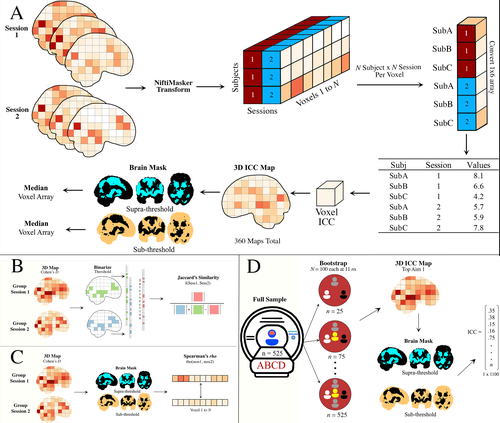 | Life Sciences, Social sciences | Dorothy Bishop | 2024-03-21 02:23:30 | View | |
09 Jul 2024
STAGE 1

Test-Retest Reliability in Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Impact of Analytical Decisions on Individual and Group Estimates in the Monetary Incentive Delay TaskMichael I. Demidenko, Jeanette A. Mumford, Russell A. Poldrack https://osf.io/rv859?view_only=deaf7a8d461641749f143504b2a3150bExploring determinants of test-retest reliabilty in fMRIRecommended by Dorothy Bishop based on reviews by Xiangzhen Kong and 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Xiangzhen Kong and 2 anonymous reviewers
Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) has been used to explore brain-behaviour relationships for many years, with proliferation of a wide range of sophisticated analytic procedures. However, rather scant attention has been paid to the reliability of findings. Concerns have been growing following failures to replicate findings in some fields, but it is hard to know how far this is a consequence of underpowered studies, flexible analytic pipelines, or variability within and between participants.
Demidenko et al. (2023) plan a study that will be a major step forward in addressing these issues. They take advantage of the availability of three existing datasets, the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) study, the Michigan Longitudinal Study, and the Adolescent Risk Behavior Study, which all included a version of the Monetary Incentive Delay task measured in two sessions. This gives ample data for a multiverse analysis, which will consider how within-subject and between-subject variance varies according to four analytic factors: smoothing (5 levels), motion correction (6 levels), task modelling (3 levels) and task contrasts (4 levels). They will also consider how sample size affects estimates of reliability. This will involve a substantial amount of analysis.
The study is essentially focused on estimation, although specific predictions are presented regarding the combinations of factors expected to give optimal reliability. The outcome will be a multiverse of results which will allow us to see how different pipeline decisions for this task affect reliability. In many ways, null results – finding that at least some factors have little effect on reliability – would be a positive finding for the field, as it would mean that we could be more relaxed when selecting an analytic pathway. A more likely outcome, however, is that analytic decisions will affect reliability, and this information can then guide future studies and help develop best practice guidelines. As one reviewer noted, we can’t assume that results from this analysis will generalise to other tasks, but this analysis with a widely-used task is an important step towards better and more consistent methods in fMRI.
The researchers present a fully worked out plan of action, with supporting scripts that have been developed in pilot testing. The Stage 1 manuscript received in-depth evaluation from three expert reviewers and the recommender. Based on detailed responses to the reviewers' comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 1 criteria and therefore awarded in-principle acceptance (IPA).
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/nqgeh
Level of bias control achieved: Level 2. At least some data/evidence that will be used to answer the research question has been accessed and partially observed by the authors, but the authors certify that they have not yet sufficiently observed the key variables within the data to be able to answer the research questions AND they have taken additional steps to maximise bias control and rigour.
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References 1. Demidenko, M. I., Mumford, J. A., & Poldrack, R. A. (2023). Test-Retest Reliability in Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Impact of Analytical Decisions on Individual and Group Estimates in the Monetary Incentive Delay Task. In principle acceptance of Version 3 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/nqgeh | Test-Retest Reliability in Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Impact of Analytical Decisions on Individual and Group Estimates in the Monetary Incentive Delay Task | Michael I. Demidenko, Jeanette A. Mumford, Russell A. Poldrack | <p>Empirical studies reporting low test-retest reliability of individual neural estimates in functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) data have resurrected interest among cognitive neuroscientists in methods that may improve reliability in fMR... | Life Sciences, Social sciences | Dorothy Bishop | 2023-04-17 22:27:54 | View | ||
01 Jul 2024
STAGE 1

The Influence of Bilingualism on Statistical Word Learning: A Registered ReportSimonetti, M. E., Lorenz, M. G., Koch, I., & Roembke, T. https://osf.io/2ch9yComparing statistical word learning in bilinguals and monolingualsRecommended by Elizabeth Wonnacott based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
Many studies have investigated the extent to which word learning is underpinned by statistical learning, i.e. tracking probabilistic relationships between forms and referents. Previous literature has investigated whether these processes differ in bilingual learners – who have to track two such sets of mappings in their linguistic environment. However, the evidence is mixed: some say bilinguals have a learning advantage and some find no evidence of differences.
The current study by Simonetti et al. (2024) aims to further explore this in an experiment using the cross-situational word learning paradigm. In this paradigm participants hear words and view arrays of object across a series of trials. Taking each trial in isolation the word is ambiguous, but there are consistent co-occurrences of words with referents across the trials. Two groups of participants will be compared: monolingual English speaker and English-German bilinguals. Using this paradigm, the study can track learning over time as well as looking at individual trial by trial analyses. The researchers predict specifically that bilingual learners will have a specific advantage in learning 1:2 mappings, where one-word maps to two objects. The study will use Bayes Factors as the method of inference when analysing the data, allowing them to differentiate evidence for "no difference" from ambiguous evidence from which no conclusion can be drawn.
The Stage 1 manuscript was evaluated over four rounds of review. Based on detailed responses to the reviewers' and recommender's comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 1 criteria and awarded in-principle acceptance (IPA).
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/8n5gh
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that will be used to answer the research question yet exists and no part will be generated until after IPA. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals: References Simonetti, M. E., Lorenz, M. G., Koch, I., & Roembke, T. C. (2024). The Influence of Bilingualism on Statistical Word Learning: A Registered Report. In principle acceptance of Version 5 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/8n5gh
| The Influence of Bilingualism on Statistical Word Learning: A Registered Report | Simonetti, M. E., Lorenz, M. G., Koch, I., & Roembke, T. | <p>While statistical word learning has been the focus of many studies on monolinguals, it has<br>received little attention in bilinguals. The results of existing studies on statistical word learning<br>in bilinguals are inconsistent, with some res... | Social sciences | Elizabeth Wonnacott | 2023-06-28 15:37:58 | View | ||
27 Jun 2024
STAGE 1

Learning from comics versus non-comics material in education: Systematic review and meta-analysisMarianna Pagkratidou, Neil Cohn, Phivos Phylactou, Marietta Papadatou-Pastou, Gavin Duffy https://osf.io/preprints/metaarxiv/ceda3/Comics in EducationRecommended by Veli-Matti Karhulahti based on reviews by Adrien Fillon, Benjamin Brummernhenrich, Solip Park and Pavol Kačmár based on reviews by Adrien Fillon, Benjamin Brummernhenrich, Solip Park and Pavol Kačmár
Especially after the impactful experiments in modern comics (e.g. McCloud 1993), research interest in the medium increased with new practical developments (Kukkonen 2013). Some of these developments now manifest in educational settings where comics are used for various pedagogical purposes in diverse cultural contexts. To what degree comics are able to reach educational outcomes in comparison to other pedagogical tools remains largely unknown, however.
In the present registered report, Pagkratidou and colleagues (2024) respond to the research gap by investigating the effectiveness of educational comics materials. By means of systematic review and meta-analysis, the authors assess all empirical studies on educational comics to map out what their claimed benefits are, how the reported effectiveness differs between STEM and non-STEM groups, and what moderating effects complicate the phenomenon. With the help of large language models, all publication languages are included in analysis. The research plan was reviewed over three rounds by four reviewers with diverse sets of expertise ranging from education and meta-analytic methodology to comics culture and design. After comprehensive revisions by the authors, the recommender considered the plan to meet high Stage 1 criteria and provided in-principle acceptance. URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/vdr8c Level of bias control achieved: Level 3. At least some data/evidence that will be used to the answer the research question has been previously accessed by the authors (e.g. downloaded or otherwise received), but the authors certify that they have not yet observed ANY part of the data/evidence.
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals: References 1. Kukkonen, K. (2013). Studying comics and graphic novels. John Wiley & Sons.
2. McCloud, S. (1993). Understanding comics: The invisible art. Tundra.
3. Pagkratidou, M., Cohn, N., Phylactou, P., Papadatou-Pastou, M., & Duffy, G. (2024). Learning from comics versus non-comics material in education: Systematic review and meta-analysis. In principle acceptance of Version 4 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/vdr8c
| Learning from comics versus non-comics material in education: Systematic review and meta-analysis | Marianna Pagkratidou, Neil Cohn, Phivos Phylactou, Marietta Papadatou-Pastou, Gavin Duffy | <p>The past decades have seen a growing use of comics (i.e., sequential presentation of images and/or text) educational material. However, there are inconsistent reports regarding their effectiveness. In this study, we aim to systematically review... | Social sciences | Veli-Matti Karhulahti | 2023-10-16 22:55:09 | View | ||
26 Jun 2024
STAGE 1

Do Scarcity-Related Cues Affect the Sustained Attentional Performance of the Poor and the Rich Differently?Peter Szecsi, Miklos Bognar, Barnabas Szaszi https://osf.io/5sdbpHow does economic status moderate the effect of scarcity cues on attentional performance?Recommended by Matti Vuorre based on reviews by Ernst-Jan de Bruijn and Leon Hilbert based on reviews by Ernst-Jan de Bruijn and Leon Hilbert
This Stage 1 registered report by Szecsi et al. (2024) seeks to clarify whether individuals' economic conditions moderate how scarcity cues affect their attentional performance. This idea has been previously explored: Here, the authors aim to clarify understanding of the how scarcity cues affect cognition by studying a large and diverse Hungarian sample with improved experimental methods.
Specifically, while it has been previously reported that financially less well-off individuals' are differentially affected by finance-related stimuli (e.g. Shah et al., 2018), Szecsi et al. (2024) argue that prior studies have used small samples with insufficient consideration of potentially important demographic variables. Therefore, the generalizability of prior studies might be lacking.
Second, Szecsi et al. (2024) aim to conduct a more realistic experiment by asking participants to free-associate in response to financial scarcity-related cues, whereas prior studies have often focused on simply querying for rating responses, which might not sufficiently engage the related cognitive mechanisms that could be most affected.
In the proposed study, then, the authors will rigorously test whether financially less well-off individuals have lower attentional performance while experiencing scarcity-related cues than individuals who are financially better off, and that attentional performance does not differ while experiencing non-scarcity related cues. Ultimately, Szecsi et al. propose to shed light on theories of scarcity-related cognition that posit overall decrements in attentional performance irrespective of individuals' financial status.
The Stage 1 manuscript was initially reviewed by two experts in the area, who both recommended several improvements to the study. The authors then thoroughly revised their write-up and protocol, and the two reviewers were satisfied with the substance of these revisions. Based on these evaluations, the recommender judged that the Stage 1 criteria were met and awarded in-principle acceptance. There were remaining editorial clarifications and suggestions which the authors can incorporate in their eventual Stage 2 report.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/3zdyb
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that will be used to answer the research question yet exists and no part will be generated until after IPA. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals: References
1. Shah, A. K., Zhao, J., Mullainathan, S., & Shafir, E. (2018). Money in the mental lives of the poor. Social Cognition, 36, 4-19. https://doi.org/10.1521/soco.2018.36.1.4
2. Szecsi, P., Bognar, M., & Szaszi, B., (2024). Do Scarcity-Related Cues Affect the Sustained Attentional Performance of the Poor and the Rich Differently? In principle acceptance of Version 2 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/3zdyb
| Do Scarcity-Related Cues Affect the Sustained Attentional Performance of the Poor and the Rich Differently? | Peter Szecsi, Miklos Bognar, Barnabas Szaszi | <p>Cues related to financial scarcity are commonly present in the daily environment shaping people’s mental lives. However, the results are mixed on whether such scarcity-related cues disproportionately deteriorate the cognitive performance of poo... | Social sciences | Matti Vuorre | Leon Hilbert, Ernst-Jan de Bruijn | 2024-01-18 14:29:03 | View | |
25 Jun 2024
STAGE 1

Does ‘virtuality’ affect the role of prior expectations in perception and action? Comparing predictive grip and lifting forces in real and virtual environmentsDavid J. Harris, Tom Arthur, & Gavin Buckingham https://osf.io/q3ktsThe role of prior expectations for lifting objects in virtual realityRecommended by Robert McIntosh based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
As virtual reality environments become more common, it is important to understand our sensorimotor interactions with them. In real world settings, sensory information is supplemented by prior expectations from past experiences, aiding efficient action control. In VR, the relative role of expectations could decrease due to a lack of prior experience with the environment, or increase because sensory information is impoverished or ambiguous. Harris, Arthur and Buckingham (2024) propose to test these possibilities by comparing a real-world object lifting task and a VR version in which the same objects are lifted but visual feedback is substituted by a virtual view. The experiment uses the Size-Weight Illusion (SWI) and the Material Weight Illusion (MWI). In these paradigms, the visual appearance of the object induces expectations about weight that can affect the perception of weight during lifting, and the fingertip forces generated. The degree to which the visual appearance of objects induces differences in perceived weight, and in measured fingertip forces, will index the influence of prior expectations for these two paradigms. The analyses will test whether the influence of prior expectations is lower or higher in the VR set-up than in real-world lifting. The outcomes across tasks (SWI and MWI) and measures (perceived weight, fingertip forces) will broaden our understanding of the role of predictive sensorimotor control in novel virtual environments.
After three rounds of evaluation, with input from two external reviewers, the recommender judged that the Stage 1 manuscript met the criteria for in-principle acceptance (IPA).
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/36jhb
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that will be used to answer the research question yet exists and no part will be generated until after IPA. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References 1. Harris, D. J., Arthur, T., & Buckingham, G. (2024). Does ‘virtuality’ affect the role of prior expectations in perception and action? Comparing predictive grip and lifting forces in real and virtual environments. In principle acceptance of Version 4 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/36jhb
| Does ‘virtuality’ affect the role of prior expectations in perception and action? Comparing predictive grip and lifting forces in real and virtual environments | David J. Harris, Tom Arthur, & Gavin Buckingham | <p>Recent theories in cognitive science propose that prior expectations strongly influence how individuals perceive the world and control their actions. This influence is particularly relevant in novel sensory environments, such as virtual reality... | Life Sciences | Robert McIntosh | Ben van Buren | 2023-11-22 12:25:57 | View | |
Test-Retest Reliability of the STRAQ-1: A Registered ReportOlivier Dujols, Siegwart Lindenberg, Caspar J. van Lissa, Hans IJzerman https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/392g6We may not be measuring physical closeness in interpersonal relationships as reliably as we thinkRecommended by Moin Syed based on reviews by Maanasa Raghavan and Jacek Buczny based on reviews by Maanasa Raghavan and Jacek Buczny
Attachment and interpersonal relationships are a major subject of research and clinical work in psychology. There are, accordingly, a proliferation of measurement instruments to tap into these broad constructs. The emphasis in these measures tends to be on the emotional dimensions of the relationships—how people feel about their partners and the support that they receive. However, that is not all there is to relationship quality. Increasing attention has been paid to the physical and physiological aspects of relationships, but there are few psychometrically sound measures available to assess these dimensions.
In the current study, Dujols et al. (2024) assessed the psychometric properties of the Social Thermoregulation and Risk Avoidance Questionnaire (STRAQ-1), a measure of physical relationships that targets social thermoregulation, or how physical proximity is used to promote warmth and closeness. The project consists of a thorough assessment of the measure’s reliability over time—that is, the degree to which the measure assesses the construct similarly across administrations, in a sample of 183 French university students.
The authors assessed the longitudinal measurement invariance and test-restest reliability of the STRAQ-1. Longitudinal measurement invariance across two time points was only found for two of the four subscales. Similarly, test-retest reliability varied by subscale, ranging from poor to good. Taken together, the study suggests caution in using the STRAQ-1 scale as a reliable measure of physical relationships. The study highlights the need for continued assessment of the reliability of widely used measures, particularly reliability over time, and serves as a model for a rigorous analytic approach for doing so.
The Stage 2 manuscript was evaluated over two rounds of in-depth review, the first round consisting of comments from two reviewers and the second round consisting of a close read by the recommender. Based on detailed responses to the reviewers' comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 2 criteria and therefore awarded a positive recommendation.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/pmnk2
Level of bias control achieved: Level 3. At least some data/evidence that was used to the answer the research question was accessed by the authors prior to Stage 1 IPA (e.g. downloaded or otherwise received) but the authors certify that they had not observed ANY part of the data/evidence until after Stage 1 IPA. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Dujols, O., Klein, R. A., Lindenberg, S., Van Lissa, C. J., & IJzerman, H. (2024). Test-Retest Reliability of the STRAQ-1: A Registered Report [Stage 2]. Acceptance of Version 10 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/preprints/psyarxiv/392g6
| Test-Retest Reliability of the STRAQ-1: A Registered Report | Olivier Dujols, Siegwart Lindenberg, Caspar J. van Lissa, Hans IJzerman | <p>This Registered Report provides the first test of measurement invariance across time points and estimates of test-retest reliability for the Social Thermoregulation, Risk Avoidance Questionnaire (STRAQ-1, Vergara et al., 2019). The scale was de... | Social sciences | Moin Syed | 2024-01-11 16:01:41 | View | ||
Insufficient evidence of a positive association between chronic loneliness and anthropomorphism: Replication and extension Registered Report of Epley et al. (2008)Qinyu Xiao, Mahmoud Elsherif, Hoi Yan Chu, Ming Chun Tang, Ting Hin (Angus) Wong, Yiming Wu, Christina Pomareda, Gilad Feldman https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/2SB7XWeak-to-no evidence for a positive link between loneliness and anthropomorphismRecommended by Chris Chambers based on reviews by John Protzko based on reviews by John Protzko
Anthropomorphism is a widespread phenomenon in which people instil non-human entities or objects with human-like characteristics, such as motivations, intentions, and goals. Although common, the tendency to anthropomorphise varies between people, and a growing body of psychological research has examined the importance of various individual differences. One major theoretical account of anthropomorphism (Epley et al. 2007) suggests that sociality motivation – the drive to establish social relationships – is a key moderator of the phenomenon. In support of this account, some evidence suggests that people who experience greater loneliness (a proposed marker of sociality motivation) are more likely to anthropomorphise. In an influential series of studies, Epley et al. (2008) found that anthropomorphism and loneliness were positively correlated and that inducing participants experimentally to feel more lonely led to greater anthropomorphism. Later studies, however, produced more mixed results, particularly concerning the effectiveness of the experimental interventions.
In the current study, Elsherif et al. (2024) undertook a partial replication of Epley et al. (2008), focusing on the correlational relationship between anthropomorphism and loneliness, with extensions to examine free will beliefs, anthropomorphism for supernatural beings (in addition to objects/gadgets), and the extent to which participants judged objects/gadgets to be controllable. The results revealed no reliable evidence for a positive relationship between anthropomorphism and loneliness. Analyses of the extended questions revealed that the perceived controllability of gadgets was associated negatively with anthropomorphism and that free will belief was associated positively with belief in anthropomorphism of supernatural beings. Broadly, the current findings constitute a non-replication of Epley et al. (2008). The authors conclude by calling for more direct and conceptual replications to establish the link (if any) between sociality motivation and anthropomorphism.
The Stage 2 manuscript was evaluated over one round of in-depth review. Based on detailed responses to the reviewer's and recommender's comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 2 criteria and awarded a positive recommendation.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/by89c Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that was used to answer the research question was generated until after IPA.
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Epley, N., Waytz, A., & Cacioppo, J. T. (2007). On seeing human: A three-factor theory of anthropomorphism. Psychological Review, 114, 864–886. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295X.114.4.864
2. Epley, N., Akalis, S., Waytz, A., & Cacioppo, J. T. (2008). Creating social connection through inferential reproduction: Loneliness and perceived agency in gadgets, Gods, and greyhounds. Psychological Science, 19, 114–120. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9280.2008.02056.x
3. Elsherif, M., Pomareda, C., Xiao, Q., Chu, H. Y., Tang, M. C., Wong, T. H., Wu, Y. & Feldman, G. (2024). Insufficient evidence of a positive association between chronic loneliness and anthropomorphism: Replication and extension Registered Report of Epley et al. (2008) [Stage 2]. Acceptance of Version 6 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/x96kn
| Insufficient evidence of a positive association between chronic loneliness and anthropomorphism: Replication and extension Registered Report of Epley et al. (2008) | Qinyu Xiao, Mahmoud Elsherif, Hoi Yan Chu, Ming Chun Tang, Ting Hin (Angus) Wong, Yiming Wu, Christina Pomareda, Gilad Feldman | <p>Human beings have a fundamental need to connect with others. Epley, Akalis, et al. (2008) found that people higher in chronic loneliness had a stronger tendency to anthropomorphize non-human objects, presumably for fulfilling unmet needs for so... | Social sciences | Chris Chambers | 2024-03-27 16:17:16 | View | ||
21 Jun 2024
STAGE 1

Is it Worth the Hustle? A Multi-Country Replication of the Effort Moralization Effect and an Extension to Generational Differences in the Appreciation of EffortTassilo T. Tissot, Leopold H. O. Roth https://osf.io/5tkfrAre people who exert more effort in a task seen as more moral?Recommended by Adrien Fillon based on reviews by Jared Celniker, Ignazio Ziano and Michael Inzlicht based on reviews by Jared Celniker, Ignazio Ziano and Michael Inzlicht
This study seeks to understand cultural and age differences in the effort moralization effect, a phenomenon in which people who put more effort into a task are considered more moral, regardless of the quality or the morality associated with the task. This is shown in common phrases such as the “great resignation” or “quiet quitting”, which are mostly used against younger members of the population, in particular generation Z.
Tissot and Roth (2024) propose to conduct a replication of a study from Celniker et al. (2023) which found evidence for this effect, with new samples from Mexico and Germany to test potential cultural differences. They will also test the effect of age on the effort moralization effect. Therefore, the study will be a quantitative analysis.
The authors included an adequate power analysis, alternatives for non-supported hypotheses, and filtering to ensure a high quality of data collection. They already provided an R script and dummy data to ensure the quality of the analysis. The Stage 1 manuscript was evaluated over three rounds of in-depth review. Based on detailed responses to reviewers’ and the recommender’s comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 1 criteria and therefore awarded in-principle acceptance.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/tvgw2
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that will be used to answer the research question yet exists and no part will be generated until after IPA.
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References 1. Celniker, J. B., Gregory, A., Koo, H. J., Piff, P. K., Ditto, P. H., & Shariff, A. F. (2023). The moralization of effort. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 152, 60–79. https://doi.org/10.1037/xge0001259
2. Tissot, T. T. & Roth, L. H. O. (2024). Is it Worth the Hustle? A Multi-Country Replication of the Effort Moralization Effect and an Extension to Generational Differences in the Appreciation of Effort. In principle acceptance of Version 4 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/tvgw2
| Is it Worth the Hustle? A Multi-Country Replication of the Effort Moralization Effect and an Extension to Generational Differences in the Appreciation of Effort | Tassilo T. Tissot, Leopold H. O. Roth | <p>Inferring the character of individuals is an adaptive need for partner and mating decisions as well as to avoid harm. The effort moralization effect is the finding that people who exert more effort in a task are seen as more moral, even if high... | Social sciences | Adrien Fillon | 2024-01-18 14:58:04 | View | ||
19 Jun 2024
STAGE 1

Culture-Driven Neural Plasticity and Imprints of Body-Movement Pace on Musical Rhythm ProcessingSégolène M. R. Guérin, Emmanuel Coulon, Tomas Lenc, Rainer Polak, Peter E. Keller, Sylvie Nozaradan https://zenodo.org/doi/10.5281/zenodo.10221480The interplay of music, movement, and culture on rhythm processingRecommended by Juan David Leongómez based on reviews by Anne Keitel and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Anne Keitel and 1 anonymous reviewer
The interplay of music, movement, and cultural experience shapes rhythm perception. From bouncing babies and children at play, to tapping, clapping, and dancing, music often triggers synchronous body movements that can influence how we process rhythm. And, at the same time, long-term exposure to specific musical traditions shapes how we perceive and interpret rhythms.
However, direct behavioural and neuroscientific evidence on how these processes occur remains scarce. In this programmatic submission, comprising two complementary Stage 2 reports, Guérin et al. (2024) will investigate how body movements shape the processing of auditory information, and how previous short-term motor practice and long-term cultural experience interact to shape neural and behavioural responses to rhythmic stimuli. The authors will record in separate sessions both electroencephalography (EEG) and hand clapping, in response to rhythms from West/Central Africa. These recordings will be conducted before and after a session in which participants will clap/step to either a three or a four-beat metre that is expected to influence how they interpret a rhythm.
The first Stage 2 report, which will be conducted on African-enculturated participants, aims to demonstrate how body-movement pace flexibly imprints on human sensory processing. The authors build on various theoretical models that emphasise the role of motor production in metre perception, and predict that both neural and behavioural entrainment will improve following movement, matching the rhythmic pattern set by the previous body movements.
The second Stage 2 report aims to uncover how short-term motor practice and long-term cultural experience interact to shape responses to rhythmic stimuli, by integrating short-term motor practice and long-term cultural experience. For this, the authors will test separate groups of participants from distinct cultural backgrounds (African vs. Western-enculturated), which are predicted to show neural and behavioural differences in their preferred metric mapping before body movement, and expect that neural and behavioural entrainment will improve after movement, especially for the metre set by prior movements, and more significantly for the metre common in the participant's culture.
Together, the findings from the planned Stage 2 reports are expected to clarify how long-term cultural background and short-term motor practice imprint onto rhythm processing in humans. This research will enhance our understanding of how cultural experience, body movement, and neural plasticity interact in music processing.
The Stage 1 manuscript was evaluated over three rounds of in-depth review. Based on detailed responses to the reviewers' and recommender's comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 1 criteria and awarded in-principle acceptance (IPA).
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/skuyc
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. Data collection commenced during the later part of Stage 1 peer review; however, since no changes to the design were made after this point, the risk of bias due to prior data observation remains zero and the manuscript therefore qualifies for Level 6. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals: References
Guérin, S. M. R., Coulon, E., Lenc, T., Polak, R., Keller, P. E., & Nozaradan, S. (2024). Culture-Driven Neural Plasticity and Imprints of Body-Movement Pace on Musical Rhythm Processing. In principle acceptance of Version 2.1 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/skuyc
| Culture-Driven Neural Plasticity and Imprints of Body-Movement Pace on Musical Rhythm Processing | Ségolène M. R. Guérin, Emmanuel Coulon, Tomas Lenc, Rainer Polak, Peter E. Keller, Sylvie Nozaradan | <p>The proposed programmatic registered report aims at capturing direct neuroscientific evidence for the rhythmic, movement-related shaping of auditory information with a cross-cultural perspective. Specifically, West/Central African- and Western-... |  | Life Sciences | Juan David Leongómez | Anonymous | 2023-11-30 11:36:06 | View |
FOLLOW US
MANAGING BOARD
Chris Chambers
Zoltan Dienes
Corina Logan
Benoit Pujol
Maanasa Raghavan
Emily S Sena
Yuki Yamada










