Announcements
=============================================================================
IMPORTANT ANNOUNCEMENT: To accommodate reviewer and recommender holiday schedules, we will be closed to ALL submissions from 1st Jul - 1st Sep. During this time, reviewers can submit reviews and recommenders can issue decisions, but no new or revised submissions can be made by authors.
The one exception to this rule is that authors using the scheduled track who submit their initial Stage 1 snapshot prior to 1st Jul can choose a date within the shutdown period to submit their full Stage 1 manuscript.
We recommend that authors submit at least 1-2 weeks prior to commencement of the shutdown period to enable time to make any required revisions prior to in-depth review.
=============================================================================
We are recruiting recommenders (editors) from all research fields!
Your feedback matters! If you have authored or reviewed a Registered Report at Peer Community in Registered Reports, then please take 5 minutes to leave anonymous feedback about your experience, and view community ratings.
Latest recommendations
| Id | Title * | Authors * | Abstract * | Picture | Thematic fields * | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
06 Mar 2025
STAGE 1

The role of extra-striate areas in conscious motor behavior: a registered report with Fast-Optical ImagingElisabetta Colombari, Giorgia Parisi, Sonia Mele, Chiara Mazzi, Silvia Savazzi https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2024.04.23.590726v5.full.pdfNeural underpinning of conscious perception of visual stimuli disentangled from motor confoundsRecommended by Anoushiravan Zahedi based on reviews by 3 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 3 anonymous reviewers
The debate about consciousness and its neural underpinnings is a hot topic in cognitive neuroscience that has driven innovative original research and theoretical frameworks (Dehaene et al., 2006; Lamme, 2006). Consciousness itself can be defined and studied from different perspectives, such as neuropsychology (Laureys et al., 2004; Monti, 2012), applied philosophy (Blanke & Metzinger, 2009), and experimental cognitive neuroscience (Dehaene & Changeux, 2011). However, after several decades of research via different methods and from different perspectives, basic questions regarding consciousness and its neural underpinnings are still debated (Chalmers, 2010). One of the reasons for this ongoing debate is that consciousness cannot be easily disentangled from confounds, such as involvement of other cognitive processes like memory, language, and so forth (Dehaene & Changeux, 2011).
In the current study, Colombari et al. (2025) focus on disentangling neural markers of conscious visual perception from motoric responses. To this end, the study uses a cutting-edge neuroimaging technique, Event-Related Optical Signal (EROS), to measure the neural responses during a Go/No-Go detection task, which is especially designed to gauge visual perception regardless of response production. The study, therefore, is instrumental in addressing the neural foundation of conscious visual perception and is well situated to advance our understanding of consciousness and its neural underpinnings.
The Stage 1 submission was evaluated by three expert reviewers. After several rounds of revision, the recommender determined that the manuscript met the Stage 1 criteria and awarded in-principle acceptance (IPA).
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/8ya2t
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that will be used to answer the research question yet exists and no part will be generated until after IPA. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Blanke, O., & Metzinger, T. (2009). Full-body illusions and minimal phenomenal selfhood. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 13, 7-13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2008.10.003
2. Chalmers, D. J. (2010). Facing Up to the Problem of Consciousness. In The Character of Consciousness (pp. 3-34). Oxford University Press. https://doi.org/10.1093/acprof:oso/9780195311105.003.0001 3. Colombari, E., Parisi, G., Mele, S., Mazzi, C., & Savazzi, S. (2025). The role of extra-striate areas in conscious motor behavior: a registered report with Fast-Optical Imaging. In principle acceptance of Version 5 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/8ya2t
4. Dehaene, S., & Changeux, J. P. (2011). Experimental and theoretical approaches to conscious processing. Neuron, 70, 200-227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2011.03.018
5. Dehaene, S., Changeux, J. P., Naccache, L., Sackur, J., & Sergent, C. (2006). Conscious, preconscious, and subliminal processing: a testable taxonomy. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 10, 204-211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2006.03.007
6. Lamme, V. A. (2006). Towards a true neural stance on consciousness. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 10, 494-501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2006.09.001
7. Laureys, S., Owen, A. M., & Schiff, N. D. (2004). Brain function in coma, vegetative state, and related disorders. The Lancet Neurology, 3, 537-546. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(04)00852-x
8. Monti, M. M. (2012). Cognition in the vegetative state. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 8, 431-454. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-032511-143050
| The role of extra-striate areas in conscious motor behavior: a registered report with Fast-Optical Imaging | Elisabetta Colombari, Giorgia Parisi, Sonia Mele, Chiara Mazzi, Silvia Savazzi | <p>Disclosing the brain areas responsible for the emergence of visual awareness and their timing of activation represents one of the major challenges in consciousness research. In particular, isolating the neural processes strictly related to cons... | Life Sciences, Social sciences | Anoushiravan Zahedi | 2024-04-26 22:44:25 | View | ||
05 Mar 2025
STAGE 1
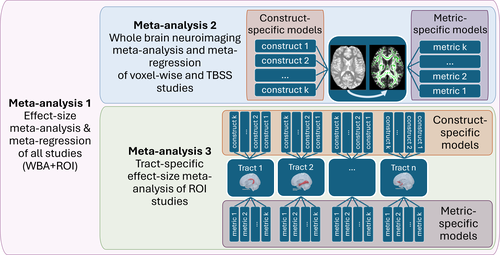
Social cognition as a matter of structural brain connections? A systematic review and diffusion weighted imaging meta-analysisRita Hansl, Lara Z. Maliske, Sofie L. Valk, Philipp Kanske https://osf.io/6n3jySocial cognition and white matter integrity: Systematic review and diffusion weighted imaging meta-analysisRecommended by Marietta Papadatou-Pastou based on reviews by Sebastian Ocklenburg and Katie Lavigne based on reviews by Sebastian Ocklenburg and Katie Lavigne
Social cognition involves complex processes including empathy, mentalizing, and compassion, which rely on structural connectivity and specifically white matter (WM) integrity. Prior research suggests that deficits in social cognition are linked to deficient structural connectivity, indicating that the latter might be an essential foundation for social cognitive abilities. In the current study, Hansl et al. (2025) explore the relationship between social cognition and white matter (WM) integrity in the brain across different populations, by means of a systematic review and meta-analyses. Using diffusion-weighted imaging data, the authors aim to identify specific WM tracts most associated with social cognition. Meta-analyses of region-of-interest (ROI)-based studies will provide further insights, while meta-regression and subgroup analyses will examine differences across social cognitive constructs, imaging metrics, clinical conditions, and age groups. The findings could clarify global and specific WM contributions to social cognition, guiding future research on brain structure-function relationships in social cognition across various populations.
The Stage 1 submission was evaluated by two expert reviewers. After two rounds of revision, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 1 criteria and awarded in-principle acceptance (IPA).
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/6n3jy (under temporary private embargo)
Level of bias control achieved: Level 2. At least some data/evidence that will be used to answer the research question has been accessed and partially observed by the authors, but the authors certify that they have not yet observed the key variables within the data that will be used to answer the research question and they have taken additional steps to maximise bias control and rigour.
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Hansl, R., Maliske, L. Z., Valk, S. L., & Kanske, P. (2025). Social cognition as a matter of structural brain connections? A systematic review and diffusion weighted imaging meta-analysis. In principle acceptance of Version 3 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/6n3jy
| Social cognition as a matter of structural brain connections? A systematic review and diffusion weighted imaging meta-analysis | Rita Hansl, Lara Z. Maliske, Sofie L. Valk, Philipp Kanske | <p>Social cognition encompasses several cognitive and affective processes essential for successful social interaction and communication (e.g. empathy, mentalizing, compassion). The interplay of the various processes necessary for understanding the... |  | Life Sciences | Marietta Papadatou-Pastou | 2024-09-20 13:51:12 | View | |
03 Mar 2025
STAGE 1

Shape of SNARC: How task-dependent are Spatial-Numerical Associations? A highly powered online experimentLilly Roth, Krzysztof Cipora, Annika T. Overlander, Hans-Christoph Nuerk, Ulf-Dietrich Reips https://osf.io/gsajbShedding light on task influence in the SNARC effectRecommended by Mario Dalmaso based on reviews by Michele Vicovaro, Christian Seegelke and Peter Wühr based on reviews by Michele Vicovaro, Christian Seegelke and Peter Wühr
The Spatial-Numerical Association of Response Codes (SNARC) effect (Dehaene et al., 1993) is a key phenomenon in numerical cognition. It describes the tendency for individuals to respond faster to smaller numbers with a left-side key and to larger numbers with a right-side key, suggesting a mental mapping of numerical magnitudes onto space. While this effect has been widely replicated, its precise nature remains debated, particularly regarding its task dependency.
In this Stage 1 Registered Report, Roth et al. (2025) present a highly powered study that systematically investigates whether the SNARC effect differs in two widely used numerical cognition tasks: magnitude classification (MC) and parity judgment (PJ). In the MC task, participants determine whether a presented number is smaller or larger than a reference value (typically 5). This task explicitly requires magnitude processing, making numerical magnitude directly relevant to the response. In contrast, the PJ task requires participants to judge whether a number is odd or even, a decision that does not explicitly involve numerical magnitude.
The authors address a fundamental theoretical question in numerical cognition: while the SNARC effect in PJ is often considered continuous, does it follow a categorical pattern in MC? To investigate this, the study directly compares continuous and categorical representations of the SNARC effect across these two tasks, using Bayesian statistical approaches to determine the best-fitting model. By systematically analysing the SNARC effect in these widely used paradigms, this work aims to refine our understanding of how numerical magnitudes are mapped onto space and whether this mapping depends on task demands. The findings of this study will provide crucial insights into the cognitive mechanisms underlying numerical-spatial associations, highlighting the extent to which task structure shapes the emergence of the SNARC effect.
Three expert reviewers provided valuable feedback across multiple rounds of review. Based on detailed responses to the reviewers’ and recommender’s comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 1 criteria and therefore awarded in-principle acceptance.
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that will be used to answer the research question yet exists and no part will be generated until after IPA.
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Dehaene, S., Bossini, S., & Giraux, P. (1993). The mental representation of parity and number magnitude. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 122(3), 371–396. https://doi.org/10.1037/0096-3445.122.3.371
2. Roth, L., Cipora, K., Overlander, A. T., Nuerk, H.-C., & Reips, U.-D. (2025). Shape of SNARC: How task-dependent are Spatial-Numerical Associations? A highly powered online experiment. In principle acceptance of Version 3 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/968ad
| Shape of SNARC: How task-dependent are Spatial-Numerical Associations? A highly powered online experiment | Lilly Roth, Krzysztof Cipora, Annika T. Overlander, Hans-Christoph Nuerk, Ulf-Dietrich Reips | <p>Spatial-Numerical Associations (SNAs) are fundamental to numerical cognition. They are essential for number representation and mathematics learning. However, SNAs are highly dependent on the experimental situation and task. Understanding this d... | Life Sciences | Mario Dalmaso | Peter Wühr | 2024-05-27 13:14:25 | View | |
Is it Worth the Hustle? A Multi-Country Replication of the Effort Moralization Effect and an Extension to Generational Differences in the Appreciation of EffortTassilo T. Tissot, Leopold H. O. Roth https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/ck4st_v6Are people who exert more effort in a task seen as more moral?Recommended by Adrien Fillon based on reviews by Jared Celniker, Ignazio Ziano and Michael Inzlicht based on reviews by Jared Celniker, Ignazio Ziano and Michael Inzlicht
This study seeks to understand cultural and age differences in the effort moralization effect, a phenomenon in which people who put more effort into a task are considered more moral, regardless of the quality or the morality associated with the task. This is shown in common phrases such as the “great resignation” or “quiet quitting”, which are mostly used against younger members of the population, in particular generation Z.
Tissot and Roth (2025) conducted a replication of a study from Celniker et al. (2023) which found evidence for this effect, with new samples from Mexico and Germany, to test potential cultural and age differences.
The results indicated a generalization of the effort moralization effect in Germany and Mexico, with important heterogeneity in the effect found, and effects sizes that were smaller than in the original study conducted in the USA. However, no effect was found regarding age, as younger individuals judged effort as being important in the same way as older individuals. It is possible, therefore, that the effort moralization effect is a consistent bias that persists regardless of age.
The Stage 2 manuscript was evaluated over three rounds of in-depth review. Based on detailed responses to the reviewers’ and recommender’s comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 2 criteria and awarded a positive recommendation.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/tvgw2
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that was used to answer the research question was generated until after IPA.
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References 1. Celniker, J. B., Gregory, A., Koo, H. J., Piff, P. K., Ditto, P. H., & Shariff, A. F. (2023). The moralization of effort. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 152, 60–79. https://doi.org/10.1037/xge0001259
2. Tissot, T. T. & Roth, L. H. O. (2025). Is it Worth the Hustle? A Multi-Country Replication of the Effort Moralization Effect and an Extension to Generational Differences in the Appreciation of Effort [Stage 2]. Acceptance of Version 6 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/ck4st_v6
| Is it Worth the Hustle? A Multi-Country Replication of the Effort Moralization Effect and an Extension to Generational Differences in the Appreciation of Effort | Tassilo T. Tissot, Leopold H. O. Roth | <p>Inferring moral character of individuals is an adaptive need for social decision-making. The effort moralization effect describes the finding that people who exert more effort in a task are seen as more moral, even if higher effort does not enh... | Social sciences | Adrien Fillon | 2024-11-15 10:14:56 | View | ||
24 Feb 2025
STAGE 1

Gold in, gold out. Quality appraisal and risk of bias tools to assess non-intervention studies for systematic reviews in the behavioural sciences: A scoping reviewLucija Batinović, Jade S. Pickering, Olmo R. van den Akker, Dorothy Bishop, Mahmoud Elsherif, Thomas Rhys Evans, Melissa Gibbs, Tamara Kalandadze, Janneke Staaks, Marta Topor https://osf.io/7p8bmScoping review of quality appraisal and risk of bias tools and their relevance for behavioral sciencesRecommended by Antica Culina based on reviews by Alejandro Sandoval-Lentisco based on reviews by Alejandro Sandoval-Lentisco
Systematic reviews and meta-analyses are becoming more popular across sciences, often influencing future research, policies, interventions, and similar. The conclusions of evidence synthesis will depend on the quality of the primary studies (i.e. evidence) included. Thus, the quality and risk of bias in these primary studies must be essential components of evidence synthesis. However, in many scientific fields, including behavioural sciences, this is rarely so.
In this Stage 1 manuscript, Batinović et al. (2025) propose to conduct a systematic map of the existing tools to assess methodological quality of risk of bias tools across scientific fields, and map their applicability for primary studies within the broad field of behavioral sciences. The review will provide a comprehensive overview of how existing tools can be applied to the behavioral sciences, and identify gaps for future development of relevant tools in the field. The protocol and its methods were thoroughly developed, and are suitable to reach the research aims.
The Stage 1 submission was evaluated by two expert reviewers. After two rounds of revision, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 1 criteria, and the manuscript was awarded in-principle acceptance (IPA).
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/4gy5b
Level of bias control achieved: Level 4. At least some of the data/evidence that will be used to answer the research question already exists AND is accessible in principle to the authors (e.g. residing in a public database or with a colleague) BUT the authors certify that they have not yet accessed any part of that data/evidence. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Batinović, L., Pickering, J. S., van den Akker, O. R., Bishop, D., Elsherif, M., Evans, T. R., Gibbs, M., Kalandadze, T., Staaks, J., & Topor, M., Gold in, gold out. Quality appraisal and risk of bias tools to assess non-intervention studies for systematic reviews in the behavioural sciences: A scoping review. In principle acceptance of Version 3 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/4gy5b | Gold in, gold out. Quality appraisal and risk of bias tools to assess non-intervention studies for systematic reviews in the behavioural sciences: A scoping review | Lucija Batinović, Jade S. Pickering, Olmo R. van den Akker, Dorothy Bishop, Mahmoud Elsherif, Thomas Rhys Evans, Melissa Gibbs, Tamara Kalandadze, Janneke Staaks, Marta Topor | <p>Systematic reviews depend critically on the methodological quality and bias levels of the studies they synthesise to provide the highest standard of evidence available for informing future research, practice, and policy. Despite the development... | Social sciences | Antica Culina | 2024-06-30 20:24:39 | View | ||
Does learning more about others impact liking them?: Replication and extension Registered Report of Norton et al. (2007)’s Lure of AmbiguityZöe Horsham, Ashleigh Haydock-Symonds, Hirotaka Imada, Hiu Ching Tai, Wing Lam Lau, Tsz Lui Shum, Yuqing Zeng, Hiu Tang Chow, Gilad Feldman https://osf.io/ygkftRevisiting ‘less is more’: A failure to replicate the association between increased knowing and decreased likingRecommended by Yuki Yamada based on reviews by Philipp Schoenegger and Zoltan Kekecs based on reviews by Philipp Schoenegger and Zoltan Kekecs
Does knowing more about others necessarily lead to greater liking, or might it breed contempt, as suggested by Norton et al. (2007)? In the current study, Horsham et al. (2025) tried to replicate and extend that original question. Collecting data from a large sample of U.S. undergraduates and employing carefully revised designs reviewed at Stage 1, they replicated Norton et al.’s initial studies (1a, 1b, and 2) while also adding new measures. Their primary aim was to see if the “less is more” effect, where increased familiarity decreases liking, would hold under rigorous modern standards, including pre-registration and several open science practices.
Results indicated that people indeed believe they will like someone more if they know more about that person, replicating Norton et al.’s initial finding from Studies 1a and 1b. However, the association between greater knowledge and reduced liking, the core of the “less is more” claim, was not consistently observed. Instead, the data showed little evidence that accumulating information inevitably decreases liking. Moreover, an added examination of curiosity as a potential mediator revealed that although curiosity and liking are positively related, curiosity itself was not strongly contingent on the amount of knowledge participants had. These findings help clarify why previous literature has sometimes presented mixed outcomes, and they underline the distinction between what people predict will happen and what actually does happen in forming impressions of others.
Peer review involved thorough evaluations by experts. Following multiple revisions through Stages 1 and 2, the manuscript has been deemed a carefully executed Registered Report, providing transparent methods, open data, and full reproducibility. It adds nuance to discussions around how knowledge, familiarity, and curiosity jointly shape our interpersonal attitudes. On this basis, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 2 criteria and awarded a positive recommendation.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/7mc4y
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that was used to answer the research question was generated until after IPA. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Norton, M. I., Frost, J. H., & Ariely, D. (2007). Less is more: The lure of ambiguity, or why familiarity breeds contempt. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 92, 97-105. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.92.1.97
2. Horsham, Z., Haydock-Symonds, A., Imada, H., Tai, H. C., Lau, W. L., Shum, T. L., Zeng, Y., Chow, K., & Feldman, G. (2025). Does learning more about others impact liking them?: Replication and extension Registered Report of Norton et al. (2007)’s Lure of Ambiguity [Stage 2]. Acceptance of Version 6 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/ygkft
| Does learning more about others impact liking them?: Replication and extension Registered Report of Norton et al. (2007)’s Lure of Ambiguity | Zöe Horsham, Ashleigh Haydock-Symonds, Hirotaka Imada, Hiu Ching Tai, Wing Lam Lau, Tsz Lui Shum, Yuqing Zeng, Hiu Tang Chow, Gilad Feldman | <p>Norton et al. (2007) demonstrated a counterintuitive phenomenon that knowing other people better and/or having more information about them is associated with decreased liking. They summarized it as - ambiguity leads to liking, whereas familiari... | Social sciences | Yuki Yamada | Zoltan Kekecs, Philipp Schoenegger | 2024-11-22 04:27:45 | View | |
The effect of stimulus saliency on the modulation of ongoing neural oscillations related to thermonociception: a Registered ReportChiara Leu, Sébastien Forest, Valéry Legrain, Giulia Liberati https://osf.io/98edqAre there oscillatory markers of pain intensity?Recommended by Zoltan Dienes based on reviews by Markus Ploner and Bjoern Horing based on reviews by Markus Ploner and Bjoern Horing
Rhythmic changes in pain can lead to corresponding modulations of EEG amplitudes in theta, alpha, and beta bands. But the question remains open as to whether these modulations are actually tracking pain, or maybe rather saliency or stimulus intensity. The question is of some importance because a marker of pain per se could be useful for tracking felt pain without a verbal response, and could be useful in investigating interventions for treating pain (such as suggestion). Here, Leu et al. (2025) addressed the question of whether modulations reflect saliency or else the intensity of pain, by using an oddball paradigm in which most trials are a pain stimulus of a certain intensity, and oddball trials will sometimes occur, at either a higher intensity or a lower intensity than the baseline ones. If the modulations reflected salience, the modulation at the frequency of the oddball would be similar for high and low intensity oddballs. However, if the modulations reflected pain intensity, the modulations for the low rather than high oddball condition would be lower.
In fact, the baseline and oddball stimulations were found to be perceived significantly differently only in the high oddball condition; and consistantly, the oddballl stimulus significantly modulated ongoing oscillations in only the high oddball condition. Thus, whether oscillations are modulated by pain intensity or salience could not be picked apart in this study. The study does however raise an important isssue, indicate how it could be addressed, and provide data relevant for clearly resolving the issue in the future.
The Stage 2 manuscript was evaluated over two rounds of in-depth peer review. Based on detailed responses to the reviewers' comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 2 criteria for acceptance.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/qbrf2
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that was used to answer the research question was generated until after IPA. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Leu, C., Forest, S., Legrain, V., & Liberati, G. (2025). The effect of stimulus saliency on the modulation of pain-related ongoing neural oscillations: a Registered Report [Stage 2]. Acceptance of Version 3 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/98edq | The effect of stimulus saliency on the modulation of ongoing neural oscillations related to thermonociception: a Registered Report | Chiara Leu, Sébastien Forest, Valéry Legrain, Giulia Liberati | <p>Ongoing oscillations have been shown to be modulated in different frequency bands following phasic, tonic as well as periodic thermonociceptive stimulation. Yet, it remains unclear whether these modulations are related to pain perception, salie... | Life Sciences, Medical Sciences | Zoltan Dienes | 2024-11-11 14:11:31 | View | ||
Neophobia across social contexts in juvenile Herring gullsReinoud Allaert, Sophia Knoch, Simon Braem, Dries Debeer, An Martel, Wendt Müller, Eric Stienen, Luc Lens, Frederick Verbruggen https://osf.io/b58haHerring gulls exhibit reduced neophobia when tested in groupsRecommended by Ljerka Ostojic based on reviews by Claudia Mettke-Hofmann and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Claudia Mettke-Hofmann and 1 anonymous reviewer
How well animals may be able to cope with changes of habitat, specifically with rapid changes and thus novelty they encounter in an environment densely populated by humans, may be influenced by how they respond to novelty in general (Batisteli et al., 2022; Biondi et al., 2024; Castano et al., 2024; Heales et al., 2024). In considering this, it may be important to account for any difference in behavioural responses that animals exhibit when encountering a novel situation alone versus when they are doing so as part of a group.
Here, Allaert et al. (2025) tested how neophobia – the fear of unfamiliar objects – is affected by the social context in gulls, birds that are increasingly forced to live in urban environments due to the loss of natural coastlines. In this study, in which they reared herring gulls from egg and tested them taking into account that nestmates are not tested within the same groups, the authors found that the birds were faster to eat and spent more time in the zone of interest when they were tested in a group than when they were tested individually, specifically when a novel object was placed next to the food compared to when that object was a familiar one. The birds were also faster to enter the testing area when tested in a group, but this was not specific to the novel object condition. In addition to these changes in the average responses, the authors also report reduced variance when tested in a group in two of their three measures, namely in the latency to enter the testing area and time spent in the zone of interest.
The authors interpret their findings as being mostly in line with the ‘risk-dilution’ hypothesis, which is often considered in terms of predation risk (Krause & Buxton, 2002). They discuss possible reasons why other studies, with different species and different methodological setups, found support for alternative explanations.
The Stage 2 report was evaluated by the same two reviewers who had also reviewed the Stage 1 manuscript. In the revision, the authors focused on adding sex as a factor in their statistical models, which was the planned procedure for the statistical analyses in the Stage 1 report, and adding information regarding the problems encountered during testing and how these were handled. This specifically refers to the planned sample size (which the authors planned in the Stage 1 report taking into account both mortality and the fact that some birds would be not herring gulls but lesser black-backed gulls, which can only be established after hatching). However, there was higher than expected mortality, leading to a larger-than-planned overall reduction in sample size. During the study, the authors had contacted the recommender and discussed this issue, and the recommender advised on continuing the study and approved of the planned changes in the Stage 2 report. During the revision process, the authors added more information and also conducted an exploratory analysis, which included all birds, i.e. herring gulls and lesser black-backed gulls. This was suggested by a reviewer and the authors present this exploratory analysis in full in the supplemental material, while the main inferences are presented in the main text. In addition, during the Stage 2 review it became apparent that some minor details regarding the procedure would be useful to be included in the Stage 2 report, which the authors included in the Stage 2 revision. This did not alter the procedure as described in the Stage 1 report, but merely added more clarity to the text.
Based on detailed engagement with these points and the reviewers' comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 2 criteria and awarded a positive recommendation.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/u4b7q
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that was used to answer the research question was generated until after IPA. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Allaert, R., Knoch, S., Braem, S., Debeer, D., Martel, A., Müller, W., Stienen, E., Lens, L., & Verbruggen, F. (2025). Neophobia across social contexts in juvenile Herring gulls [Stage 2]. Acceptance of Version 3 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/b58ha
2. Batisteli, A. F., Pizo, M. A., & Sarmento, H. (2022). Female neophobia predicts the use of buildings as nesting sites in a Neotropical songbird. Animal Behaviour, 183, 151-157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anbehav.2021.11.008
3. Biondi, L. M., Medina, A., Bonetti, E. A., Paterlini, C. A., & Bó, M. S. (2024). Cognitive flexibility in a generalist raptor: a comparative analysis along an urbanization gradient. Behavioral Ecology, 35, arae025. https://doi.org/10.1093/beheco/arae025
4. Castano, M. V., Zumpano, F., Biondi, L. M., & García, G. O. (2024). Does urbanization affect behavioral responses to novel objects in marine birds? The Olrog’s Gull as a case of study. Urban Ecosystems, 27, 427-437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11252-023-01465-2
5. Heales, H. E., Flood, N. J., Oud, M. D., Otter, K. A., & Reudink, M. W. (2024). Exploring differences in neophobia and anti-predator behaviour between urban and rural mountain chickadees. Journal of Urban Ecology, 10, juae01. https://doi.org/10.1093/jue/juae014
6. Krause, J. & Ruxton, G. (2002). Living in Groups. Oxford University Press, USA.
| Neophobia across social contexts in juvenile Herring gulls | Reinoud Allaert, Sophia Knoch, Simon Braem, Dries Debeer, An Martel, Wendt Müller, Eric Stienen, Luc Lens, Frederick Verbruggen | <p>Neophobia, the fear or avoidance of the unfamiliar, can have significant fitness consequences. It is typically assessed by exposing individuals to unfamiliar objects when they are alone, but in social species the presence of conspecifics can in... | Life Sciences | Ljerka Ostojic | 2024-11-26 13:25:23 | View | ||
Do Ecological Valid Stop Signals Aid Detour Performance? A Comparison of Four Bird SpeciesAnneleen Dewulf, Clara Garcia-Co, Wendt Müller, Joah R. Madden, An Martel, Luc Lens, Frederick Verbruggen https://osf.io/j2k9hWhat is the role of sensory perception in cognitive task performance? An improved replication of detour performance in four different bird speciesRecommended by Dieter Lukas based on reviews by Christian Nawroth and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Christian Nawroth and 1 anonymous reviewer
The detour task, where an individual has to go around a see-through barrier in order to reach a goal, is one of the oldest paradigms used in animal cognition research (Kabadayi et al. 2018). While these previous tests have documented variation in the ability of animals to inhibit going straight for the visible reward, the cognitive underpinnings of this behaviour are as yet not fully understood. In the current study, Dewulf et al. (2025) assessed one of the specific cognitive processes that might be involved in this behaviour, the ability to identify the transparent object as a barrier. Through experimental procedures relying on large samples of individuals from four bird species, they compared the role of signal detection in inhibitory response performance in a detour task. The authors found that, unlike suggested in previous work with these four species (Regolin et al. 1994, Zucca et al. 2005), changing the markings on the barriers to potentially better match those experienced by individuals in their natural environments did not improve their performance. Nevertheless, the detailed further explorations suggest that in order to understand variation in how quickly individuals and species solve the detour task, it is important to consider that different cognitive processes are involved. Their work therefore provides a basis to better understand and further investigate why species might differ in their performance in the detour task.
The Stage 2 manuscript was evaluated over two rounds of in-depth review, the first round consisting of detailed comments from two reviewers and the second round consisting of a close read by the recommender. Based on detailed responses to the reviewers' comments, the recommender judged that the manuscript met the Stage 2 criteria and awarded a positive recommendation.
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that was used to answer the research question was generated until after IPA.
URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/qvxgh
List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Dewulf, A., Garcia-Co, C., Müller, W., Madden, J.R., Martel, A., Lens, L. & Verbruggen, F. (2025). Do Ecological Valid Stop Signals Aid Detour Performance? A Comparison of Four Bird Species [Stage 2]. Acceptance of Version 3 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://osf.io/j2k9h
2. Kabadayi, C., Bobrowicz, K., & Osvath, M. (2018). The detour paradigm in animal cognition. Animal Cognition, 21, 21-35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10071-017-1152-0
3. Regolin, L., Vallortigara, G., & Zanforlin, M. (1995). Object and spatial representations in detour problems by chicks. Animal Behaviour, 49, 195-199. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-3472(95)80167-7
4. Zucca, P., Antonelli, F., & Vallortigara, G. (2005). Detour behaviour in three species of birds: quails (Coturnix sp.), herring gulls (Larus cachinnans) and canaries (Serinus canaria). Animal Cognition, 8, 122-128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10071-004-0243-x
| Do Ecological Valid Stop Signals Aid Detour Performance? A Comparison of Four Bird Species | Anneleen Dewulf, Clara Garcia-Co, Wendt Müller, Joah R. Madden, An Martel, Luc Lens, Frederick Verbruggen | <p>Response inhibition, or the stopping of actions, is considered a key component of flexible and adaptive behaviour. Across fields, response inhibition is often treated as a unitary cognitive mechanism. However, we propose that response inhibitio... | Life Sciences, Social sciences | Dieter Lukas | 2024-10-22 14:00:30 | View | ||
Action interpretation determines the effects of go/no-go and approach/avoidance actions on food choiceZhang Chen, Pieter Van Dessel, Jordi Serverius, Daxun Zhu, Bernd Figner https://osf.io/preprints/psyarxiv/6xhw4_v2Does interpretation of actions as either avoid or inhibit influence choice behaviour for candy?Recommended by Andrew Jones based on reviews by Alexander MacLellan and Katrijn HoubenExperimental research demonstrates that executing or inhibiting motor responses (or approaching / avoiding) towards a stimulus can alter the valuation of the stimulus (Yang et al., 2022). There are competing theories as to the proposed mechanisms of value change, such as increased response conflict or prediction errors (Houben & Aulbach, 2023). However, research has mostly examined response execution/inhibition and approach/avoidance in isolation and the few studies that have examined these together have focused on stimulus evaluation as an outcome.
In the current study Chen et al. (2025) set out to examine how action interpretations (e.g. go vs approach) can impact individuals food-choices. This is important for cognitive bias modification approaches which aim to manipulate these actions to promote behaviour change (Iannazzo et al., 2024; Veling et al., 2021), but also theoretical accounts which suggest certain motor-responses acquire valence. Here there are two groups randomised to receive instructions to either go/no-go or approach/avoid images of candy in novel training task (Chen et al., 2019).
The results of the experiment suggested that despite both groups making the same responses (pressing a space bar vs not), the framing of the response as go vs approach and no-go vs avoidance influenced subsequent food-choice (i.e. responses framed as approach increased the probability of choosing approach items over avoidance items, but not go items over no-go items). As the authors state, these findings cast doubt on theoretical models which suggest there are ‘hardwired’ links between specific go/approach responses and appetitive systems or specific no-go/avoidance responses and aversive systems. They also suggest these responses aren’t valenced, but acquire valence through interpretation of the action. These findings can also inform future studies into cognitive bias modification. The Stage 2 manuscript was evaluated over two rounds of in-depth review by two reviewers with expertise in the relevant area, who also assessed the Stage 1 manuscript. Based on the authors’ careful responses and revisions, the revised manuscript was judged to meet the Stage 2 criteria and was awarded a positive recommendation. URL to the preregistered Stage 1 protocol: https://osf.io/bn5xa
Level of bias control achieved: Level 6. No part of the data or evidence that was used to answer the research question was generated until after IPA. List of eligible PCI RR-friendly journals:
References
1. Chen, Z., Van Dessel, P., Serverius, J., Zhu, D. & Figner, B. (2025). Action interpretation determines the effects of go/no-go and approach/avoidance actions on food choice. Acceptance of Version 2 by Peer Community in Registered Reports. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/6xhw4_v2
2. Chen, Z., & Van Dessel, P. (2024). Action Interpretation Determines the Effects of Go/No-Go and Approach/Avoidance Actions on Stimulus Evaluation. Open Mind, 8, 898–923. https://doi.org/10.1162/opmi_a_00151
3. Houben, K. and Aulbach, M. (2023). Is there a difference between stopping and avoiding? A review of the mechanisms underlying Go/No-Go and Approach-Avoidance training for food choice. Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences, 49, 101245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cobeha.2022.101245
4. Iannazzo, L. H., Hayden, M. J., Lawrence, N. S., Kakoschke, N., Hughes, L. K., Van Egmond, K., … Staiger, P. K. (2024). Inhibitory control training to reduce appetitive behaviour: a meta-analytic investigation of effectiveness, potential moderators, and underlying mechanisms of change. Health Psychology Review, 1–31. https://doi.org/10.1080/17437199.2024.2410018 5. Veling, H., Verpaalen, I. A. M., Liu, H., Mosannenzadeh, F., Becker, D., & Holland, R. W. (2021). How can food choice best be trained? Approach-avoidance versus go/no-go training. Appetite, 163, 105226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2021.105226 6. Yang, Y., Qi, L., Morys, F., Wu, Q. & Chen, H. (2022). Food-Specific Inhibition Training for Food Devaluation: A Meta-Analysis. Nutrients, 14, 1363. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14071363
| Action interpretation determines the effects of go/no-go and approach/avoidance actions on food choice | Zhang Chen, Pieter Van Dessel, Jordi Serverius, Daxun Zhu, Bernd Figner | <p>Executing go/no-go and approach/avoidance responses toward objects can increase people's choices of go over no-go items, and of approach over avoidance items. Some theoretical accounts explain these effects as the results of merely executing th... | Social sciences | Andrew Jones | 2024-11-24 11:21:55 | View |
FOLLOW US
MANAGING BOARD
Chris Chambers
Zoltan Dienes
Corina Logan
Benoit Pujol
Maanasa Raghavan
Emily S Sena
Yuki Yamada










